Abstract
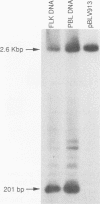
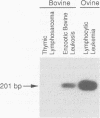
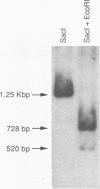
Expression of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) has been considered to be blocked at the transcriptional level in vivo, since viral RNA species are not readily detected in freshly isolated leukocytes from BLV-infected animals. However, the presence of a persistent antiviral antibody response in infected animals suggests that some degree of virus expression must occur in vivo. The purpose of this study was to determine whether BLV RNA species could be detected by using the polymerase chain reaction in normal or neoplastic lymphoid cells freshly isolated from naturally or experimentally BLV-infected cattle and sheep, respectively. Primers designed to detect a 2.1-kb doubly spliced BLV tax/rex-specific mRNA were used to amplify cDNA copies of RNA derived from infected animals. The amplified viral product was then detected with a radiolabeled BLV tax/rex-specific probe. BLV-specific RNA was detected readily in freshly isolated peripheral blood leukocytes derived from BLV-seropositive cattle or sheep with persistent lymphocytosis and less readily in peripheral blood leukocytes from BLV-seropositive but hematologically normal animals. BLV-specific RNA was also detected in fresh samples of BLV-induced lymphosarcomas. Normal and neoplastic lymphoid cells from BLV-seronegative animals were uniformly negative under similar conditions. These primers also amplified the same viral product from genomic DNA derived from BLV-seropositive animals, providing further evidence for in vivo transcription and suggesting that BLV RNA-dependent DNA polymerase is capable of reverse transcribing the 2.1-kb mRNA in vivo. The demonstration of transcriptional products of BLV in vivo proves that viral latency in BLV infection is incomplete.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baliga V., Ferrer J. F. Expression of the bovine leukemia virus and its internal antigen in blood lymphocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Nov;156(2):388–391. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bex F., Bruck C., Mammerickx M., Portetelle D., Ghysdael J., Cleuter Y., Leclercq M., Dekegel D., Burny A. Humoral antibody response to bovine leukemia virus infection in cattle and sheep. Cancer Res. 1979 Mar;39(3):1118–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhagavati S., Ehrlich G., Kula R. W., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Udani V., Poiesz B. J. Detection of human T-cell lymphoma/leukemia virus type I DNA and antigen in spinal fluid and blood of patients with chronic progressive myelopathy. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 5;318(18):1141–1147. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805053181801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Gallo R. C. Human T-cell leukemia viruses (HTLV): a unique family of pathogenic retroviruses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:321–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerell G. L., Rovnak J. The correlation between the direct and indirect detection of bovine leukemia virus infection in cattle. Leuk Res. 1988;12(6):465–469. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(88)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornil I., Delon P., Parodi A. L., Levy D. T-B cell cooperation for bovine leukemia virus expression in ovine lymphocytes. Leukemia. 1988 May;2(5):313–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D. Bovine leukemia virus transcription is controlled by a virus-encoded trans-acting factor and by cis-acting response elements. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2462–2471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2462-2471.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D. trans-acting regulation of bovine leukemia virus mRNA processing. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1115–1119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1115-1119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps J., Kettmann R., Burny A. Experiments with cloned complete tumor-derived bovine leukemia virus information prove that the virus is totally exogenous to its target animal species. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):605–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.605-609.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshayes L., Levy D., Parodi A. L., Levy J. P. Spontaneous immune response of bovine leukemia-virus-infected cattle against five different viral proteins. Int J Cancer. 1980 Apr 15;25(4):503–508. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer J. F. Bovine lymphosarcoma. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1980;24:1–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C. Growth of human normal and leukemic T cells: T-cell growth factor (TCGF) and the isolation of a new class of RNA tumor viruses (HTLV). Blood Cells. 1981;7(2):313–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysdael J., Bruck C., Kettmann R., Burny A. Bovine leukemia virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;112:1–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69677-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Kashmiri S. V., Ferrer J. F. Transcriptional control of the bovine leukemia virus genome: role and characterization of a non-immunoglobulin plasma protein from bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):267–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.267-270.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi K., Hanada S., Hashimoto S. Expression of HTLV-I in serum of HTLV-I-related subjects and the early detection of overt ATL in HTLV-I carriers. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1509–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Cleuter Y., Gregoire D., Burny A. Role of the 3' long open reading frame region of bovine leukemia virus in the maintenance of cell transformation. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):899–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.899-901.