Abstract
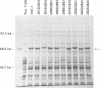
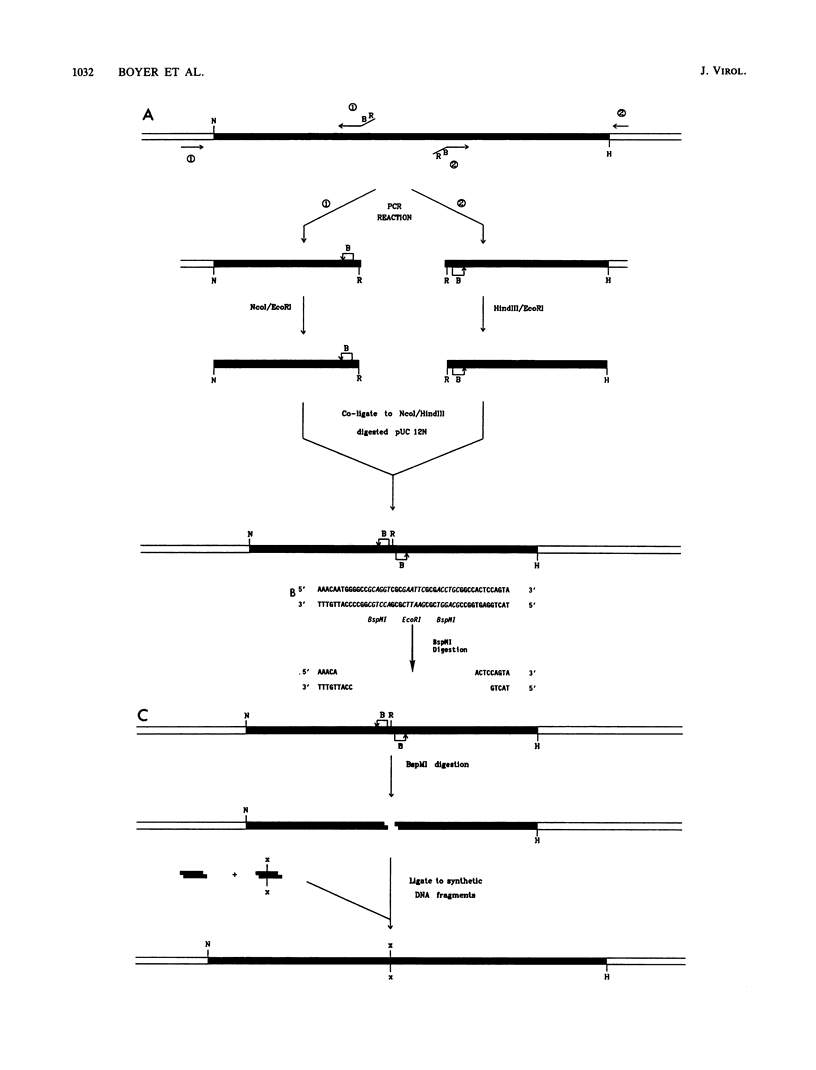
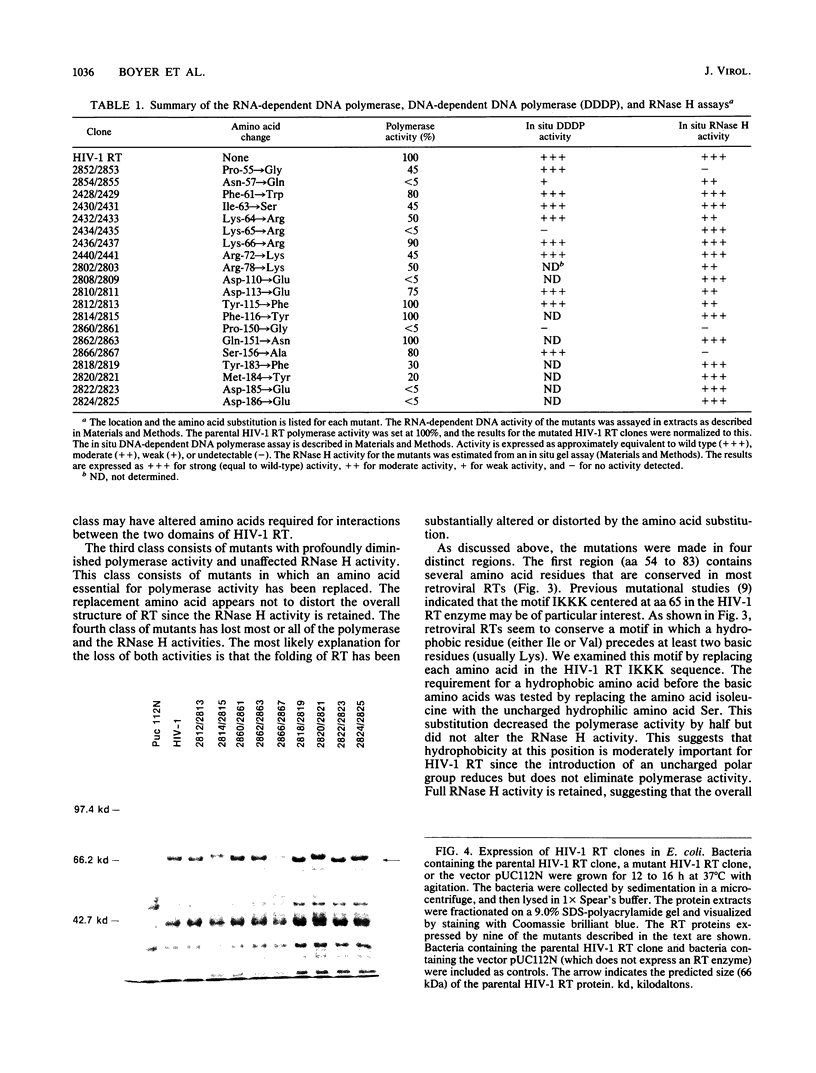
We constructed a series of BspMI cassettes that simplify the introduction of specific point mutations in the polymerase domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. A series of point mutants were constructed by using these cassette vectors. The RNA-dependent DNA polymerase and RNase H activities of 20 point mutations in the conserved portion of the polymerase domain were assayed. All the mutations analyzed are conservative substitutions of evolutionarily conserved amino acids. The mutations were divided into four classes. The first class has little effect on either polymerase or RNase H activity. The second class affects RNase H but not polymerase activity, while the third class has a normal RNase H activity with diminished polymerase activity. The fourth class affects both activities.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber A. M., Hizi A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Hughes S. H. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: structure predictions for the polymerase domain. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Sep;6(9):1061–1072. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becerra S. P., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Karlström A. R., Stahl S. J., Wilson S. H., Wingfield P. T. Purification and characterization of the RNase H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase expressed in recombinant Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81238-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark P. K., Ferris A. L., Miller D. A., Hizi A., Kim K. W., Deringer-Boyer S. M., Mellini M. L., Clark A. D., Jr, Arnold G. F., Lebherz W. B., 3rd HIV-1 reverse transcriptase purified from a recombinant strain of Escherichia coli. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jun;6(6):753–764. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. F., 2nd, Hostomska Z., Hostomsky Z., Jordan S. R., Matthews D. A. Crystal structure of the ribonuclease H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):88–95. doi: 10.1126/science.1707186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafkemeyer P., Ferrari E., Brecher J., Hübscher U. The p15 carboxyl-terminal proteolysis product of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase p66 has DNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5262–5266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Mellert W., Moelling K. Identification and characterization of HIV-specific RNase H by monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):239–243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., Barber A., Hughes S. H. Effects of small insertions on the RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):326–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90389-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., Hughes S. H., Shaharabany M. Mutational analysis of the ribonuclease H activity of human immunodeficiency virus 1 reverse transcriptase. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):575–580. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90444-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., McGill C., Hughes S. H. Expression of soluble, enzymatically active, human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli and analysis of mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1218–1222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., Tal R., Hughes S. H. Mutational analysis of the DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H activities of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 reverse transcriptase expressed in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90038-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostomsky Z., Hostomska Z., Hudson G. O., Moomaw E. W., Nodes B. R. Reconstitution in vitro of RNase H