Abstract
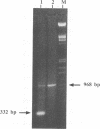
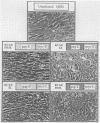
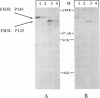
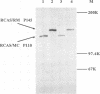
The avian retrovirus FH3, like MC29 and CMII, encodes a Gag-Myc fusion protein. However, the FH3-encoded protein is larger, about 145 kDa, and contains almost the entire retroviral gag gene. In contrast to the other gag-myc avian retroviruses, FH3 fails to transform fibroblasts in vitro, although macrophages are transformed both in vitro and in vivo (C. Chen, B. J. Biegalke, R. N. Eisenman, and M. L. Linial, J. Virol. 63:5092-5100, 1989). We have used the polymerase chain reaction technique to obtain a molecular clone of FH3. Sequence analysis of the FH3 myc oncogene revealed a single proline----histidine change (position 223) relative to c-myc. However, substitution of the FH3 myc sequence with the chicken c-myc sequence did not alter the transformation potential of the virus. Hence, overexpression of the proto-oncogene as a Gag-Myc retroviral protein is sufficient for macrophage, but not fibroblast, transformation. After passage of FH3 in fibroblast cultures, a virus (FH3L) that is capable of rapidly transforming fibroblasts appears. The Gag-Myc protein encoded by FH3L is smaller (ca. 130 kDa) than that encoded by the original viral stock (FH3E). Sequencing of an FH3L molecular clone revealed a 212-amino-acid deletion within the Gag portion. Using FH3E/FH3L recombinants, we have demonstrated that the ability of encoded viruses to transform fibroblasts directly correlates with the presence of this deletion. Moreover, the addition of the Gag sequence deleted from FH3L to the MC29 oncoprotein significantly reduces its transforming activity as measured by focus assay. These data suggest that the C-terminal segment of Gag attenuates the oncogenic potential of Gag-Myc fusion proteins.
Full text
PDF

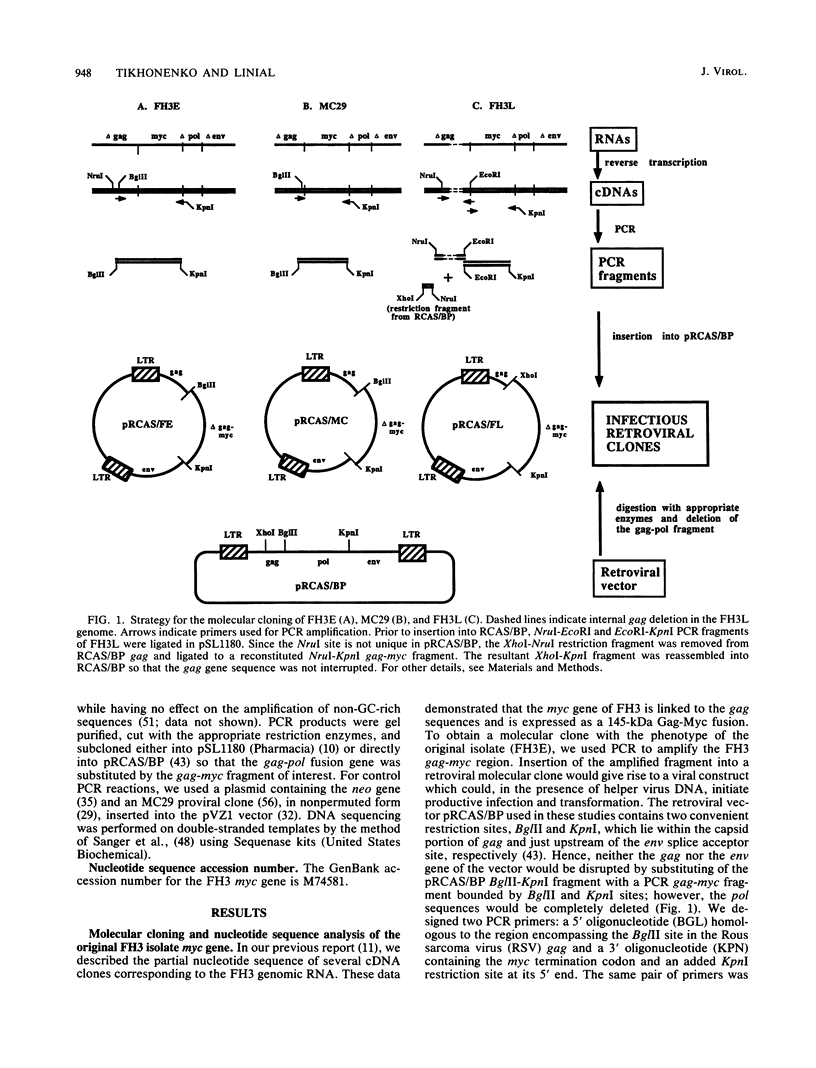

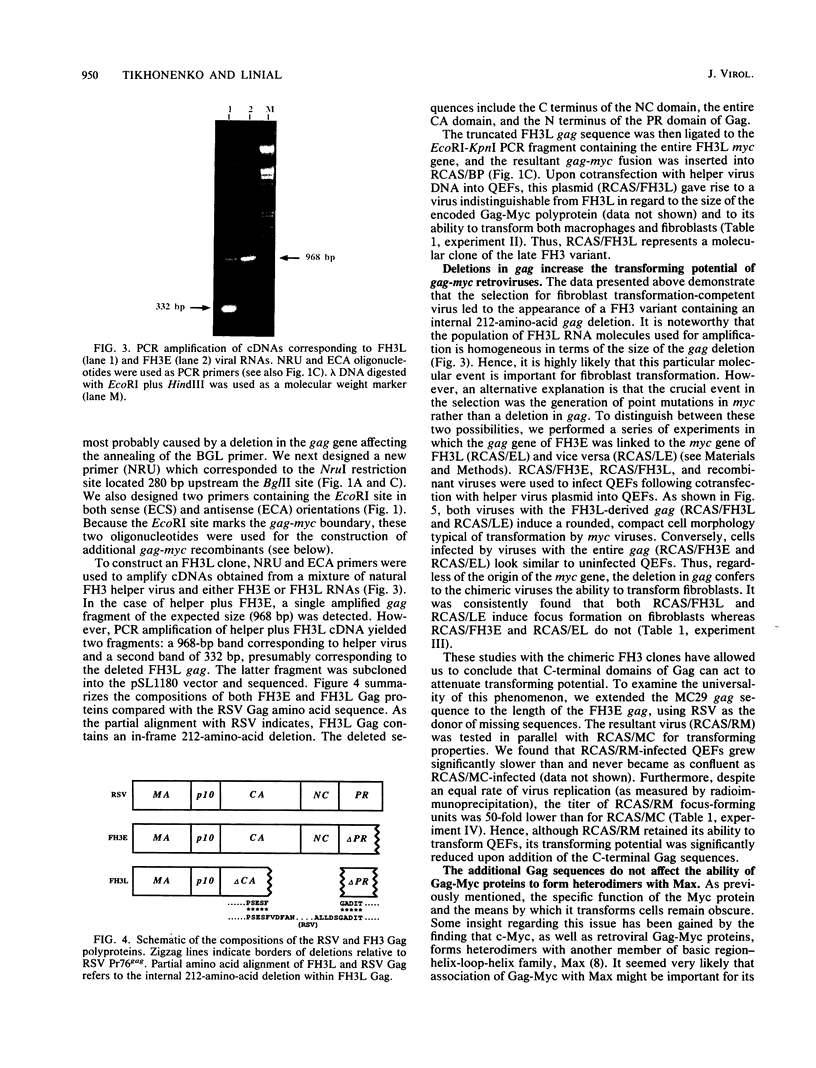
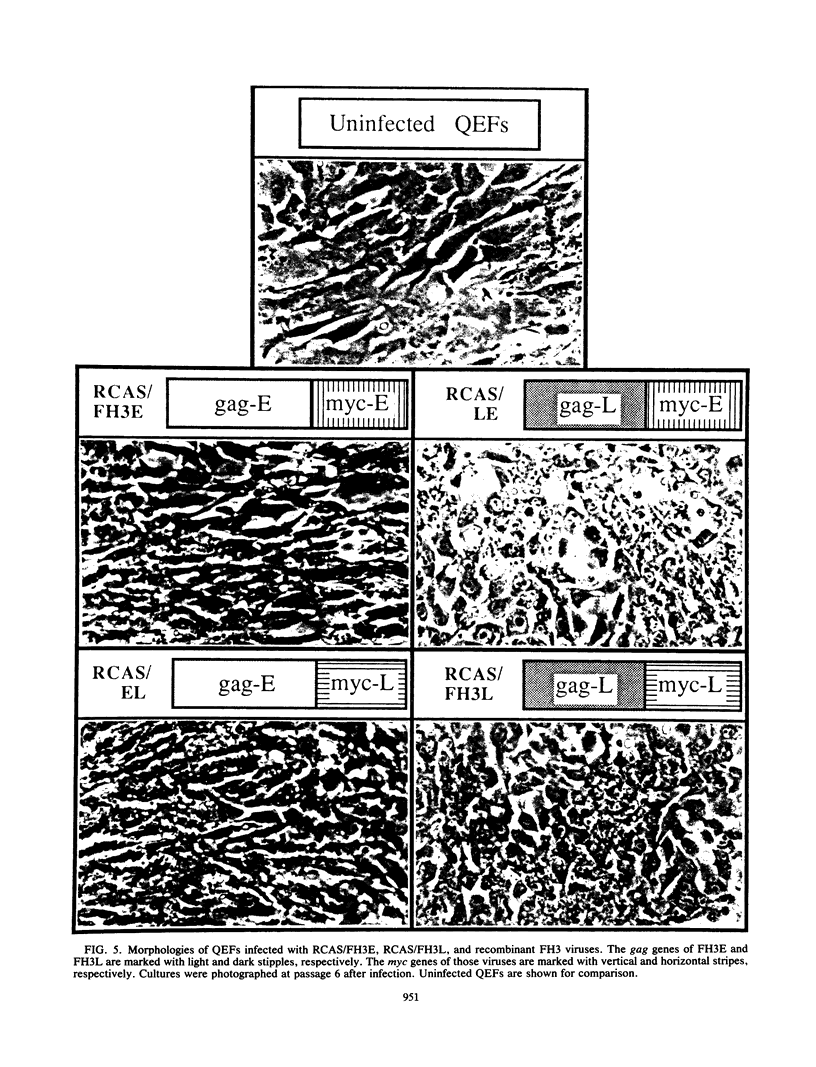
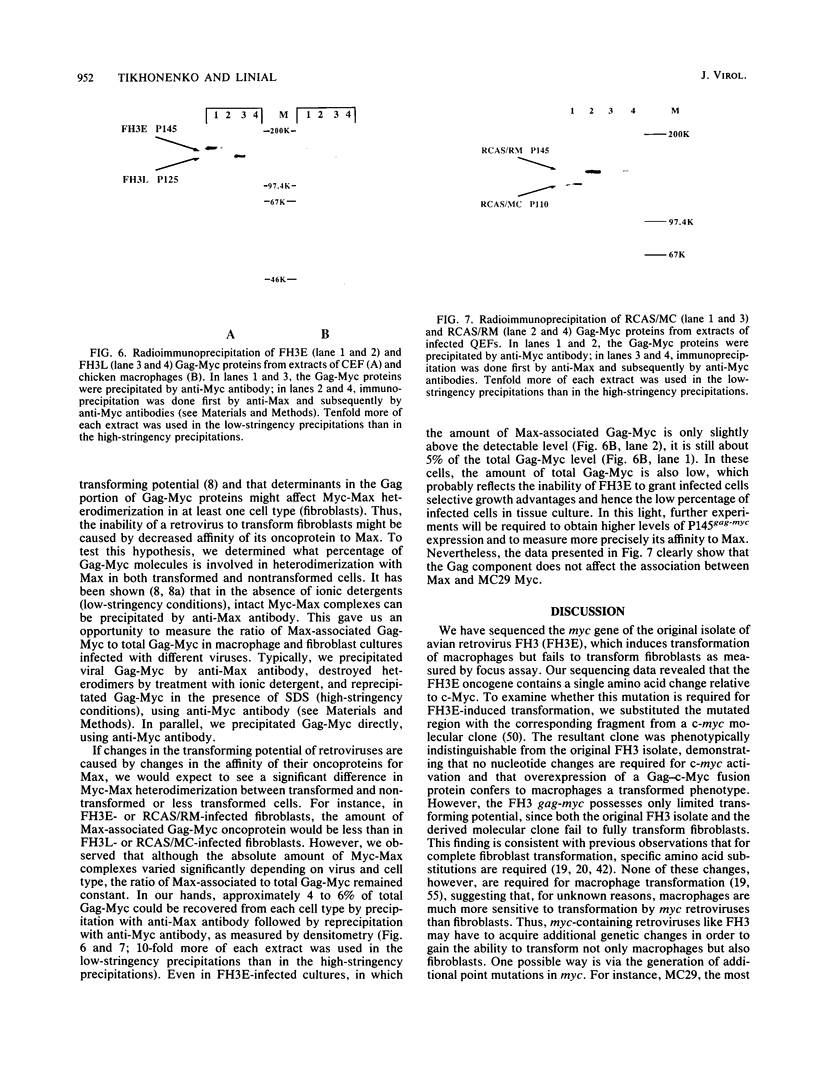



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Bishop J. M., Smith D. H., Chen E. Y., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Nucleotide sequence to the v-myc oncogene of avian retrovirus MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S., Yun M., Beemon K. cis-acting regulatory elements within gag genes of avian retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):388–397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegalke B. J., Heaney M. L., Bouton A., Parsons J. T., Linial M. MC29 deletion mutants which fail to transform chicken macrophages are competent for transformation of quail macrophages. