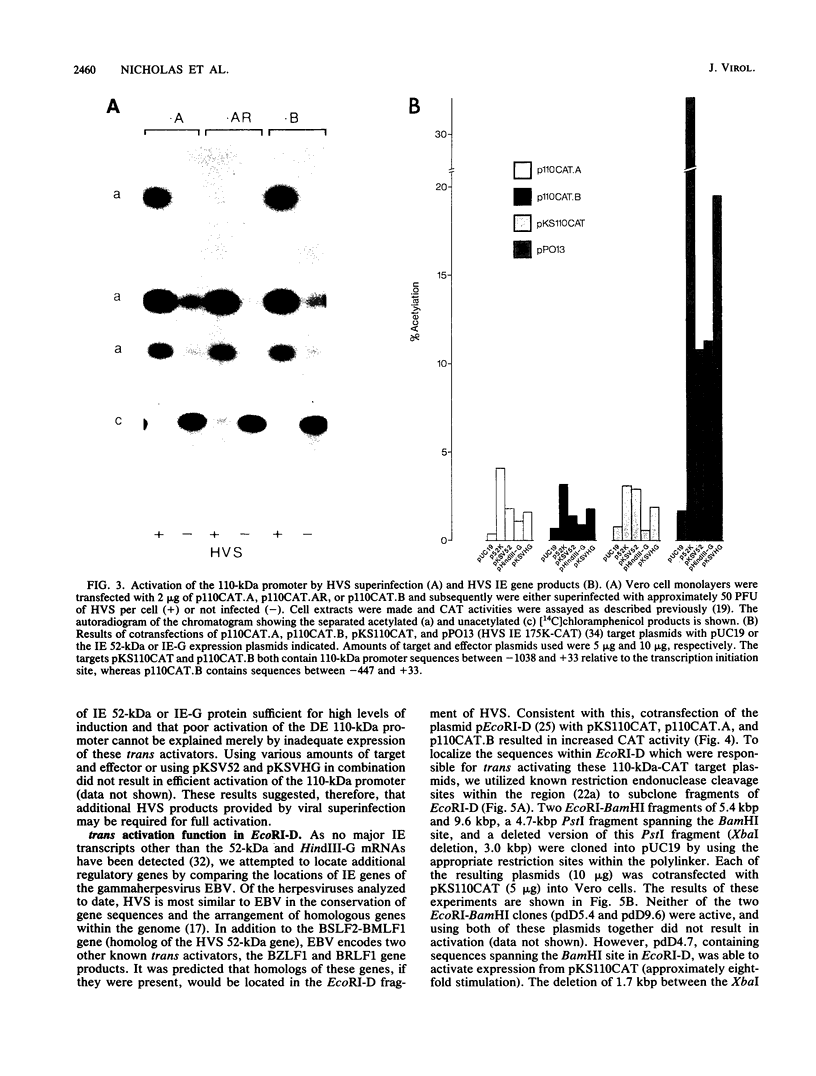
Abstract
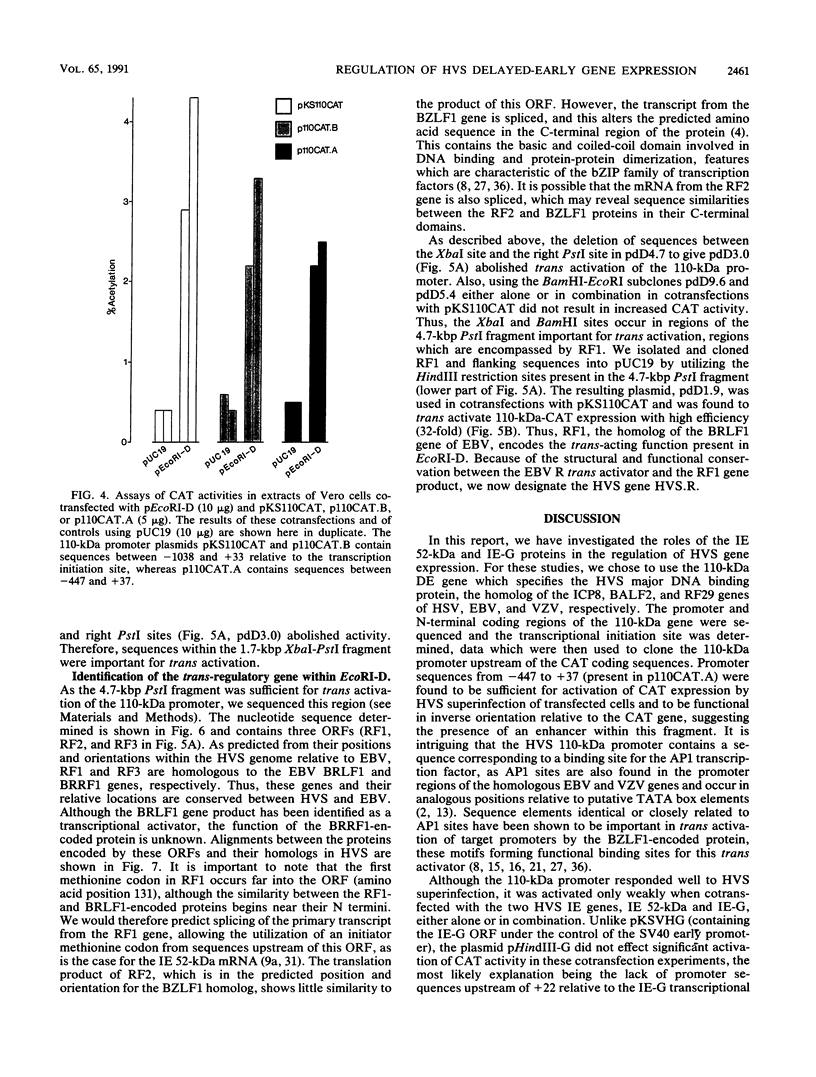
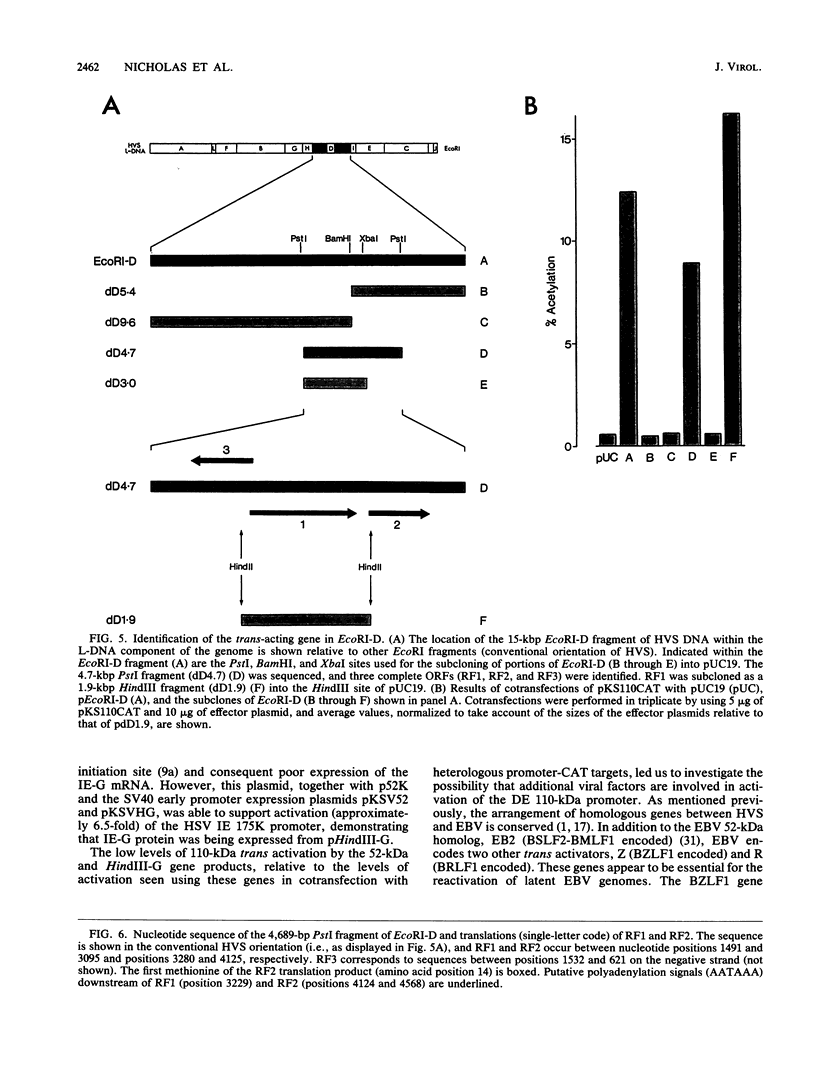
We have reported previously the detection of two stable immediate-early (IE) transcripts that accumulate in cycloheximide-treated cells infected with herpesvirus saimiri (HVS). These are the 1.6-kb mRNA from the 52-kDa gene (which is homologous to the BSLF2-BMLF1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus) and the 1.3-kb mRNA from the HindIII-G fragment of virus DNA. In order to study the roles of the HVS IE gene products in the progression of a lytic infection, the promoter region of the delayed-early 110-kDa gene of HVS was sequenced, the transcription initiation site was mapped by RNase protection, and the promoter sequences were cloned upstream of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene. Sequences between -447 and +37 (relative to the 110-kDa transcription initiation site) were sufficient for response to HVS superinfection of transfected cells, but the 110-kDa promoter was activated only poorly by the 52-kDa and HindIII-G IE (IE-G) proteins in cotransfection experiments. However, a distinct region of the genome, EcoRI-D (15 kbp), was able to activate 110-kDa-CAT expression relatively efficiently in similar experiments. A 4.7-kbp PstI fragment encoding this function was isolated and sequenced, and further subcloning identified the gene encoding the EcoRI-D trans activator. This gene, which we now designate HVS.R, is homologous to the BRLF1-encoded transcriptional effector of Epstein-Barr virus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht J. C., Fleckenstein B. Structural organization of the conserved gene block of Herpesvirus saimiri coding for DNA polymerase, glycoprotein B, and major DNA binding protein. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M., Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in P3HR1-superinfected Raji cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3120–3132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3120-3132.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair E. D., Honess R. W. DNA-binding proteins specified by herpesvirus saimiri. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2697–2715. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair E. D., Randall R. E., Honess R. W. Evidence that the major delayed-early DNA-binding proteins of herpesvirus saimiri are bound to DNA in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):759–764. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron K. R., Stamminger T., Craxton M., Bodemer W., Honess R. W., Fleckenstein B. The 160,000-Mr virion protein encoded at the right end of the herpesvirus saimiri genome is homologous to the 140,000-Mr membrane antigen encoded at the left end of the Epstein-Barr virus genome. