Abstract
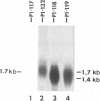
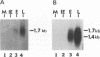
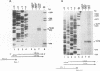
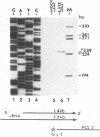
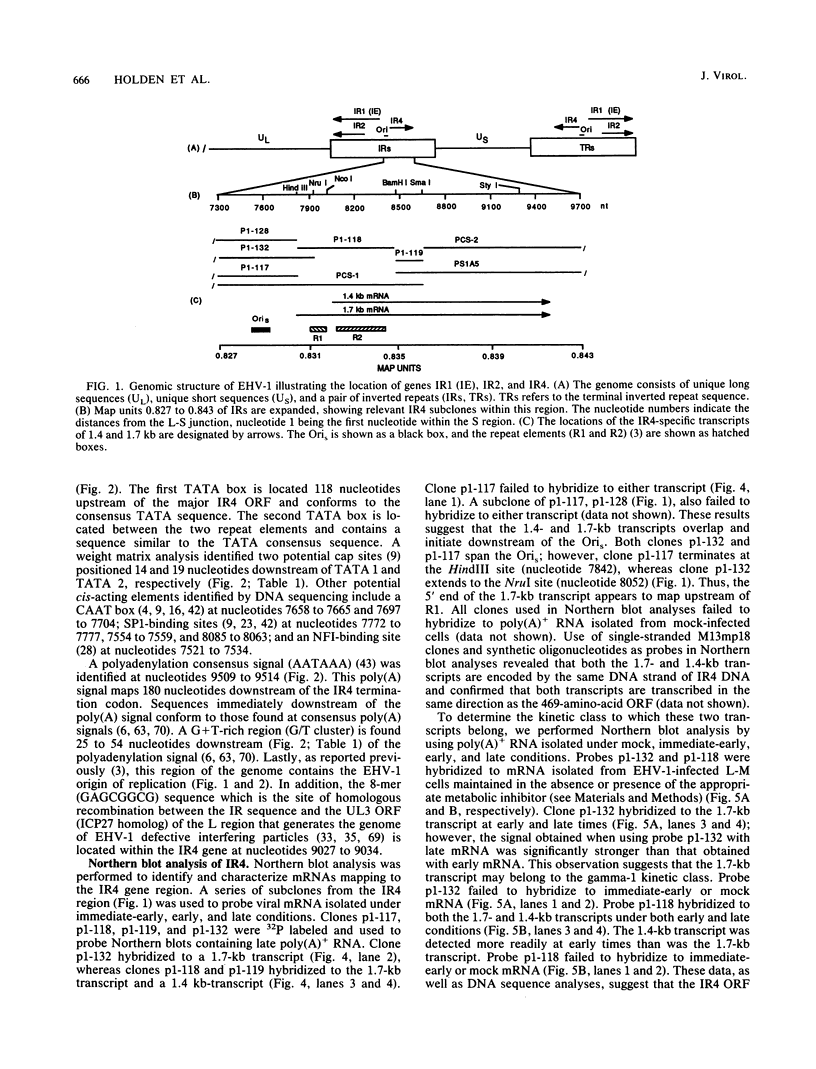
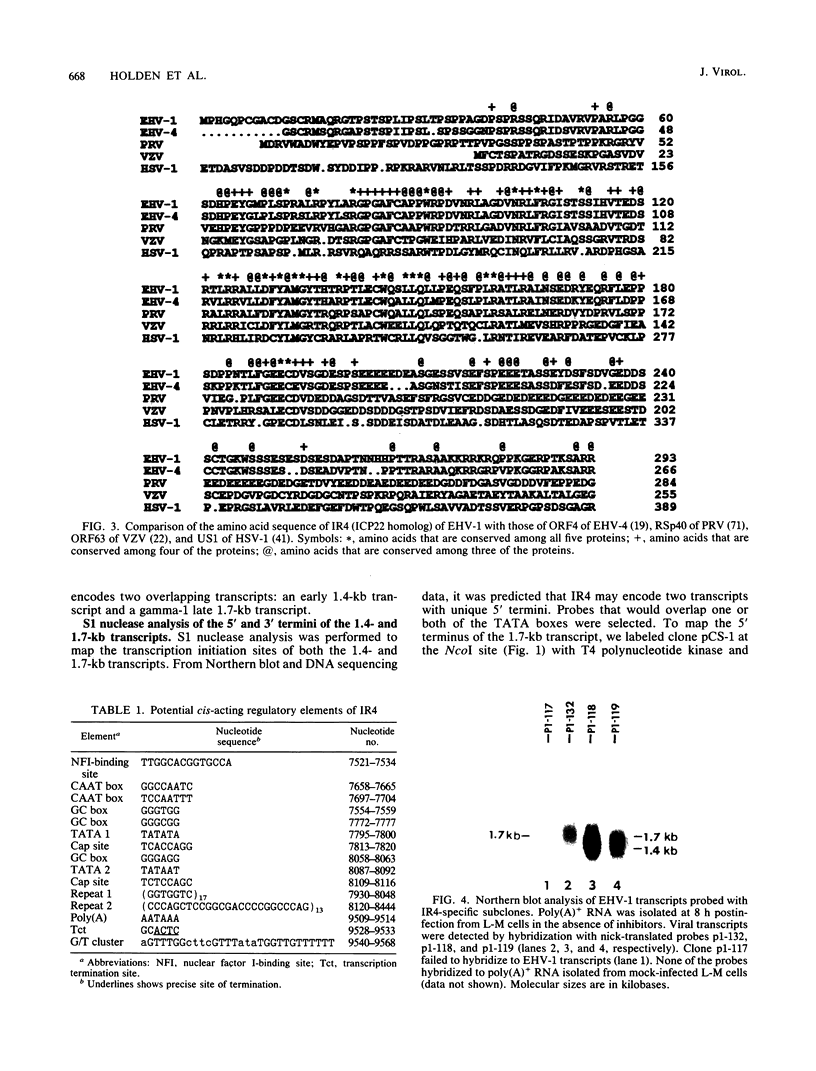
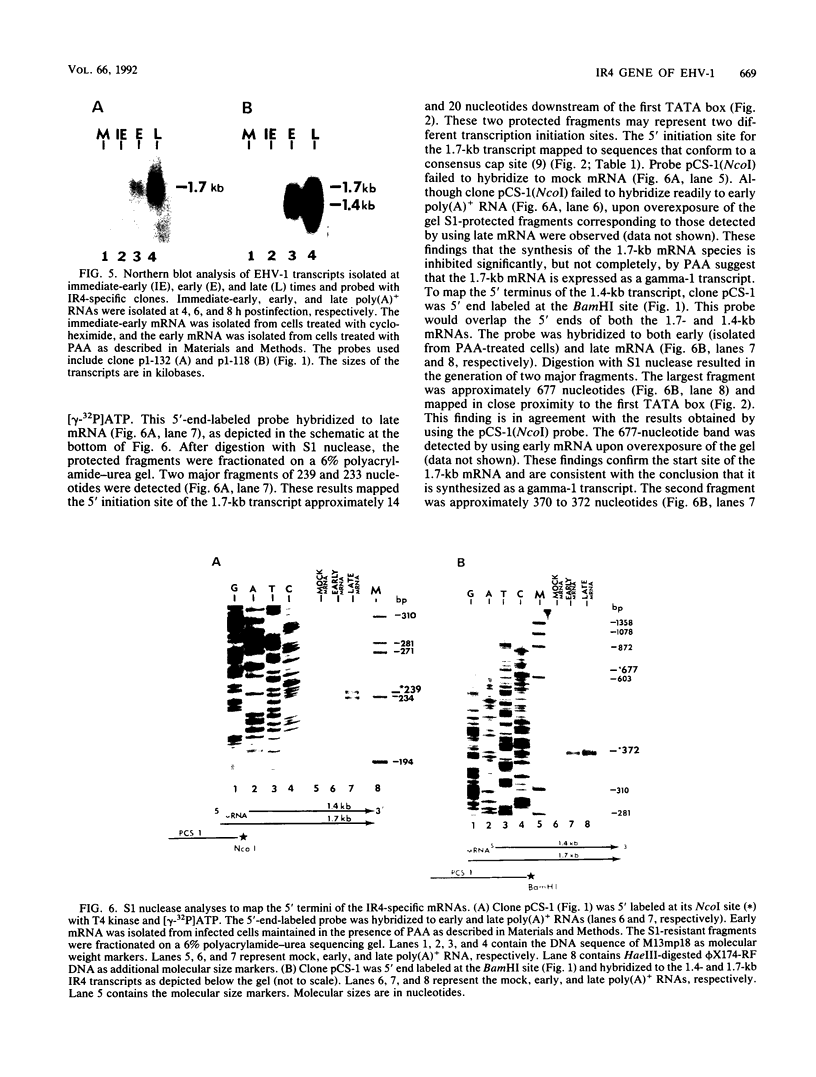
The complete nucleotide sequence of the short region, made up of a unique segment (Us; 6.5 kb) bracketed by a pair of inverted repeat sequences (IR; 12.8 kb each), of the equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) genome has been determined recently in our laboratory. Analysis of the IR segment revealed a major open reading frame (ORF) designated IR4. The IR4 ORF exhibits significant homology to the immediate-early gene US1 (ICP22) of herpes simplex virus type 1 and to the ICP22 homologs of varicella-zoster virus (ORF63), pseudorabies virus (RSp40), and equine herpesvirus 4 (ORF4). The IR4 ORF is located entirely within each of the inverted repeat sequences (nucleotides [nt] 7918 to 9327) and has the potential to encode a polypeptide of 469 amino acids (49,890 Da). Within the IR4 ORF are two reiterated sequences: a 7-nt sequence tandemly repeated 17 times and a 25-nt sequence tandemly repeated 13 times. Nucleotide sequence analyses of IR4 also revealed several potential cis-regulatory sequences, two TATA sequences separated by 287 nt, an in-frame translation initiation codon following each TATA sequence, and a single polyadenylation site. To address the nature of the mRNA species encoded by IR4, we used Northern (RNA) blot and S1 nuclease analyses. RNA mapping data revealed that IR4 has two promoters that are regulated differentially during a lytic infection. A 1.4-kb mRNA appears initially at 2 h postinfection and is an early transcript since its synthesis is not affected by the presence of phosphonoacetic acid, an inhibitor of EHV-1 DNA replication. In contrast, a 1.7-kb mRNA appears at later times postinfection and is designated as a gamma-1 transcript, since its synthesis is significantly reduced by phosphonoacetic acid. These IR4-specific mRNAs are 3' coterminal, have unique 5' termini, and would code for in-frame, overlapping, carboxy-coterminal proteins of 293 and 469 amino acids, respectively. Interestingly, the site of homologous recombination to generate the genome of EHV-1 defective interfering particles that initiate persistent infection occurs between nt 3244 and 3251 of UL3 (ICP27 homolog) and nt 9027 and 9034 of IR4 (ICP22 homolog). Thus, this recombination event would generate a unique ORF that would encode a potential protein whose amino end was derived from the N-terminal 193 amino acids of the ICP22 homolog and whose carboxyl end was derived from the C-terminal 68 amino acids of the ICP27 homolog.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Sarmiento M., Roizman B. Application of antibody to synthetic peptides for characterization of the intact and truncated alpha 22 protein specified by herpes simplex virus 1 and the R325 alpha 22- deletion mutant. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):207–215. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.207-215.