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2138–2142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2138-2142.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Defectiveness of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: isolation of long-term nonproducer cultures and analysis of virus-specific polypeptide synthesis. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Jansen H. W. Oncogenes in retroviruses and cells: biochemistry and molecular genetics. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;47:99–188. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Trachmann C., Jansen H. W., Schroeer B., Patschinsky T. Structure of mutant and wild-type MC29 v-myc alleles and biochemical properties of their protein products. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):97–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M. J., Deininger P. L., Casey J. W. Nucleotide sequence of a transduced myc gene from a defective feline leukemia provirus. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):177–183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.177-183.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Superpolylinkers in cloning and expression vectors. DNA. 1989 Dec;8(10):759–777. doi: 10.1089/dna.1989.8.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Biegalke B. J., Eisenman R. N., Linial M. L. FH3, a v-myc avian retrovirus with limited transforming ability. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5092–5100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5092-5100.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collum R. G., Alt F. W. Are myc proteins transcription factors? Cancer Cells. 1990 Mar;2(3):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch D. H., Lang C., Gillespie D. A. The leucine zipper domain of avian cMyc is required for transformation and autoregulation. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):683–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett D. L., Drake A. L., Hirsch V., Rowe M. E., Stallard V., Mullins J. I. Structure, origin, and transforming activity of feline leukemia virus-myc recombinant provirus FTT. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2108–2117. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2108-2117.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schirm S., Bishop J. M. The MYC protein activates transcription of the alpha-prothymosin gene. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enrietto P. J. A small deletion in the carboxy terminus of the viral myc gene renders the virus MC29 partially transformation defective in avian fibroblasts. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):256–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frykberg L., Graf T., Vennström B. The transforming activity of the chicken c-myc gene can be potentiated by mutations. Oncogene. 