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2063–2070. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2063-2070.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. N., Dong D. L., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. The Epstein-Barr virus Zta transactivator: a member of the bZIP family with unique DNA-binding specificity and a dimerization domain that lacks the characteristic heptad leucine zipper motif. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3358–3369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3358-3369.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Miller G. Activation of expression of latent Epstein-Barr herpesvirus after gene transfer with a small cloned subfragment of heterogeneous viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4085–4089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. A., Leahy J., Hardwick J. M. An enhancer within the divergent promoter of Epstein-Barr virus responds synergistically to the R and Z transactivators. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.313-321.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk L. A., Wolfe L. G., Deinhardt F. Isolation of Herpesvirus saimiri from blood of squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 May;48(5):1499–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Rowe D. T., Rooney C. M., Kouzarides T. Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator specifically binds to a consensus AP-1 site and is related to c-fos. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Identification of phorbol ester response elements in the promoter of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1217–1226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1217-1226.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gompels U. A., Craxton M. A., Honess R. W. Conservation of gene organization in the lymphotropic herpesviruses herpesvirus Saimiri and Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):757–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.757-767.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gompels U. A., Craxton M. A., Honess R. W. Conservation of glycoprotein H (gH) in herpesviruses: nucleotide sequence of the gH gene from herpesvirus saimiri. J Gen Virol. 1988 Nov;69(Pt 11):2819–2829. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-11-2819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Lieberman P. M., Hayward S. D. A new Epstein-Barr virus transactivator, R, induces expression of a cytoplasmic early antigen. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2274–2284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2274-2284.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley-Guthrie E. A., Quinlivan E. B., Mar E. C., Kenney S. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BMRF1 promoter for early antigen (EA-D) is regulated by the EBV transactivators, BRLF1 and BZLF1, in a cell-specific manner. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3753–3759. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3753-3759.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Gompels U. A., Barrell B. G., Craxton M., Cameron K. R., Staden R., Chang Y. N., Hayward G. S. Deviations from expected frequencies of CpG dinucleotides in herpesvirus DNAs may be diagnostic of differences in the states of their latent genomes. J Gen Virol. 1989 Apr;70(Pt 4):837–855. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-4-837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W. Herpes simplex and 'the herpes complex': diverse observations and a unifying hypothesis. The eighth Fleming lecture. J Gen Virol. 1984 Dec;65(Pt 12):2077–2107. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-12-2077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Holley-Guthrie E., Mar E. C., Smith M. The Epstein-Barr virus BMLF1 promoter contains an enhancer element that is responsive to the BZLF1 and BRLF1 transactivators. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3878–3883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3878-3883.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knust E., Schirm S., Dietrich W., Bodemer W., Kolb E., Fleckenstein B. Cloning of Herpesvirus saimiri DNA fragments representing the entire L-region of the genome. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J. In vitro transcriptional activation, dimerization, and DNA-binding specificity of the Epstein-Barr virus Zta protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2560–2568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2560-2568.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., O'Hare P., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. Promiscuous trans activation of gene expression by an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded early nuclear protein. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.140-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manet E., Gruffat H., Trescol-Biemont M. C., Moreno N., Chambard P., Giot J. F., Sergeant A. Epstein-Barr virus bicistronic mRNAs generated by facultative splicing code for two transcriptional trans-activators. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1819–1826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J., Gompels U. A., Craxton M. A., Honess R. W. Conservation of sequence and function between the product of the 52-kilodalton immediate-early gene of herpesvirus saimiri and the BMLF1-encoded transcriptional effector (EB2) of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3250–3257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3250-3257.