Abstract
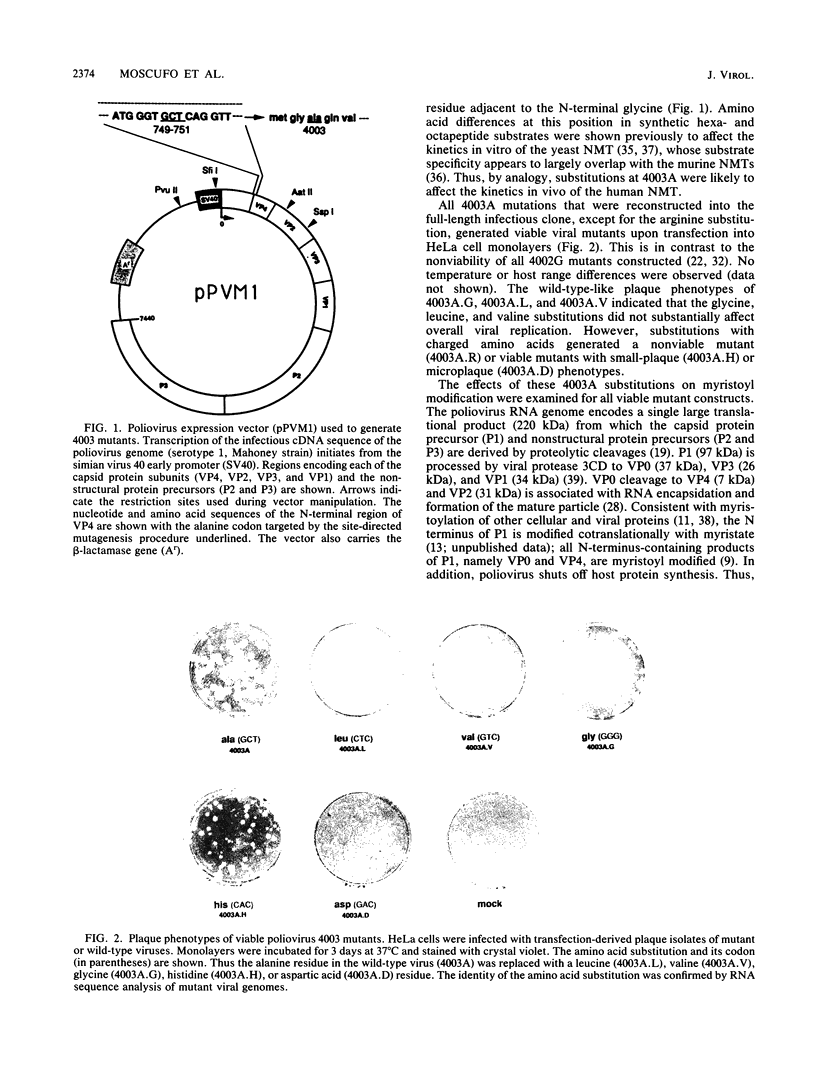
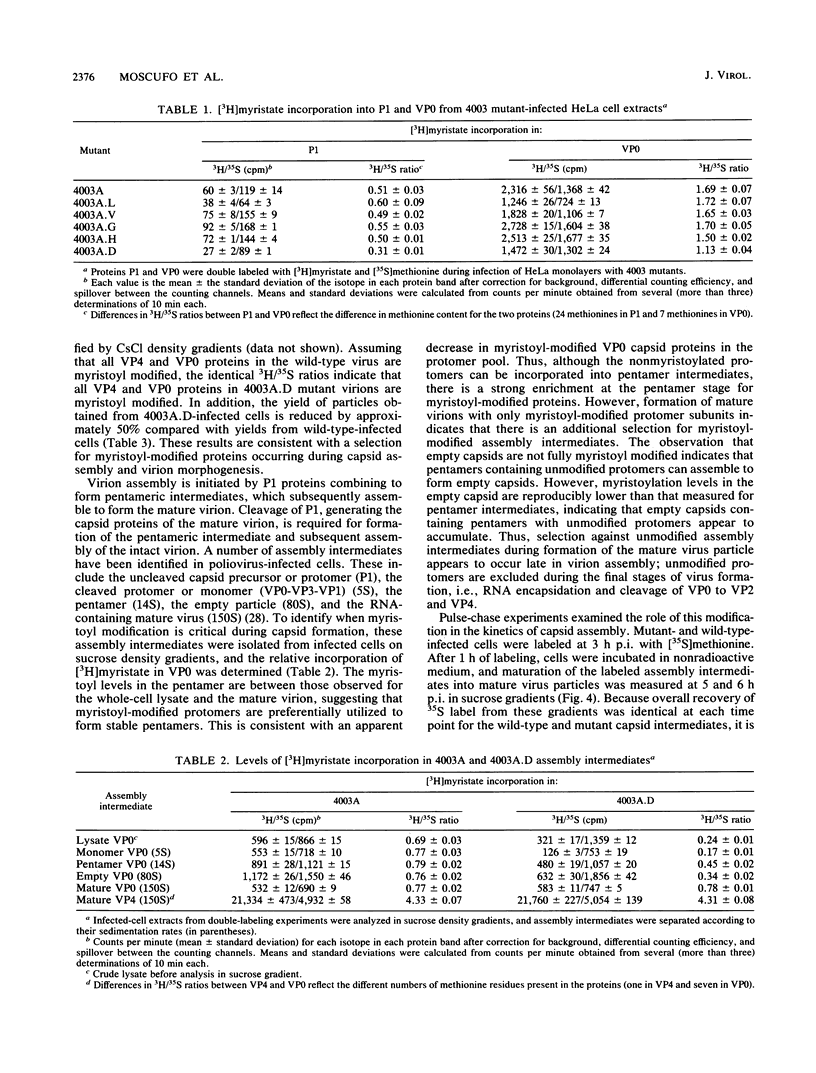
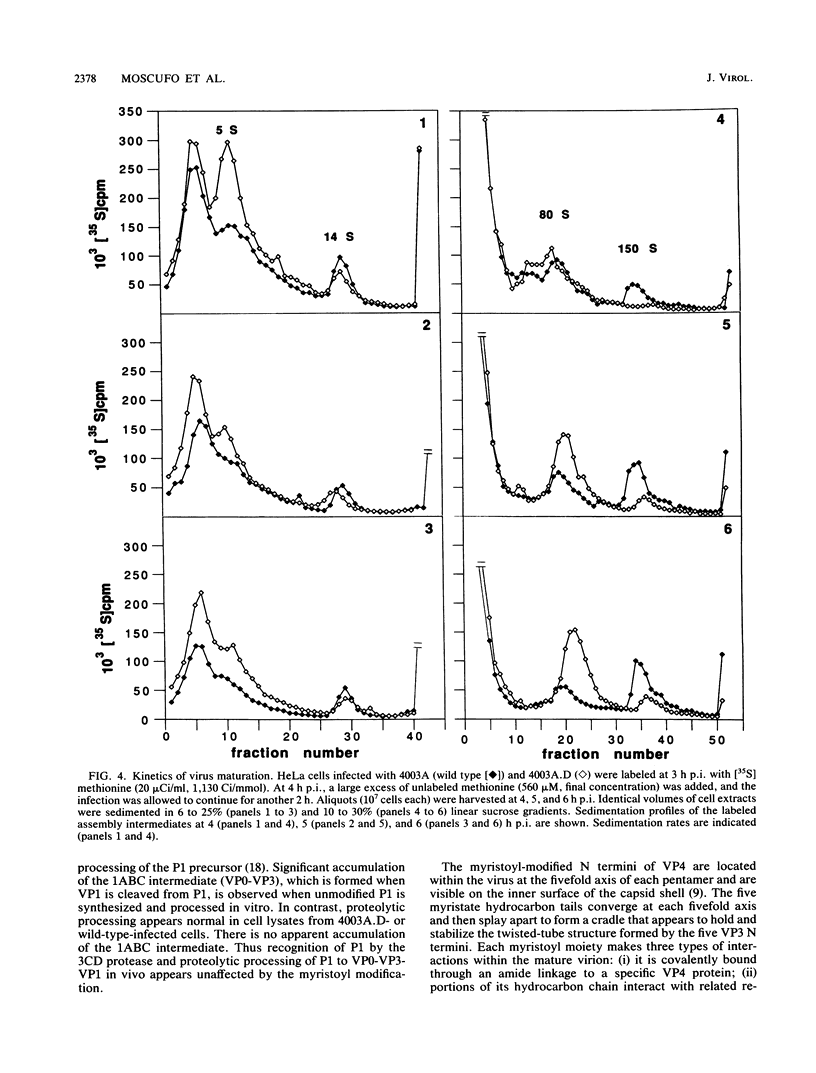
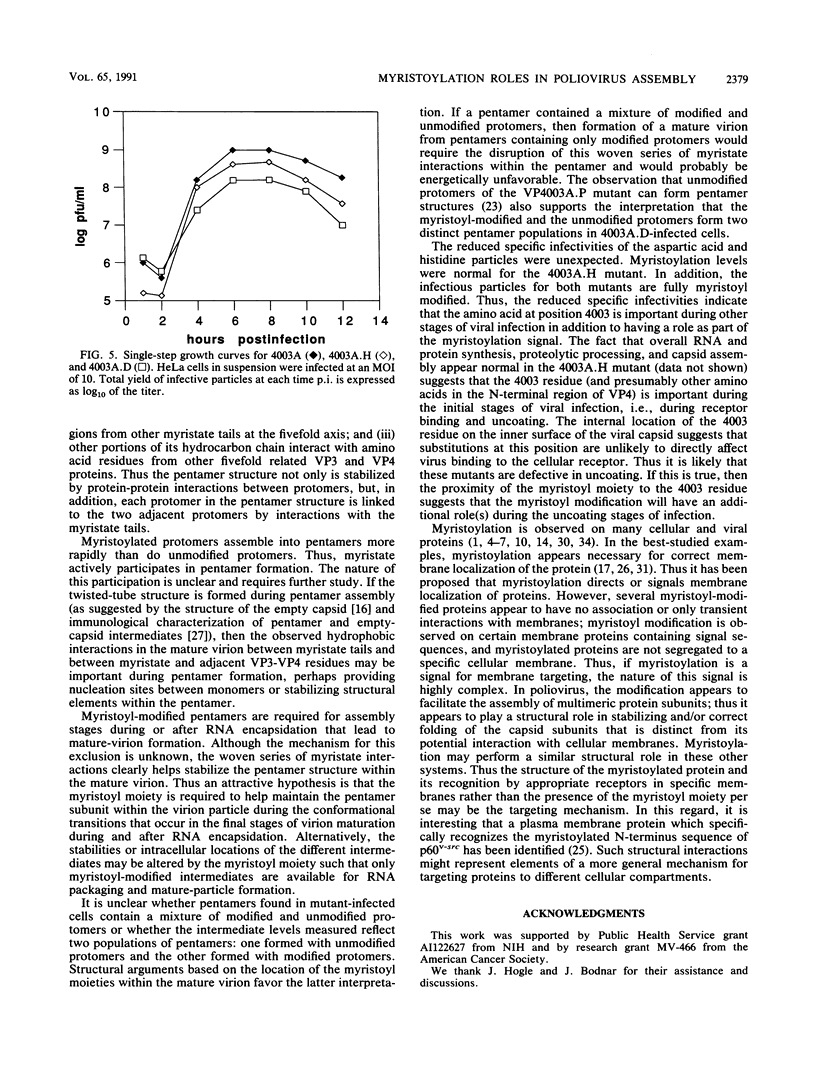
The N-terminal glycine of the VP4 capsid subunit of poliovirus is covalently modified with myristic acid (C14 saturated fatty acid). To investigate the function of VP4 myristoylation in poliovirus replication, amino acid substitutions were placed within the myristoylation consensus sequence at the alanine residue (4003A) adjacent to the N-terminal glycine by using site-directed mutagenesis methods. Mutants which replace the alanine residue with a small hydrophobic residue such as leucine, valine, or glycine displayed normal levels of myristoylation and normal growth kinetics. Replacement with the polar amino acid histidine (4003A.H) also resulted in a level of myristoylation comparable to that of the wild type. However, replacement of the alanine residue with aspartic acid (4003A.D) caused a dramatic reduction (about 40 to 60%) in myristoylation levels of the VP4 precursors (P1 and VP0). In contrast, no differences in modification levels were found in either VP0 and VP4 proteins isolated from mature mutant virions, indicating that myristoylation is required for assembly of the infectious virion. The myristoylation levels of the VP0 proteins found in capsid assembly intermediates indicate that there is a strong but not absolute preference for myristoyl-modified subunits during pentamer formation. Complete myristoylation was observed in mature virions but not in assembly intermediates, indicating that there is a selection for myristoyl-modified subunits during stable RNA encapsidation to form the mature virus particle. In addition, even though mutant infectious virions are fully modified, the severe reduction in specific infectivity of both 4003A.D and 4003A.H purified viruses indicates that the amino acid residue adjacent to the N-terminal glycine apparently has an additional role early during viral infection and that mutations at this position induce pleiotropic effects.