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen G. P., Bryans J. T. Molecular epizootiology, pathogenesis, and prophylaxis of equine herpesvirus-1 infections. Prog Vet Microbiol Immunol. 1986;2:78–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann R. P., Yalamanchili V. R., O'Callaghan D. J. Functional mapping and DNA sequence of an equine herpesvirus 1 origin of replication. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1275–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1275-1283.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P. Weight matrix descriptions of four eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoter elements derived from 502 unrelated promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Fromm M., Berg P. Complex regulation of simian virus 40 early-region transcription from different overlapping promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1900–1914. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughman G. B., Robertson A. T., Gray W. L., Sullivan D. C., O'Callaghan D. J. Characterization of equine herpesvirus type 1 immediate early proteins. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughman G. B., Staczek J., O'Callaghan D. J. Equine herpesvirus type 1 infected cell polypeptides: evidence for immediate early/early/late regulation of viral gene expression. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. A human cytomegalovirus early gene has three inducible promoters that are regulated differentially at various times after infection. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.281-290.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of a yeast his3 "TATA element": genetic evidence for a specific TATA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2691–2695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 gene for ICP34.5, which maps in inverted repeats, is conserved in several limited-passage isolates but not in strain 17syn+. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1014–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1014-1020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C., Perdue M. L., Randall C. C., O'Callaghan D. J. Herpesvirus transcription: altered regulation induced by FUdR. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):621–633. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C., Randall C. C., O'Callaghan D. J. Transcription of equine herpesvirus type 1: evidence for classes of transcripts differing in abundance. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):561–565. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullinane A. A., Rixon F. J., Davison A. J. Characterization of the genome of equine herpesvirus 1 subtype 2. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1575–1590. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauenhauer S. A., Robinson R. A., O'Callaghan D. J. Chronic production of defective-interfering particles by hamster embryo cultures of herpesvirus persistently infected and oncogenically transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1982 May;60(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., McGeoch D. J. Evolutionary comparisons of the S segments in the genomes of herpes simplex virus type 1 and varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):597–611. