Abstract
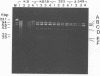
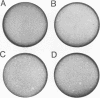
Human adenovirus type 40 (Ad40) cannot propagate in conventional established human cell lines such as KB or HeLa cells. However, it has been shown that Ad40 DNA replicates in KB18 cells which express Ad2 E1B genes, suggesting that Ad40 is defective in the E1B gene function in KB or HeLa cells. We show here that Ad40 can propagate and produce plaques on A549 cells which do not contain Ad E1B genes. Our experiments show that the levels of replication of Ad40 DNA and production of infectious Ad40 virus in A549 cells are the same as or higher than those in 293 or KB18 cells. Dot blot analysis shows that the levels of Ad40 E1A and E1B mRNAs expressed in A549 cells at early to intermediate times postinfection are at least 10-fold higher than those in KB or KB18 cells. Northern (RNA) blot analysis shows that large E1B mRNA species (approximately 24S to 26S) are synthesized prior to the onset of DNA replication in A549 cells. No E1B mRNA species are synthesized in KB or KB18 cells at early times postinfection, and no differences in the expression of E1B mRNAs are seen between KB and KB18 cells. The experiment suggests that A549 cells have a cellular factor(s) which activates Ad40 E1B mRNA synthesis and that the E1B mRNA synthesis helps Ad40 propagation. In contrast, Ad40 can propagate in KB18 cells by using Ad2 E1B gene products that are constitutively expressed in this cell line. Furthermore, this result shows that Ad40 cannot propagate in KB cells because of the failure in the expression of E1B genes at early times postinfection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S. Adenovirus type 5 early region 1b gene product is required for efficient shutoff of host protein synthesis. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):202–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.202-212.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Adenovirus E1B proteins are required for accumulation of late viral mRNA and for effects on cellular mRNA translation and transport. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2552–2558. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Young C. S., Fisher P. B., Ginsberg H. S. Expression of adenovirus E1a and E1b gene products and the Escherichia coli XGPRT gene in KB cells. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):454–465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.454-465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt C. D., Kim H. W., Rodriguez W. J., Arrobio J. O., Jeffries B. C., Parrott R. H. Simultaneous infections with different enteric and respiratory tract viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):177–179. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.177-179.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt C. D., Kim H. W., Rodriguez W. J., Arrobio J. O., Jeffries B. C., Stallings E. P., Lewis C., Miles A. J., Gardner M. K., Parrott R. H. Adenoviruses and pediatric gastroenteritis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):437–443. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt C. D., Kim H. W., Yolken R. H., Kapikian A. Z., Arrobio J. O., Rodriguez W. J., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Comparative epidemiology of two rotavirus serotypes and other viral agents associated with pediatric gastroenteritis. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Sep;110(3):243–254. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiding D. E., Edbauer C. A., Tong J. Y., Byrd P., Grand R. J., Gallimore P. H., Williams J. Isolation and characterization of adenovirus type 12 E1 host-range mutants defective for growth in nontransformed human cells. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Petric M., Middleton P. J. Diagnosis of fastidious enteric adenoviruses 40 and 41 in stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):334–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.334-338.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büttner W., Veres-Molnár Z., Green M. Isolation of DNA Strand-specific early messenger RNA species in cells infected by human adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2951–2955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Nakata S., Nakamura I., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Fujinaga K., Nakao T. Outbreak of infantile gastroenteritis due to type 40 adenovirus. Lancet. 1983 Oct 22;2(8356):954–957. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90463-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbauer C., Lamberti C., Tong J., Williams J. Adenovirus type 12 E1B 19-kilodalton protein is not required for oncogenic transformation in rats. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3265–3273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3265-3273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Wold W. S. Human adenoviruses: growth, purification, and transfection assay. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:425–435. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishino M., Ohashi Y., Emoto T., Sawada Y., Fujinaga K. Characterization of adenovirus type 40 E1 region. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90662-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishino M., Sawada Y., Yaegashi T., Demura M., Fujinaga K. Nucleotide sequence of the adenovirus type 40 inverted terminal repeat: close relation to that of adenovirus type 5. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):414–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd A. H., Cosgrove B. P., Brown R. A., Madeley C. R. Faecal adenoviruses from Glasgow babies. Studies on culture and identity. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Jun;88(3):463–474. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd A. H. Genome variants of adenovirus 41 (subgroup G) from children with diarrhoea in South Africa. J Med Virol. 1984;14(1):49–59. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumai H., Takemori N., Hashimoto S. Role of adenovirus type 2 early region 1B 19K protein stability in expression of the cyt and deg phenotypes. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):1975–1986. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-1975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassam N. J., Bayley S. T., Graham F. L. Synthesis of DNA, late polypeptides, and infectious virus by host-range mutants of adenovirus 5 in nonpermissive cells. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppard K. N., Shenk T. The adenovirus E1B 55 kd protein influences mRNA transport via an intranuclear effect on RNA metabolism. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2329–2336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak I., Mak S. Separate regions of an adenovirus E1B protein critical for different biological functions. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):553–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90026-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mautner V., Mackay N., Steinthorsdottir V. Complementation of enteric adenovirus type 40 for lytic growth in tissue culture by E1B 55K function of adenovirus types 5 and 12. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):619–622. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90634-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilder S., Moore M., Logan J., Shenk T. The adenovirus E1B-55K transforming polypeptide modulates transport or cytoplasmic stabilization of viral and host cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):470–476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Hearing P., Anderson C. W., Halbert D. N., Shenk T., Levine A. J. Adenovirus early region 1B 58,000-dalton tumor antigen is physically associated with an early region 4 25,000-dalton protein in productively infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):692–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.692-700.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroki K., Ohshima K., Fukui Y., Ariga H. The adenovirus type 12 early-region 1B 58,000-Mr gene product is required for viral DNA synthesis and for initiation of cell transformation. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):792–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.792-801.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson L., Wadell G., Uhnoo I., Johansson M., Von Bonsdorff C. H. Cross-reactivity between enteric adenoviruses and adenovirus type 4: analysis of epitopes by solid-phase immune electron microscopy. J Gen Virol. 1983 Nov;64(Pt 11):2517–2520. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-11-2517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiff H. E., Reinhold W., Garon C. F., Straus S. E. Cloning and physical mapping of enteric adenoviruses (candidate types 40 and 41). J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):131–136. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.131-136.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiff H. E., Straus S. E., Garon C. F. Propagation and in vitro studies of previously non-cultivable enteral adenoviruses in 293 cells. Lancet. 1981 Oct 17;2(8251):832–834. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhnoo I., Wadell G., Svensson L., Johansson M. E. Importance of enteric adenoviruses 40 and 41 in acute gastroenteritis in infants and young children. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):365–372. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.365-372.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos H. L., van der Lee F. M., Reemst A. M., van Loon A. E., Sussenbach J. S. The genes encoding the DNA binding protein and the 23K protease of adenovirus types 40 and 41. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G., Hammarskjöld M. L., Winberg G., Varsanyi T. M., Sundell G. Genetic variability of adenoviruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:16–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigand R., Baumeister H. G., Maass G., Kühn J., Hammer H. J. Isolation and identification of enteric adenoviruses. J Med Virol. 1983;11(3):233–240. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890110306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. E., Gilardi P., Perricaudet M., Rozijn T. H., Sussenbach J. S. Transcriptional activation by the E1A regions of adenovirus types 40 and 41. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):305–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. E., Ligtenberg M., Reemst A. M., Sussenbach J. S., Rozijn T. H. Structure and organization of the left-terminal DNA regions of fastidious adenovirus types 40 and 41. Gene. 1987;58(1):109–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]