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Cleuter Y., Mammerickx M., Meunier-Rotival M., Bernardi G., Burny A., Chantrenne H. Genomic integration of bovine leukemia provirus: comparison of persistent lymphocytosis with lymph node tumor form of enzootic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2577–2581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Deschamps J., Cleuter Y., Couez D., Burny A., Marbaix G. Leukemogenesis by bovine leukemia virus: proviral DNA integration and lack of RNA expression of viral long terminal repeat and 3' proximate cellular sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Marbaix G., Cleuter Y., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Burny A. Genomic integration of bovine leukemia provirus and lack of viral RNA expression in the target cells of cattle with different responses to BLV infection. Leuk Res. 1980;4(6):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(80)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Shimoyama M., Tobinai K., Ito M., Ito S., Ikeda S., Tajima K., Shimotohno K., Sugimura T. Detection of mRNA for the tax1/rex1 gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells of adult T-cell leukemia patients and viral carriers by using the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5620–5624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa T., Seiki M., Iwashita S., Imagawa K., Shimizu F., Yoshida M. p27x-III and p21x-III, proteins encoded by the pX sequence of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8359–8363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagarias D. M., Radke K. Transcriptional activation of bovine leukemia virus in blood cells from experimentally infected, asymptomatic sheep with latent infections. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2099–2107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2099-2107.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando Z., Sarin P., Megson M., Greene W. C., Waldman T. A., Gallo R. C., Broder S. Association of human T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma virus with the Tac antigen marker for the human T-cell growth factor receptor. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):733–736. doi: 10.1038/305733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Coligan J. E., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Salahuddin S. Z., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Essex M. Antigens encoded by the 3'-terminal region of human T-cell leukemia virus: evidence for a functional gene. Science. 1984 Oct 5;226(4670):57–61. doi: 10.1126/science.6089350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D., Deshayes L., Parodi A. L., Levy J. P., Stephenson J. R., Devare S. G., Gilden R. V. Bovine leukemia virus specific antibodies among French cattle. II. Radioimmunoassay with the major structural protein (BLV p24). Int J Cancer. 1977 Oct 15;20(4):543–550. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Creation of a processed pseudogene by retroviral infection. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90759-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamoun R. Z., Astier-Gin T., Kettmann R., Deschamps J., Rebeyrotte N., Guillemain B. J. The pX region of the bovine leukemia virus is transcribed as a 2.1-kilobase mRNA. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):625–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.625-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Shibuya H., Harada H., Hatakeyama M., Seiki M., Fujita T., Inoue J., Yoshida M., Taniguchi T. Evidence for aberrant activation of the interleukin-2 autocrine loop by HTLV-1-encoded p40x and T3/Ti complex triggering. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Miller L. D., Olson C., Gillette K. G. Virus-like particles in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocyte cultures with reference to bovine lymphosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Dec;43(6):1297–1305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima K., Yoshida M., Seiki M. A single species of pX mRNA of human T-cell leukemia virus type I encodes trans-activator p40x and two other phosphoproteins. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):394–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.394-399.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Simek S. L., Dubois G. C., Showalter S. D., Gilden R. V., Stephens R. M. Expression of the bovine leukemia virus X region in virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1577–1585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1577-1585.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Nagayoshi-Aida M., Shimizu F., Imagawa K., Ikawa Y. Identification and some biochemical properties of the major XBL gene product of bovine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7879–7883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Ohishi K., Ogawa Y., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of bovine leukemia virus: its evolutionary relationship to other retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Shimotohno K., Cline M. J., Golde D. W., Chen I. S. Identification of the putative transforming protein of the human T-cell leukemia viruses HTLV-I and HTLV-II. Science. 1984 Oct 5;226(4670):61–65. doi: 10.1126/science.6089351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Reverse transcription in the eukaryotic genome: retroviruses, pararetroviruses, retrotransposons, and retrotranscripts. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):455–468. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broeke A., Cleuter Y., Chen G., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Zagury D., Fouchard M., Coulombel L., Kettmann R., Burny A. Even transcriptionally competent proviruses are silent in bovine leukemia virus-induced sheep tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9263–9267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsman W., Shimotohno K., Clark S. C., Golde D. W., Chen I. S. Expression of the 3' terminal region of human T-cell leukemia viruses. Science. 1984 Oct 12;226(4671):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.6091270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. The family of human T-lymphotropic leukemia viruses: HTLV-I as the cause of adult T cell leukemia and HTLV-III as the cause of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]