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's contain multiple 5' termini upstream and downstream from a Hogness-Goldberg sequence; a shift in 5' termini during the lytic cycle is mediated by large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):224–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.224-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. L., Baumann R. P., Robertson A. T., Caughman G. B., O'Callaghan D. J., Staczek J. Regulation of equine herpesvirus type 1 gene expression: characterization of immediate early, early, and late transcription. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. L., Baumann R. P., Robertson A. T., O'Callaghan D. J., Staczek J. Characterization and mapping of equine herpesvirus type 1 immediate early, early, and late transcripts. Virus Res. 1987 Sep;8(3):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. L., Yalamanchili R., Raengsakulrach B., Baumann R. P., Staczek J., O'Callaghan D. J. Viral transcripts in cells infected with defective interfering particles of equine herpesvirus type 1. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Adhya S., Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Site-specific DNA binding of nuclear factor I: analyses of cellular binding sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):964–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy F. J., Baumann R. P., O'Callaghan D. J. DNA sequence and comparative analyses of the equine herpesvirus type 1 immediate early gene. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):223–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harty R. N., Colle C. F., Grundy F. J., O'Callaghan D. J. Mapping the termini and intron of the spliced immediate-early transcript of equine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5101–5110. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5101-5110.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harty R. N., O'Callaghan D. J. An early gene maps within and is 3' coterminal with the immediate-early gene of equine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3829–3838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3829-3838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harty R. N., Yalamanchili R. R., O'Callaghan D. J. Transcriptional analysis of the UL1 gene of equine herpesvirus 1: a gene conserved in the genome of defective interfering particles. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):830–833. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91020-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry B. E., Robinson R. A., Dauenhauer S. A., Atherton S. S., Hayward G. S., O'Callaghan D. J. Structure of the genome of equine herpesvirus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):97–114. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. L., Szabocsik J. M., Randall C. C., Gentry G. A. Equine abortion (herpes) virus-specific RNA. Virology. 