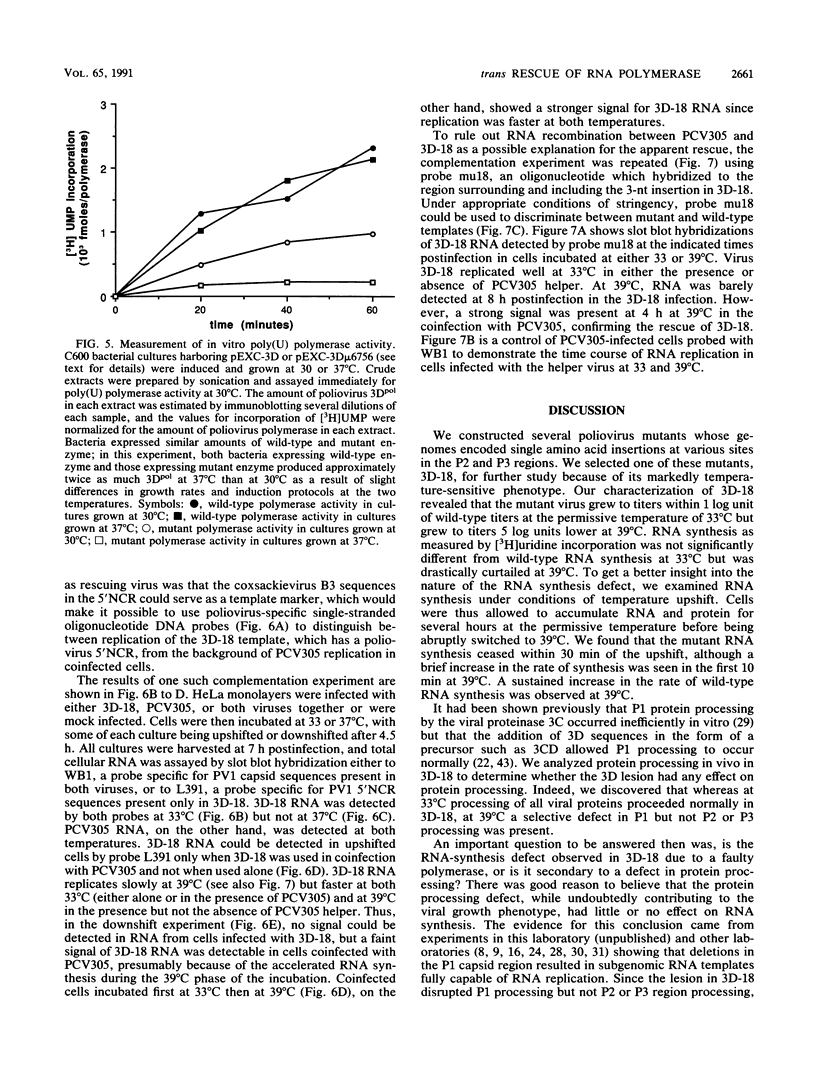
Abstract
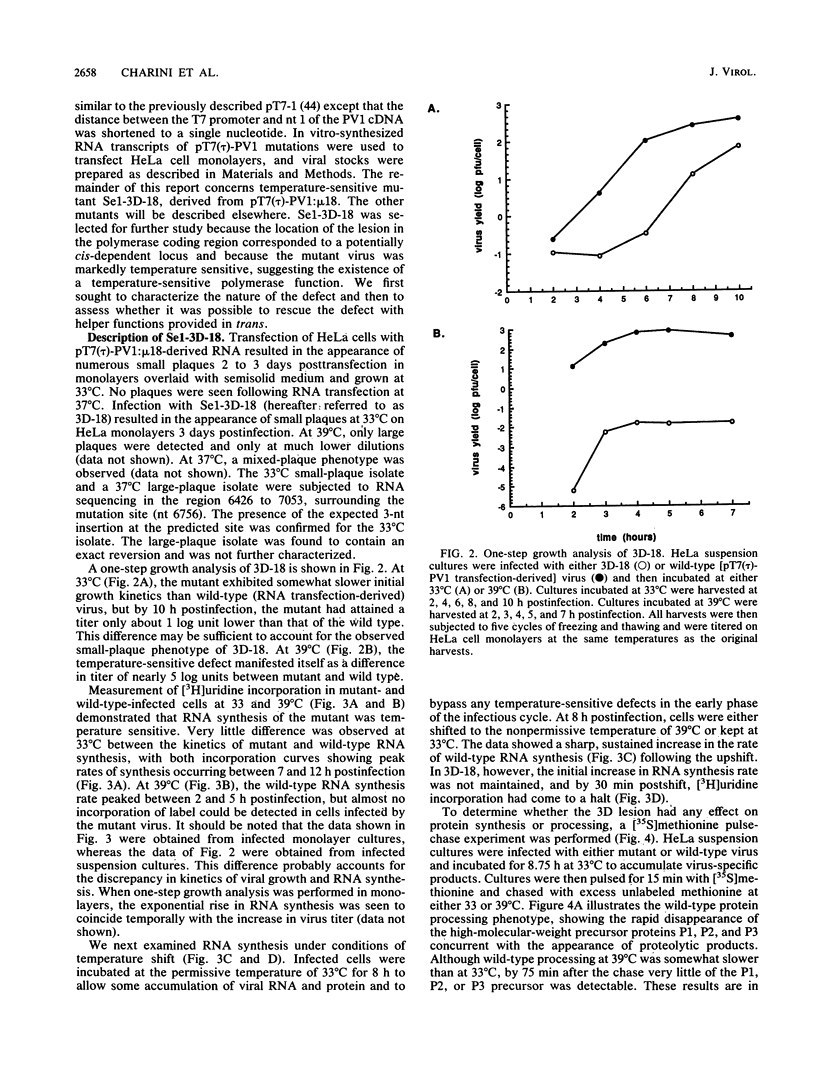
A series of three-nucleotide insertions was engineered into the P2 and P3 coding regions of the T7 expression plasmid pT7(tau)-PV1, which encodes a full-length copy of poliovirus type 1 (Mahoney) cDNA. When RNA derived in vitro from these mutated templates was used to transfect HeLa cells, viable virus mutants were recovered. One mutant, Sel-3D-18, which contained a single amino acid insertion in the 3Dpol coding region, was temperature sensitive for growth at 39 degrees C and showed defects in both RNA synthesis and P1 protein processing at the nonpermissive temperature. The RNA replication defect in Se1-3D-18 was identified at the level of RNA chain elongation. A highly specific and sensitive method was developed for analyzing the ability of mutant RNA templates to replicate in the presence or absence of helper functions provided in trans. This approach was used to demonstrate that RNA synthesis in Se1-3D-18 can be rescued by helper functions provided in trans.
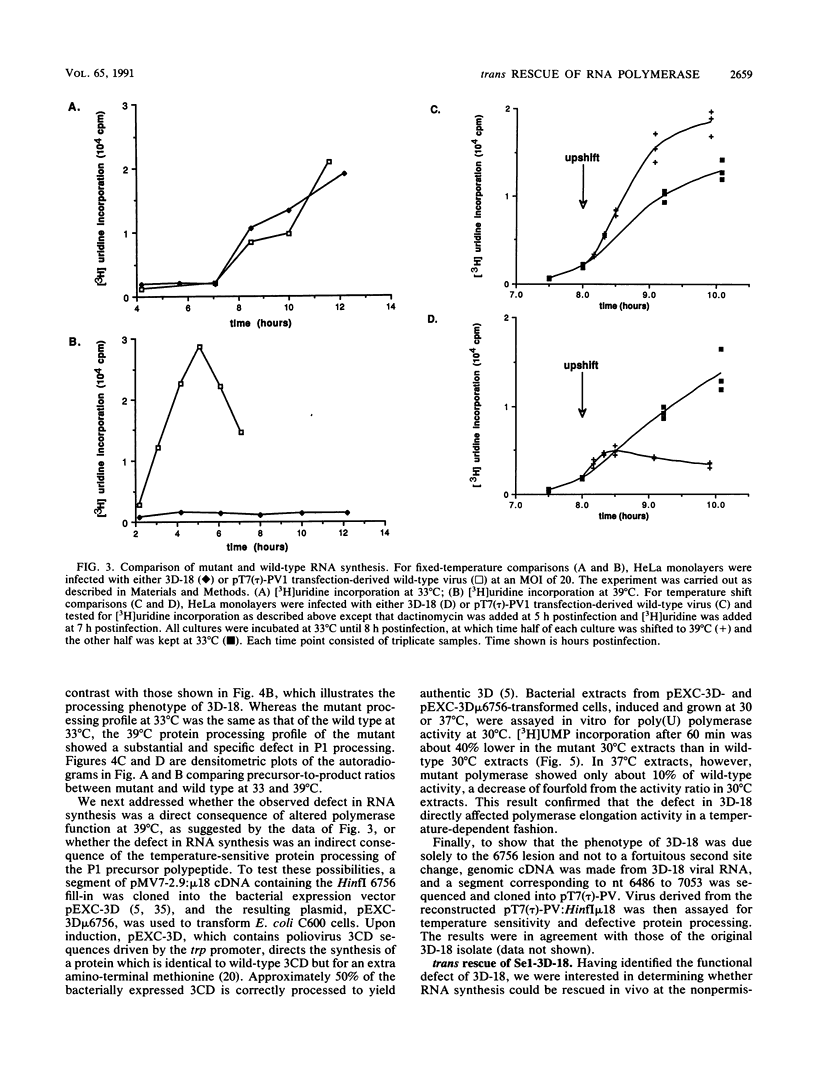
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agut H., Kean K. M., Fichot O., Morasco J., Flanegan J. B., Girard M. A point mutation in the poliovirus polymerase gene determines a complementable temperature-sensitive defect of RNA replication. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):302–311. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90270-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Baltimore D. A functional ribonucleoprotein complex forms around the 5' end of poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90170-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns C. C., Lawson M. A., Semler B. L., Ehrenfeld E. Effects of mutations in poliovirus 3Dpol on RNA polymerase activity and on polyprotein cleavage. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4866–4874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4866-4874.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos R., Villarreal L. P. An SV40 deletion mutant accumulates late transcripts in a paranuclear extract. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caton A. J., Brownlee G. G., Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W. The antigenic structure of the influenza virus A/PR/8/34 hemagglutinin (H1 subtype). Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. II. Nature of the defect. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):325–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Smoler D., Wimmer E., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. I. Isolation and physical properties. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):478–485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.478-485.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewalt P. G., Semler B. L. Site-directed mutagenesis of proteinase 3C results in a poliovirus deficient in synthesis of viral RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2162–2170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2162-2170.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildine S. L., Semler B. L. The deletion of 41 proximal nucleotides reverts a poliovirus mutant containing a temperature-sensitive lesion in the 5' noncoding region of genomic RNA. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):847–862. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.847-862.