1987;1(4):415–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick J., Seeburg P. H., Ohlsson R., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Watson D., Papas T., Duesberg P. H. Nucleotide sequence of two overlapping myc-related genes in avian carcinoma virus OK10 and their relation to the myc genes of other viruses and the cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2718–2722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Kitchener G., Graf T. Cells transformed by avian myelocytomatosis virus strain CMII contain a 90K gag-related protein. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90537-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong S. M., Wang L. H. Role of gag sequence in the biochemical properties and transforming activity of the avian sarcoma virus UR2-encoded gag-ros fusion protein. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5997–6009. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5997-6009.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata N., Jotte R. M., Holt J. T. Myristylation alters DNA-binding activity and transactivation of FBR (gag-fos) protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):765–772. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan N. C., Flordellis C. S., Mark G. E., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence of avian carcinoma virus MH2: two potential onc genes, one related to avian virus MC29 and the other related to murine sarcoma virus 3611. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3000–3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Dang C. V. An amino-terminal c-myc domain required for neoplastic transformation activates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5914–5920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J., Baltimore D., Bishop J. M., Coffin J., Fleissner E., Goff S. P., Oroszlan S., Robinson H., Skalka A. M., Temin H. M. Standardized and simplified nomenclature for proteins common to all retroviruses. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1808–1809. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1808-1809.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J., Jentoft J. Characteristics and regulation of interaction of avian retrovirus pp12 protein with viral RNA. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.361-369.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine K. L., Steiner B., Johnson K., Aronoff R., Quinton T. J., Linial M. L. Unusual features of integrated cDNAs generated by infection with genome-free retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1891–1900. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy L. S., Gardner M. B., Casey J. W. Isolation of a feline leukaemia provirus containing the oncogene myc from a feline lymphosarcoma. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):853–856. doi: 10.1038/308853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Creation of a processed pseudogene by retroviral infection. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90759-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Two retroviruses with similar transforming genes exhibit differences in transforming potential. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):382–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luban J., Goff S. P. Binding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA to recombinant HIV-1 gag polyprotein. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3203–3212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3203-3212.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Brody D. S., Binari R. C., Jr, Cotter S. M. Viral transduction of c-myc gene in naturally occurring feline leukaemias. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):856–858. doi: 10.1038/308856a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méric C., Gouilloud E., Spahr P. F. Mutations in Rous sarcoma virus nucleocapsid protein p12 (NC): deletions of Cys-His boxes. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3328–3333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3328-3333.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Hughes D., McFarlane R., Wilkie N. M., Onions D. E., Lees G., Jarrett O. Transduction and rearrangement of the myc gene by feline leukaemia virus in naturally occurring T-cell leukaemias. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):814–820. doi: 10.1038/308814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nottenburg C., Varmus H. E. Features of the chicken c-myc gene that influence the structure of c-myc RNA in normal cells and bursal lymphomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2800–2806. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri S., Kahn P., Graf T. Quail embryo fibroblasts transformed by four v-myc-containing virus isolates show enhanced proliferation but are non tumorigenic. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2385–2389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01750.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos C. J., Hughes S. H. Replication-competent retrovirus vectors for the transfer and expression of gene cassettes in avian cells. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3728–3737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3728-3737.