1971 Aug;45(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90339-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalili K., Feigenbaum L., Khoury G. Evidence for a shift in 5'-termini of early viral RNA during the lytic cycle of JC virus. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Roizman B. The promoter, transcriptional unit, and coding sequence of herpes simplex virus 1 family 35 proteins are contained within and in frame with the UL26 open reading frame. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):206–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.206-212.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom J. L., Hall S. L., Kessler M. M. Polyadenylylation of sea urchin histone RNA sequences in transfected COS cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1094–1098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan D. J., Hyde J. M., Gentry G. A., Randall C. C. Kinetics of viral deoxyribonucleic acid, protein, and infectious particle production and alterations in host macromolecular syntheses in equine abortion (herpes) virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1968 Aug;2(8):793–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.8.793-804.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Berk A. J. Far upstream initiation sites for adenovirus early region 1A transcription are utilized after the onset of viral DNA replication. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):594–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.594-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Roizman B. A generalized technique for deletion of specific genes in large genomes: alpha gene 22 of herpes simplex virus 1 is not essential for growth. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., McGeoch D. J. A 3' co-terminal family of mRNAs from the herpes simplex virus type 1 short region: two overlapping reading frames encode unrelated polypeptide one of which has highly reiterated amino acid sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2473–2487. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson A. T., Caughman G. B., Gray W. L., Baumann R. P., Staczek J., O'Callaghan D. J. Analysis of the in vitro translation products of the equine herpesvirus type 1 immediate early mRNA. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):451–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson R. A., Tucker P. W., Dauenhauer S. A., O'Callaghan D. J. Molecular cloning of equine herpesvirus type 1 DNA: analysis of standard and defective viral genomes and viral sequences in oncogenically transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6684–6688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson R. A., Vance R. B., O'Callaghan D. J. Oncogenic transformation by by equine herpesviruses. II. Coestablishment of persistent infection and oncogenic transformation of hamster embryo cells by equine herpesvirus type 1 preparations enriched for defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):204–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.204-219.