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus polyuridylic acid polymerase and RNA replicase have the same viral polypeptide. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.352-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., McLAREN L. C. Improved method for staining cell monolayers for virus plaque counts. J Bacteriol. 1959 Oct;78:596–597. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.4.596-597.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagino-Yamagishi K., Nomoto A. In vitro construction of poliovirus defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5386–5392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5386-5392.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn P. H., Browniee G. G., Cheng C. C., Gait M. J., Milstein C. Complete sequence of constant and 3' noncoding regions of an immunoglobulin mRNA using the dideoxynucleotide method of RNA sequencing. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1067–1075. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey T. D., Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Synthesis of plus- and minus-strand RNA from poliovirion RNA template in vitro. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):790–796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.790-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanoff L. A., Towatari T., Ray J., Korant B. D., Petteway S. R., Jr Expression and site-specific mutagenesis of the poliovirus 3C protease in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson V. H., Semler B. L. Defined recombinants of poliovirus and coxsackievirus: sequence-specific deletions and functional substitutions in the 5'-noncoding regions of viral RNAs. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jore J., De Geus B., Jackson R. J., Pouwels P. H., Enger-Valk B. E. Poliovirus protein 3CD is the active protease for processing of the precursor protein P1 in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1627–1636. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Construction and characterization of poliovirus subgenomic replicons. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1687–1696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1687-1696.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Saito I., Nomoto A. Primary structure of poliovirus defective-interfering particle genomes and possible generation mechanisms of the particles. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):473–487. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Meriam C., Racaniello V. R. Mapping of sequences required for mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):515–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.515-525.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Baltimore D. Isolation of poliovirus 2C mutants defective in viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4016–4021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4016-4021.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Sullivan M., Maizel J. V., Jr Characterization of a new isolate of poliovirus defective interfering particles. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):759–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin M. J., Harris K. S., Pallai P. V., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 3C: large-scale expression, purification, and specific cleavage activity on natural and synthetic substrates in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4586–4593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4586-4593.