Abstract
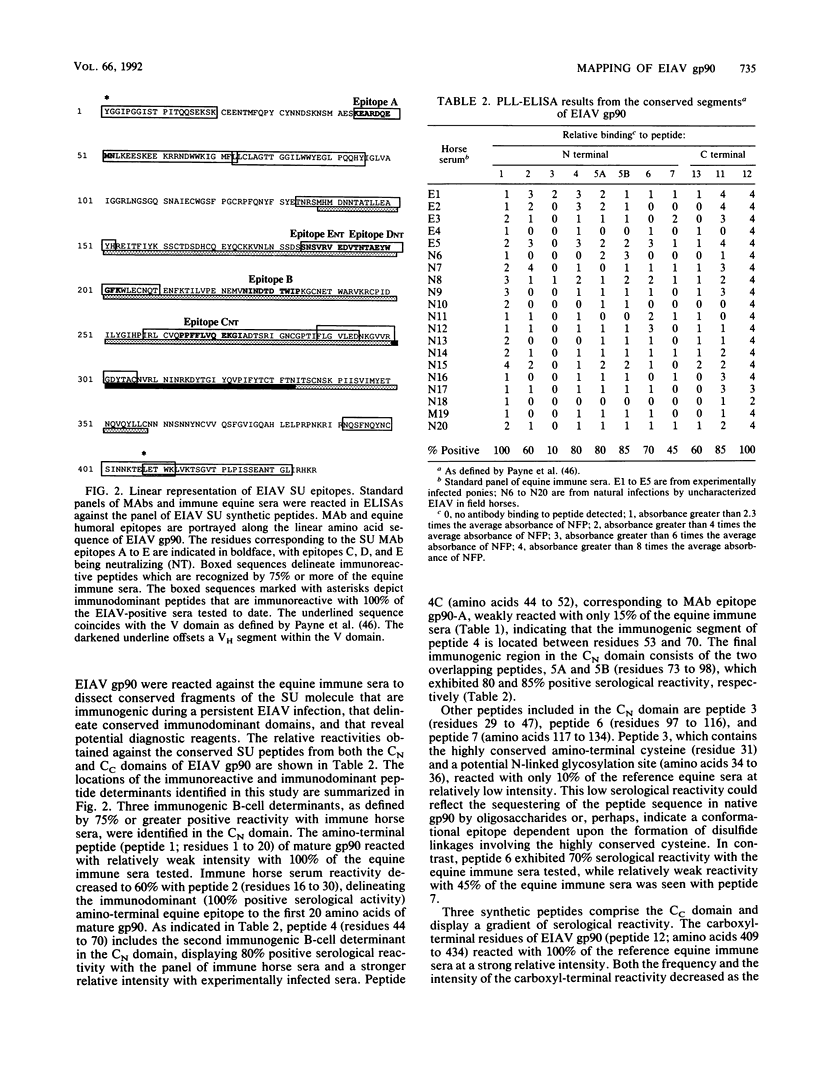
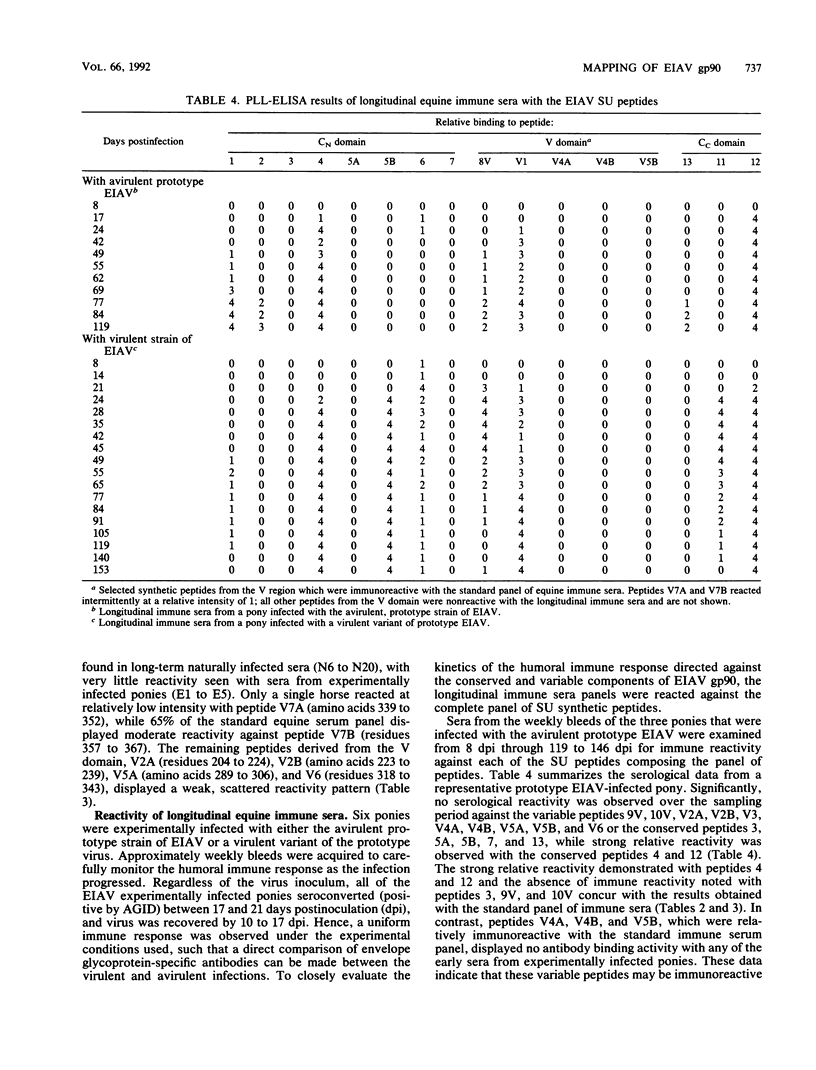
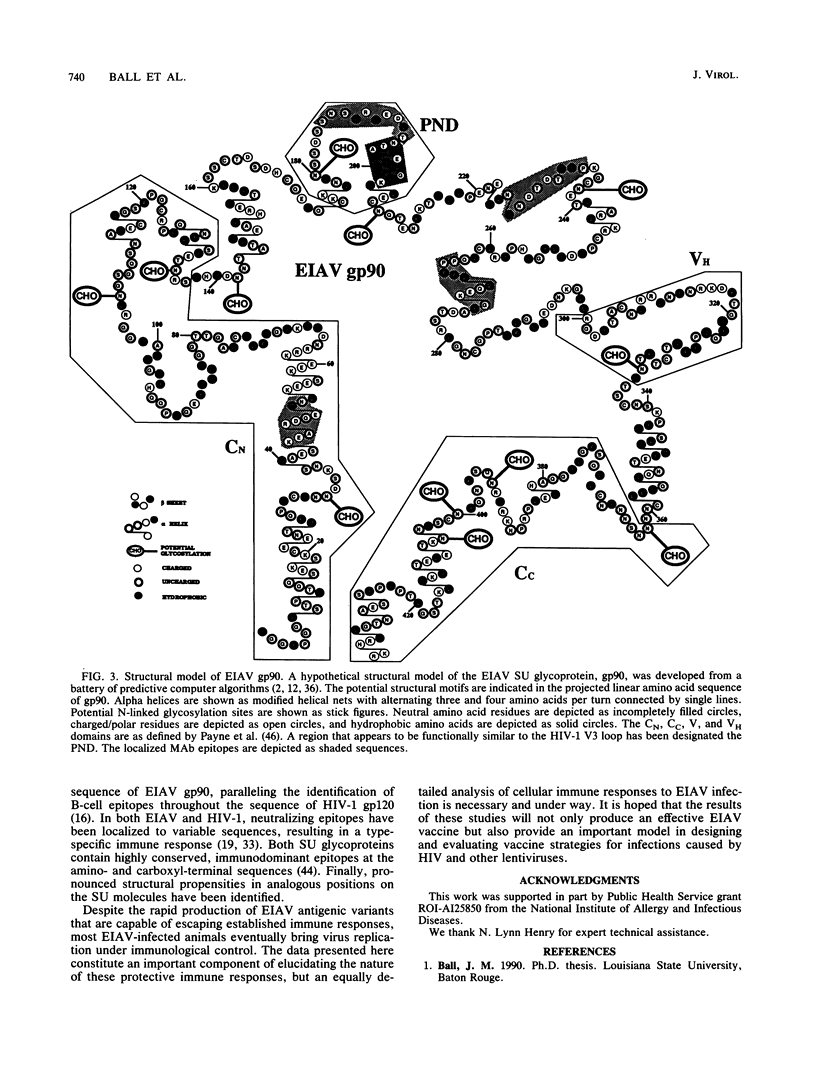
We describe here a detailed analysis of the antigenic determinants of the surface unit glycoprotein (gp90) of equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV), using a comprehensive panel of synthetic peptides in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with immune serum from naturally and experimentally infected horses and with a panel of gp90-specific neutralizing and nonneutralizing monoclonal antibodies. The results of these studies identify immunoreactive segments throughout the conserved and variable domains of gp90 but localize immunodominant (100% reactivity) determinants to the amino and carboxyl termini of the glycoprotein molecule. Analysis of peptide reactivities with longitudinal serum samples taken from experimentally infected ponies revealed that antibody responses to conserved B-cell determinants appeared earlier and at higher titers than do antibodies specific for determinants contained in the variable domain of gp90. These observations suggest an evolution of antibody responses in EIAV-infected ponies that may correspond to the establishment of immunological control of virus replication and disease routinely observed in EIAV infections. In addition, the mapping of monoclonal antibody epitopes to peptides of 9 to 12 amino acids demonstrated that all of the neutralizing epitopes are located in the variable domain of gp90. The arrangement of neutralizing epitopes and critical structural considerations suggest that EIAV gp90 contains a principal neutralizing domain similar to the V3 loop of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. These antigenic analyses provide an important foundation for further analyzing the protective immune response generated during persistent EIAV infections and also provide potential peptide substrates for diagnostic assays and for vaccine strategies.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball J. M., Payne S. L., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. EIAV genomic organization: further characterization by sequencing of purified glycoproteins and cDNA. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):601–605. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90605-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cease K. B., Berzofsky J. A. Antigenic structures recognized by T cells: towards the rational design of an AIDS vaccine. AIDS. 1988;2 (Suppl 1):S95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong Y. H., Ball J. M., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C., Rushlow K. E. Analysis of equine humoral immune responses to the transmembrane envelope glycoprotein (gp45) of equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):1013–1018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.1013-1018.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontenot J. D., Ball J. M., Miller M. A., David C. M., Montelaro R. C. A survey of potential problems and quality control in peptide synthesis by the fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl procedure. Pept Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;4(1):19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Myers D. J., Risser R. Identification of the principal neutralizing determinant of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 as a fusion domain. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):190–194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.190-194.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R., Ball J. M., Garry R. F., Griffin M. C., Montelaro R. C. A general model for the transmembrane proteins of HIV and other retroviruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):431–440. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibrat J. F., Garnier J., Robson B. Further developments of protein secondary structure prediction using information theory. New parameters and consideration of residue pairs. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):425–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Schwimmbeck P. L., Nelson J. A., Truax A. B., Oldstone M. B. Diagnosis of AIDS by using a 12-amino acid peptide representing an immunodominant epitope of the human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):261–267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Boucher C. A., Meloen R. H., Epstein L. G., Smit L., van der Hoek L., Bakker M. Human antibody response to a strain-specific HIV-1 gp120 epitope associated with cell fusion inhibition. AIDS. 1988 Jun;2(3):157–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J. Immunodominant B-cell epitopes of the HIV-1 envelope recognized by infected and immunized hosts. AIDS. 1988;2 (Suppl 1):S41–S45. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198800001-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigwood N. L., Shuster J. R., Moore G. K., Lee H., Skiles P. V., Higgins K. W., Barr P. J., George-Nascimento C., Steimer K. S. Importance of hypervariable regions of HIV-1 gp120 in the generation of virus neutralizing antibodies. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jul;6(7):855–869. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Sarngadharan M. G., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Rota T. R., Kennedy R. C., Chanh T. C., Sato V. L. Human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibodies recognize several conserved domains on the envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2024–2028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2024-2028.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain K. A., Issel C. J., Schnorr K. L., Rwambo P. M., Montelaro R. C. Antigenic analysis of equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV) variants by using monoclonal antibodies: epitopes of glycoprotein gp90 of EIAV stimulate neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2956–2961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2956-2961.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain K. A., Issel C. J., Schnorr K. L., Rwambo P. M., West M., Montelaro R. C. Antigenic mapping of the envelope proteins of equine infectious anemia virus: identification of a neutralization domain and a conserved region on glycoprotein 90. Arch Virol. 1988;98(3-4):213–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01322170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issel C. J., Coggins L. Equine infectious anemia: current knowledge. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1979 Apr 1;174(7):727–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Langlois A. J., McDanal C., Ross K. L., Eckler L. I., Jellis C. L., Profy A. T., Rusche J. R., Bolognesi D. P., Putney S. D. Principal neutralizing domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6768–6772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E., Colescott R. L., Bossinger C. D., Cook P. I. Color test for detection of free terminal amino groups in the solid-phase synthesis of peptides. Anal Biochem. 1970 Apr;34(2):595–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasse P. J., Pipkorn R., Blomberg J. Presence of antibodies to a putatively immunosuppressive part of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) envelope glycoprotein gp41 is strongly associated with health among HIV-positive subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5225–5229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Hirasawa K., Fukunaga Y., Taniguchi T. Recrudescence of equine infectious anemia by treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1976 Spring;16(1):8–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Kobayashi K., Fukunaga Y. Antigenic drift of equine infectious anemia virus in chronically infected horses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;41(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01249923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krowka J. F., Singh B., Stites D. P., Maino V. C., Narindray D., Hollander H., Jain S., Chen H., Blackwood L., Steimer K. S. Epitopes of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope glycoproteins recognized by antibodies in the sera of HIV-1-infected individuals. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Apr;59(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90081-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard C. K., Spellman M. W., Riddle L., Harris R. J., Thomas J. N., Gregory T. J. Assignment of intrachain disulfide bonds and characterization of potential glycosylation sites of the type 1 recombinant human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein (gp120) expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10373–10382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmquist W. A., Barnett D., Becvar C. S. Production of equine infectious anemia antigen in a persistently infected cell line. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;42(4):361–370. doi: 10.1007/BF01250717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margalit H., Spouge J. L., Cornette J. L., Cease K. B., Delisi C., Berzofsky J. A. Prediction of immunodominant helper T cell antigenic sites from the primary sequence. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2213–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita S., Robert-Guroff M., Rusche J., Koito A., Hattori T., Hoshino H., Javaherian K., Takatsuki K., Putney S. Characterization of a human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing monoclonal antibody and mapping of the neutralizing epitope. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2107–2114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2107-2114.