Abstract
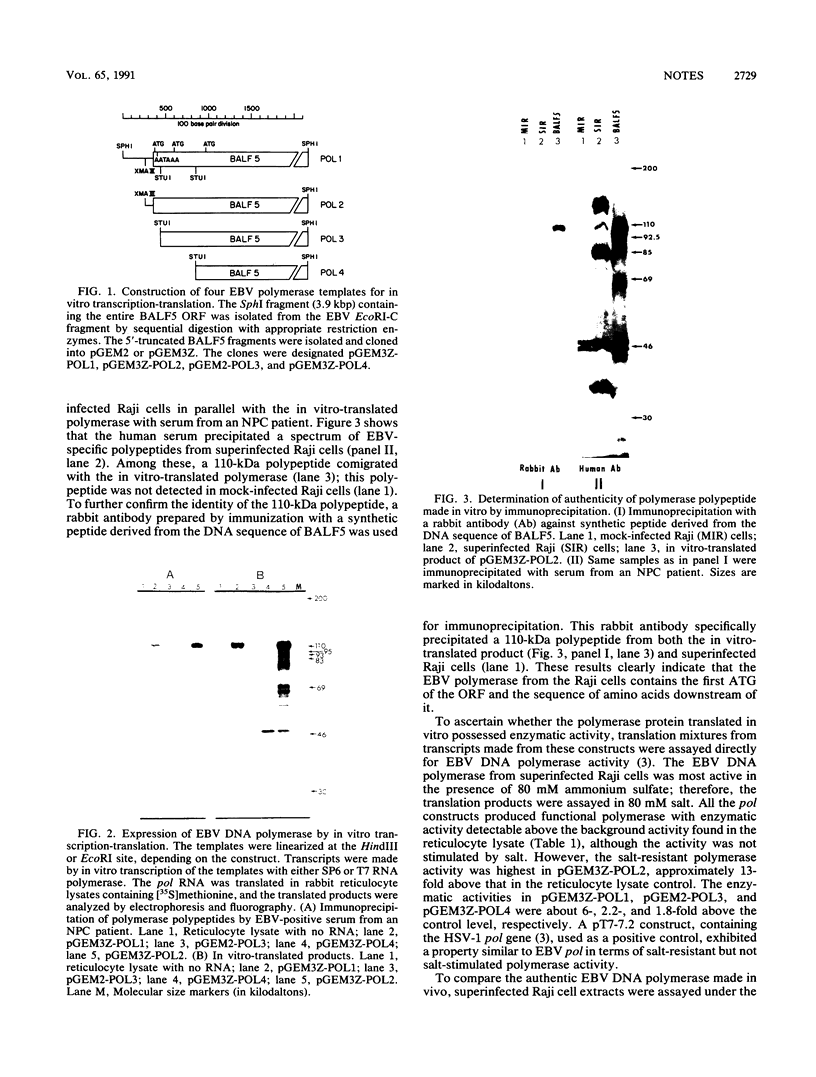
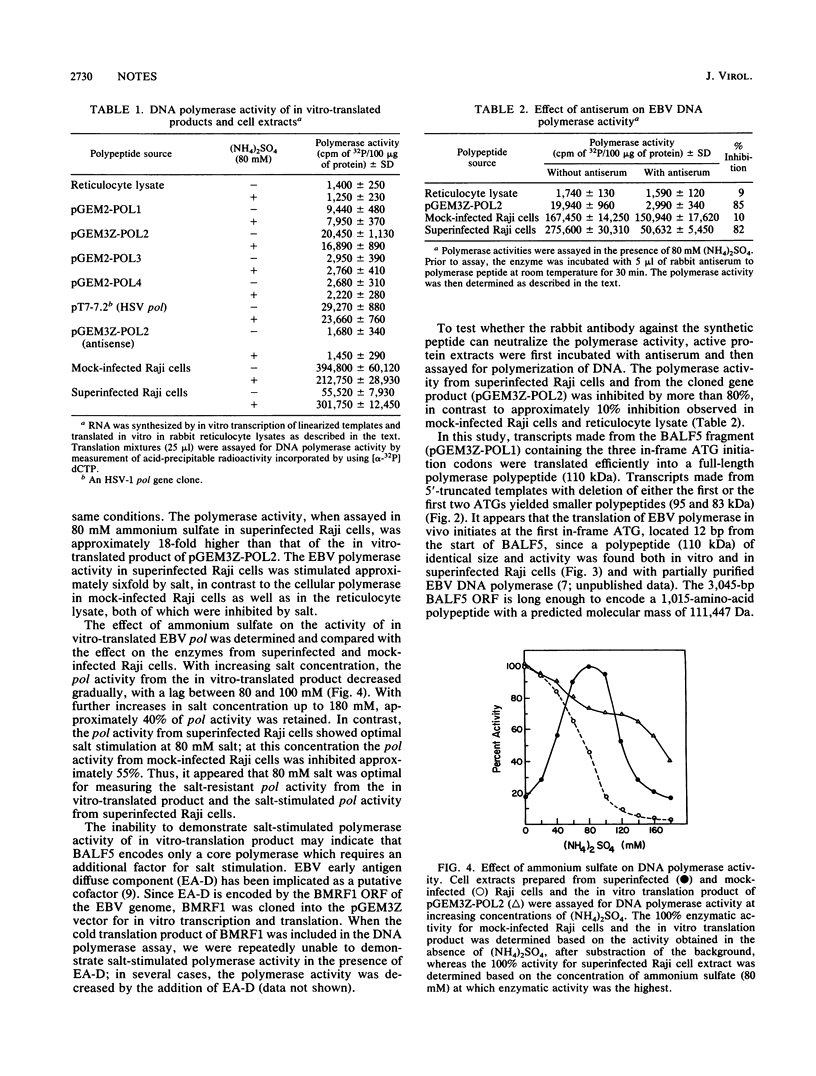
In order to identify the gene encoding the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA polymerase, a portion of the BamHI-A fragment containing the fifth leftward open reading frame (BALF5) of the EBV genome was cloned into SP6 and T7 promoter-containing vectors for in vitro transcription-translation. The RNA synthesized in vitro was used to program rabbit reticulocyte lysates, which were analyzed for the synthesis of the putative polymerase polypeptide (110 kDa) and assayed directly for EBV DNA polymerase activity. The polypeptide synthesized by the full-length BALF5 genomic fragment had a molecular mass of 110 kDa. 5'-truncated BALF5 with the first and second ATGs deleted produced 95- and 83-kDa polypeptides, respectively. All three translation products were enzymatically active and displayed resistance to high salt concentrations. The identity of the largest polypeptide as the viral polymerase was established by (i) immunoprecipitation with EBV-positive sera from patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma and by a rabbit polyclonal antiserum prepared with a synthetic peptide derived from the DNA sequence of BALF5; (ii) identification of a polypeptide of identical size (110 kDa) immunoprecipitated from superinfected Raji cell extracts by these antibodies; and (iii) salt-resistant enzymatic activity which was neutralized by the rabbit EBV antiserum. Thus, BALF5 encodes a functional polymerase identical to that induced in superinfected Raji cells.
Full text
PDF

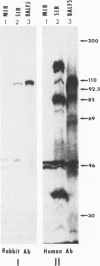
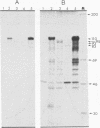
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Datta A. K., Colby B. M., Shaw J. E., Pagano J. S. Acyclovir inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5163–5166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase gene by in vitro translation and effects of gene deletions on activity. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3224–3232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3224-3232.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S. Site-specific mutagenesis of a highly conserved region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase gene. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1394–1397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1394-1397.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feighny R. J., Henry B. E., 2nd, Datta A. K., Pagano J. S. Induction of DNA polymerase activity after superinfection of Raji cells with Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Sternås L., Saemundssen A. K., Luka J., Jörnvall H., Eriksson B., Tao P. Z., Nilsson M. T., Klein G. Purification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase from P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):561–568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.561-568.