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Jacobson A., Lee Y. F., Dunn J., Wimmer E. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus: mapping of the deletion and evidence that the deletions in the genomes of DI(1), (2) and (3) are located in the same region. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 25;128(2):179–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Horie H., Kuge S., Imura N., Nomoto A. Mapping and sequencing of RNAs without recourse to molecular cloning: application to RNAs of the Sabin 1 strain of poliovirus and its defective interfering particles. J Biochem. 1986 Jan;99(1):207–217. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paeratakul U., De Stasio P. R., Taylor M. W. A fast and sensitive method for detecting specific viral RNA in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1132–1135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1132-1135.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Poliovirus RNA replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;161:89–119. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75602-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ivanoff L. A., Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Butt B., Petteway S. R., Jr, Rothstein M. A., Ehrenfeld E. Formation of poliovirus RNA polymerase 3D in Escherichia coli by cleavage of fusion proteins expressed from cloned viral cDNA. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):348–356. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein M. A., Richards O. C., Amin C., Ehrenfeld E. Enzymatic activity of poliovirus RNA polymerase synthesized in Escherichia coli from viral cDNA. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90542-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Bernstein H. D., Baltimore D. A poliovirus temperature-sensitive RNA synthesis mutant located in a noncoding region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Dorner A. J., Wimmer E. Production of infectious poliovirus from cloned cDNA is dramatically increased by SV40 transcription and replication signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5123–5141. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Johnson V. H., Dewalt P. G., Ypma-Wong M. F. Site-specific mutagenesis of cDNA clones expressing a poliovirus proteinase. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Jan;33(1):39–51. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240330105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin G. J., Young D. C., Flanegan J. B. Self-catalyzed linkage of poliovirus terminal protein VPg to poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Yang C. F., Takeda N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Analysis of RNA synthesis of type 1 poliovirus by using an in vitro molecular genetic approach. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2816–2822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2816-2822.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Dewalt P. G., Johnson V. H., Lamb J. G., Semler B. L. Protein 3CD is the major poliovirus proteinase responsible for cleavage of the P1 capsid precursor. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Semler B. L. In vitro molecular genetics as a tool for determining the differential cleavage specificities of the poliovirus 3C proteinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2069–2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]