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Dauenhauer S. A., O'Callaghan D. J. Electron microscopic study of equine herpesvirus type 1 DNA. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):297–300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.297-300.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOEHNER R. L., GENTRY G. A., RANDALL C. C. SOME PHYSICOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EQUINE ABORTION VIRUS NUCLEIC ACID. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:394–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., Halliburton I. W., Meignier B., Silver S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 mutant deleted in the alpha 22 gene: growth and gene expression in permissive and restrictive cells and establishment of latency in mice. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.338-346.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. A., Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site efficiency reflects the stability of complex formation involving the downstream element. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):215–219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalley J. M., Robertson G. R., Davison A. J. Analysis of the genome of equine herpesvirus type 1: arrangement of cleavage sites for restriction endonucleases EcoRI, BglII and BamHI. J Gen Virol. 1981 Dec;57(Pt 2):307–323. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The junctions between the repetitive and the short unique sequences of the herpes simplex virus genome are determined by the polypeptide-coding regions of two spliced immediate-early mRNAs. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):451–466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Kohn A., Sklyanskaya E., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. I. Phosphate cycles on and off some viral polypeptides and can alter their affinity for DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):167–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.167-182.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalamanchili R. R., O'Callaghan D. J. Sequence and organization of the genomic termini of equine herpesvirus type 1. Virus Res. 1990 Feb;15(2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90005-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalamanchili R. R., Raengsakulrach B., Baumann R. P., O'Callaghan D. J. Identification of the site of recombination in the generation of the genome of DI particles of equine herpesvirus type 1. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90429-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Wickens M. Formation of mRNA 3' termini: stability and dissociation of a complex involving the AAUAAA sequence. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):177–186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G., Leader D. P. The structure of the pseudorabies virus genome at the end of the inverted repeat sequences proximal to the junction with the short unique region. J Gen Virol. 1990 Oct;71(Pt 10):2433–2441. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-10-2433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]