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Hayman M. J. Analysis of cells transformed by defective leukemia virus OK10: production of noninfectious particles and synthesis of Pr76gag and an additional 200,000-dalton protein. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J., Hayman M. J., Enrietto P. J. Analysis of a deleted MC29 provirus: gag sequences are not required for fibroblast transformation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):943–950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.943-950.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. K., Linial M., Goodenow M. M., Hayward W. S. Nucleotide sequence 5' of the chicken c-myc coding region: localization of a noncoding exon that is absent from myc transcripts in most avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4697–4701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart L., Schatz G., Vogt V. M. Properties of avian retrovirus particles defective in viral protease. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5076–5092. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5076-5092.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Chang L. J., Cripe T. P., Turek L. P. Efficient transformation by Prague A Rous sarcoma virus plasmid DNA requires the presence of cis-acting regions within the gag gene. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3401–3409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3401-3409.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symonds G., Hartshorn A., Kennewell A., O'Mara M. A., Bruskin A., Bishop J. M. Transformation of murine myelomonocytic cells by myc: point mutations in v-myc contribute synergistically to transforming potential. Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):285–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Moscovici C., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian myelocytomatosis virus genome and recovery of infectious virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):625–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.625-631.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther N., Jansen H. W., Trachmann C., Bister K. Nucleotide sequence of the CMII v-myc allele. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Payne G., Varmus H. E. Proviral deletions and oncogene base-substitutions in insertionally mutagenized c-myc alleles may contribute to the progression of avian bursal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):843–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang B. S., Geddes T. J., Pogulis R. J., de Crombrugghe B., Freytag S. O. Transcriptional suppression of cellular gene expression by c-Myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2291–2295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]