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J., Smith E. P., Coles L., Honess R. Gene expression in cells infected with gammaherpesvirus saimiri: properties of transcripts from two immediate-early genes. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Honess R. W. Identification of a subset of herpesvirus saimiri polypeptides synthesized in the absence of virus DNA replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):279–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.279-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguro M. O., Shimizu N., Ono Y., Takada K. Both the rightward and the leftward open reading frames within the BamHI M DNA fragment of Epstein-Barr virus act as trans-activators of gene expression. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3310–3313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3310-3313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham G., Economou A., Rooney C. M., Rowe D. T., Farrell P. J. Structure and function of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2110–2116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2110-2116.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall R. E., Honess R. W., O'Hare P. Proteins specified by herpesvirus saimiri: identification and properties of virus-specific polypeptides in productively infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):19–35. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Rowe D. T., Ragot T., Farrell P. J. The spliced BZLF1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transactivates an early EBV promoter and induces the virus productive cycle. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3109–3116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3109-3116.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Taylor N., Countryman J., Jenson H., Kolman J., Miller G. Genome rearrangements activate the Epstein-Barr virus gene whose product disrupts latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9801–9805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urier G., Buisson M., Chambard P., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus early protein EB1 activates transcription from different responsive elements including AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1447–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. M., Levine A. J. Identification and mapping of Epstein-Barr virus early antigens and demonstration of a viral gene activator that functions in trans. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):149–156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.149-156.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]