activity by using purified N-terminal and C-terminal domains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1148–1152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. W., Kang C. Y. Enzyme activities in four different forms of human immunodeficiency virus 1 pol gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4596–4600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotewicz M. L., Sampson C. M., D'Alessio J. M., Gerard G. F. Isolation of cloned Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase lacking ribonuclease H activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):265–277. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D., Purifoy D. J. Infectious potential of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase mutants with altered inhibitor sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4803–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L., Darby G. Site-specific mutagenesis of AIDS virus reverse transcriptase. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):716–717. doi: 10.1038/327716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B., Purifoy D., Powell K., Darby G. AIDS virus reverse transcriptase defined by high level expression in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3133–3137. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02623.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grice S. F., Zehnle R., Mous J. A single 66-kilodalton polypeptide processed from the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 pol polyprotein in Escherichia coli displays reverse transcriptase activity. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2525–2529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2525-2529.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G., Crouch R. J., Post K., Hu S. C., McKelvin D., Zweig M., Court D. L., Gerwin B. I. Functional organization of the murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase: characterization of a bacterially expressed AKR DNA polymerase deficient in RNase H activity. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4376–4380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4376-4380.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. M., Aitken A., Bradley C., Darby G. K., Larder B. A., Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J., Tisdale M., Stammers D. K. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: crystallization and analysis of domain structure by limited proteolysis. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):8884–8889. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. M., Parmar V., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Mutational analysis of two conserved sequence motifs in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 6;282(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80484-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Johnson M. S., Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Sequence comparisons of retroviral proteins: relative rates of change and general phylogeny. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2469–2473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra G., Pauly G. T., Kumar R., Pei G. K., Hughes S. H., Moschel R. C., Barbacid M. Molecular analysis of O6-substituted guanine-induced mutagenesis of ras oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8650–8654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi V., Usdin M. T., Harington A., Dudding L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis of the conserved Asp-443 and Asp-498 carboxy-terminal residues of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5359–5363. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Restle T., Weiss S., Gautel M., Sczakiel G., Goody R. S. Co-expression of the subunits of the heterodimer of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):13975–13978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad V. R., Goff S. P. Linker insertion mutagenesis of the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase expressed in bacteria: definition of the minimal polymerase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3104–3108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restle T., Müller B., Goody R. S. Dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. A target for chemotherapeutic intervention. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):8986–8988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucheton M., Lelay M. N., Jeanteur P. Evidence from direct visualization after denaturing gel electrophoresis that RNase H is associated with MSV-MuLV reverse transcripase. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):221–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz O., Cromme F. V., Grüninger-Leitch F., Le Grice S. F. Point mutations in conserved amino acid residues within the C-terminal domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase specifically repress RNase H function. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81559-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaharabany M., Hizi A. The DNA-dependent and RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities of the reverse transcriptases of human immunodeficiency viruses types 1 and 2. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Nov;7(11):883–888. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanos A., Sedgwick S. G., Yarranton G. T., Hübscher U., Banks G. R. Detection of the catalytic activities of DNA polymerases and their associated exonucleases following SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1825–1839. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stammers D. K., Tisdale M., Court S., Parmar V., Bradley C., Ross C. K. Rapid purification and characterisation of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and RNaseH engineered to incorporate a C-terminal tripeptide alpha-tubulin epitope. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 3;283(2):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80613-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes M. C., Gao W. Y., Ting R. Y., Cheng Y. C. Enzyme activity gel analysis of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5132–5134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. C., Vass W. C., Willumsen B. M., Lowy D. R. p21-ras effector domain mutants constructed by "cassette" mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3565–3569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Goff S. P. Domain structure of the Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase: mutational analysis and separate expression of the DNA polymerase and RNase H activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M., Ertl P., Larder B. A., Purifoy D. J., Darby G., Powell K. L. Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase by using monoclonal antibodies: role of the C terminus in antibody reactivity and enzyme function. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3662–3667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3662-3667.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomic M., Sunjevaric I., Savtchenko E. S., Blumenberg M. A rapid and simple method for introducing specific mutations into any position of DNA leaving all other positions unaltered. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1656–1656. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. Retroviruses. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1427–1435. doi: 10.1126/science.3287617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Marzo Veronese F., Copeland T. D., DeVico A. L., Rahman R., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of highly immunogenic p66/p51 as the reverse transcriptase of HTLV-III/LAV. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1289–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.2418504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]