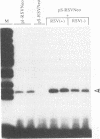
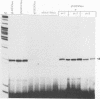
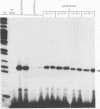
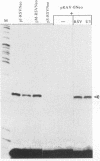
Abstract
An enhancer element is located in the U3 portion of exogenous avian retrovirus long terminal repeats (LTRs). A similar element has not been detected in the LTRs of ev-1 and ev-2, two avian endogenous viruses (evs) that normally are not expressed in vivo. Experiments were initiated to determine whether minor nucleotide differences in the U3 region of a previously untested ev that is ubiquitously expressed in vivo (ev-3) might confer enhancer function on the LTR of this provirus. This question was addressed by inserting U3 regions from ev-3 and from ev-1 and/or ev-2 both upstream of the herpesvirus thymidine kinase gene promoter and in place of the major enhancer domains of the Rous sarcoma virus LTR and determining their relative effects on transcription. U3 regions from all evs tested were unable to enhance transcription from the thymidine kinase gene promoter, indicating that nucleotide differences in the ev U3 regions do not affect their relative enhancer function and therefore are unlikely to play a role in their differential expression in vivo. Unexpectedly, however, all ev U3 regions were able to augment transcription in an orientation-independent manner in the ev-Rous sarcoma virus hybrid LTRs. Further experiments conducted to determine why this enhancer activity is not detectable in intact ev LTRs demonstrated that it was not due to removal of repressor sequences in the ev fragments used that might normally be present in intact ev LTRs. The lack of detectable enhancer activity in intact ev LTRs also was not explained by a defect in ev promoters that makes them unresponsive to enhancers in cis. These experiments therefore identify sequences that, although unable to function detectably as enhancers in their natural context, can function efficiently in a heterologous context. Data are discussed in terms of the modularity of enhancer elements and possible interactions between enhancers and promoter-specific sequences.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M. L. Enhancers: mechanisms of action and cell specificity. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:127–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B., Robison H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Analysis of endogenous avian retrovirus DNA and RNA: viral and cellular determinants of retrovirus gene expression. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):8–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulden A., Sealy L. Identification of a third protein factor which binds to the Rous sarcoma virus LTR enhancer: possible homology with the serum response factor. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):204–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Tsichlis P. N., Conklin K. F., Senior A., Robinson H. L. Genomes of endogenous and exogenous avian retroviruses. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):51–72. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90461-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin K. F., Coffin J. M., Robinson H. L., Groudine M., Eisenman R. Role of methylation in the induced and spontaneous expression of the avian endogenous virus ev-1: DNA structure and gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):638–652. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin K. F., Groudine M. Varied interactions between proviruses and adjacent host chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3999–4007. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Functional analysis of the transcription control region located within the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):438–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Transcriptional activity of avian retroviral long terminal repeats directly correlates with enhancer activity. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.515-521.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Skalka A. M., Ju G. Endogenous avian retroviruses contain deficient promoter and leader sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Parsons J. T. Identification of transcriptional elements within the long terminal repeat of Rous sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1834–1845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H. Identification of three sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins which interact with the Rous sarcoma virus enhancer and upstream promoter elements. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2186–2190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2186-2190.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greuel B. T., Sealy L., Majors J. E. Transcriptional activity of the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat correlates with binding of a factor to an upstream CCAAT box in vitro. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Conkin K. F. Chromatin structure and de novo methylation of sperm DNA: implications for activation of the paternal genome. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1061–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.2986289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Eisenman R., Weintraub H. Chromatin structure of endogenous retroviral genes and activation by an inhibitor of DNA methylation. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):311–317. doi: 10.1038/292311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Braverman S. B., Astrin S. M. Transcriptional products and DNA structure of endogenous avian proviruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1111–1121. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hishinuma F., DeBona P. J., Astrin S., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence of acceptor site and termini of integrated avian endogenous provirus ev1: integration creates a 6 bp repeat of host DNA. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H. Sequence of the long terminal repeat and adjacent segments of the endogenous avian virus Rous-associated virus 0. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):191–200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.191-200.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Toyoshima K., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Organization of the endogenous proviruses of chickens: implications for origin and expression. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):189–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90538-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries E. H., Allen R., Glover C. Clonal analysis of the integration and expression of endogenous avian retroviral DNA acquired by exogenous viral infection. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):584–596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.584-596.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Cooper G. M. Integration, expression, and infectivity of exogenously acquired proviruses of Rous-associated virus-O. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):684–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.684-691.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Tsichlis P., Khoury G. Multiple enhancer domains in the 3' terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6427–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Capecchi M. R. Location and function of retroviral and SV40 sequences that enhance biochemical transformation after microinjection of DNA. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariash C. N., Seelig S., Oppenheimer J. H. A rapid, inexpensive, quantitative technique for the analysis of two-dimensional electrophoretograms. Anal Biochem. 1982 Apr;121(2):388–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90498-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsialis S. A., Manley J. L., Guntaka R. V. Localization of active promoters for eucaryotic RNA polymerase II in the long terminal repeat of avian sarcoma virus DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):811–818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Bacterial beta-galactosidase as a marker of Rous sarcoma virus gene expression and replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):281–290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus sequences essential for viral gene expression. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1171–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1171-1179.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L. Inheritance and expression of chicken genes that are related to avian leukosis sarcoma virus genes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;83:1–36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67087-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddell A., Linial M. L., Groudine M. Tissue-specific lability and expression of avian leukosis virus long terminal repeat enhancer-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5660–5668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddell A., Linial M., Schubach W., Groudine M. Lability of leukosis virus enhancer-binding proteins in avian hematopoeitic cells. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2728–2735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2728-2735.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1155–1164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholl D. R., Kahn S., Malavarca R., Astrin S., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence of the long terminal repeat and flanking cellular sequences of avian endogenous retrovirus ev-2: variation in Rous-associated virus-0 expression cannot be explained by differences in primary sequence. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):868–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.868-871.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey L., Chalkley R. At least two nuclear proteins bind specifically to the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):787–798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A., Ju G., Hishinuma F., DeBona P. J., Astrin S. Structural analogies among avian retroviral DNAs and transposable elements. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):739–746. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., Schaffner W. Enhancer activity correlates with the oncogenic potential of avian retroviruses. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):949–956. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Identification of a functional promoter in the long terminal repeat of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90555-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]