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S. C., Weston K., Tomlinson P., Barrell B. G. Sequence and transcription analysis of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.125-133.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. S., Zhou B. S., Dutschman G. E., Grill S. P., Tan R. S., Cheng Y. C. Association of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen diffuse component and virus-specified DNA polymerase activity. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2947–2949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2947-2949.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., DeClercq E., Pagano J. S. Novel acyclic adenosine analogs inhibit Epstein-Barr virus replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1431–1433. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Machida H. Comparison of two bromovinyl nucleoside analogs, 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-E-5-(2-bromovinyl)uracil and E-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine, with acyclovir in inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):1068–1072. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Pagano J. S. Cellular transformation by the herpesviruses and antiviral drugs. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;28(2):135–161. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(85)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Smith M. C., Pagano J. S. Comparative efficacy and selectivity of some nucleoside analogs against Epstein-Barr virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jun;27(6):971–973. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.6.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Smith M. C., Pagano J. S. Prolonged inhibitory effect of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine against replication of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.50-55.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcy A. I., Yager D. R., Coen D. M. Isolation and characterization of herpes simplex virus mutants containing engineered mutations at the DNA polymerase locus. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2208–2216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2208-2216.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence of the region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1 containing the genes for DNA polymerase and the major DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8143–8163. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager D. R., Marcy A. I., Coen D. M. Translational regulation of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2217–2225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2217-2225.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]