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrow S., Höflacher B., Mellert W., Erfle V., Wahren B., Wolf H. Use of synthetic oligopeptides in identification and characterization of immunological functions in the amino acid sequence of the envelope protein of HIV-1. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(1):21–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., Parekh B., Orrego A., Issel C. J. Antigenic variation during persistent infection by equine infectious anemia virus, a retrovirus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10539–10544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Lee E. S. B cell epitope mapping of human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins with long (19- to 36-residue) synthetic peptides. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):85–95. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Chiodi F., Whalley A., Parks E., Nauclér A., Costa C. M., Torstensson R., Biberfeld G. Site-directed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a synthetic simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac peptide identifying antibodies against the HIV-2 transmembrane glycoprotein. AIDS. 1989 Jan;3(1):17–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Putkonen P., Böttiger B., Utter G., Biberfeld G. Comparison of linear antigenic sites in the envelope proteins of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 2 and type 1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Mar;7(3):279–285. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrego A., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C., Adams W. V., Jr Virulence and in vitro growth of a cell-adapted strain of equine infectious anemia virus after serial passage in ponies. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Sep;43(9):1556–1560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Clark M. E., Langlois A. J., Matthews T. J., Weinhold K. J., Randall R. R., Bolognesi D. P., Haynes B. F. Type-specific neutralization of the human immunodeficiency virus with antibodies to env-encoded synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Matthews T. J., Clark M. E., Cianciolo G. J., Randall R. R., Langlois A. J., White G. C., Safai B., Snyderman R., Bolognesi D. P. A conserved region at the COOH terminus of human immunodeficiency virus gp120 envelope protein contains an immunodominant epitope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2479–2483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. L., Fang F. D., Liu C. P., Dhruva B. R., Rwambo P., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. Antigenic variation and lentivirus persistence: variations in envelope gene sequences during EIAV infection resemble changes reported for sequential isolates of HIV. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. L., Rushlow K., Dhruva B. R., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. Localization of conserved and variable antigenic domains of equine infectious anemia virus envelope glycoproteins using recombinant env-encoded protein fragments produced in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):609–615. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. L., Salinovich O., Nauman S. M., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. Course and extent of variation of equine infectious anemia virus during parallel persistent infections. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1266–1270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1266-1270.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S., Parekh B., Montelaro R. C., Issel C. J. Genomic alterations associated with persistent infections by equine infectious anaemia virus, a retrovirus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1395–1399. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian N., Sejnowski T. J. Predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins using neural network models. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):865–884. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90564-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Taylor W. R. A sequence pattern common to T cell epitopes. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow K., Olsen K., Stiegler G., Payne S. L., Montelaro R. C., Issel C. J. Lentivirus genomic organization: the complete nucleotide sequence of the env gene region of equine infectious anemia virus. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90195-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rwambo P. M., Issel C. J., Adams W. V., Jr, Hussain K. A., Miller M., Montelaro R. C. Equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV) humoral responses of recipient ponies and antigenic variation during persistent infection. Arch Virol. 1990;111(3-4):199–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01311054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Payne S. L., Montelaro R. C., Hussain K. A., Issel C. J., Schnorr K. L. Rapid emergence of novel antigenic and genetic variants of equine infectious anemia virus during persistent infection. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.71-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Cohen J., Hosmalin A., Cease K. B., Houghten R., Cornette J. L., DeLisi C., Moss B., Germain R. N., Berzofsky J. A. An immunodominant epitope of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein gp160 recognized by class I major histocompatibility complex molecule-restricted murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3105–3109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. J., Steel S., Wisniewolski R., Wang C. Y. Detection of antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type III by using a synthetic peptide of 21 amino acid residues corresponding to a highly antigenic segment of gp41 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6159–6163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. Q., Wolf H., Shuler K. R., Eichberg J. W., Zajac R. A., Boswell R. N., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Synthetic peptides define the fine specificity of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) gp160 humoral immune response in HIV type 1-infected chimpanzees. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):486–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.486-492.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tijn D. A., Boucher C. A., Bakker M., Goudsmit J. Antigenicity of linear B-cell epitopes in the C1, V1, and V3 region of HIV-1 gp 120. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(3):303–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