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid is attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus during or immediately after synthesis and is present in both soluble and membrane-bound forms of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2697–2704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Sefton B. M. Myristoylated alpha subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7493–7497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid, a rare fatty acid, is the lipid attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.7-12.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Baltimore D. Isolated poliovirus capsid protein VP1 induces a neutralizing response in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7518–7521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B., Desselberger U. Myristylation of rotavirus proteins. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2681–2686. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deichaite I., Casson L. P., Ling H. P., Resh M. D. In vitro synthesis of pp60v-src: myristylation in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4295–4301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Tomas C. B., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. II. Demonstration of a new intermediate, the proviron. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1122–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1122-1130.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinea R., Carrasco L. Phospholipid biosynthesis and poliovirus genome replication, two coupled phenomena. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):2011–2016. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein lacking myristic acid phosphorylates known polypeptide substrates without inducing transformation. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Hölscher C., Reuer Q., Harber J., Wimmer E. Myristoylation of the poliovirus polyprotein is required for proteolytic processing of the capsid and for viral infectivity. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2433–2436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2433-2436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:701–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Drugeon G., Haenni A. L., Girard M., van der Werf S. Role of myristoylation of poliovirus capsid protein VP4 as determined by site-directed mutagenesis of its N-terminal sequence. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2661–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Masson G., Girard M., van der Werf S. Lack of myristoylation of poliovirus capsid polypeptide VP0 prevents the formation of virions or results in the assembly of noninfectious virus particles. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4099–4107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4099-4107.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Mosser A. G., Hogle J. M., Filman D. J., Rueckert R. R., Chow M. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus serotype 1 neutralizing determinants. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1781–1794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1781-1794.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D., Ling H. P. Identification of a 32K plasma membrane protein that binds to the myristylated amino-terminal sequence of p60v-src. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):84–86. doi: 10.1038/346084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Myristylation is required for intracellular transport but not for assembly of D-type retrovirus capsids. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1045–1053. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1045-1053.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombaut B., Boeyé A., Ferguson M., Minor P. D., Mosser A., Rueckert R. Creation of an antigenic site in poliovirus type 1 by assembly of 14 S subunits. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):305–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90080-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Amino terminal myristylation of the protein kinase p60src, a retroviral transforming protein. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):427–429. doi: 10.1126/science.3917576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Rein A. Unmyristylated Moloney murine leukemia virus Pr65gag is excluded from virus assembly and maturation events. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2370–2373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2370-2373.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli C. H., Griffin B. E. Myristic acid is coupled to a structural protein of polyoma virus and SV40. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):619–622. doi: 10.1038/326619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Adams S. P., Eubanks S. R., Towery D. S., Jackson-Machelski E., Glaser L., Gordon J. I. Myristoyl CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase activities from rat liver and yeast possess overlapping yet distinct peptide substrate specificities. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1784–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Adams S. P., Eubanks S. R., Towery D. S., Jackson-Machelski E., Glaser L., Gordon J. I. Purification and characterization of yeast myristoyl CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Eubanks S. R., Towery D. S., Adams S. P., Glaser L. Amino-terminal processing of proteins by N-myristoylation. Substrate specificity of N-myristoyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1030–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C., Hu J. S., Olson E. N. Acylation of proteins with myristic acid occurs cotranslationally. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1275–1278. doi: 10.1126/science.3685978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Dewalt P. G., Johnson V. H., Lamb J. G., Semler B. L. Protein 3CD is the major poliovirus proteinase responsible for cleavage of the P1 capsid precursor. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]