Abstract
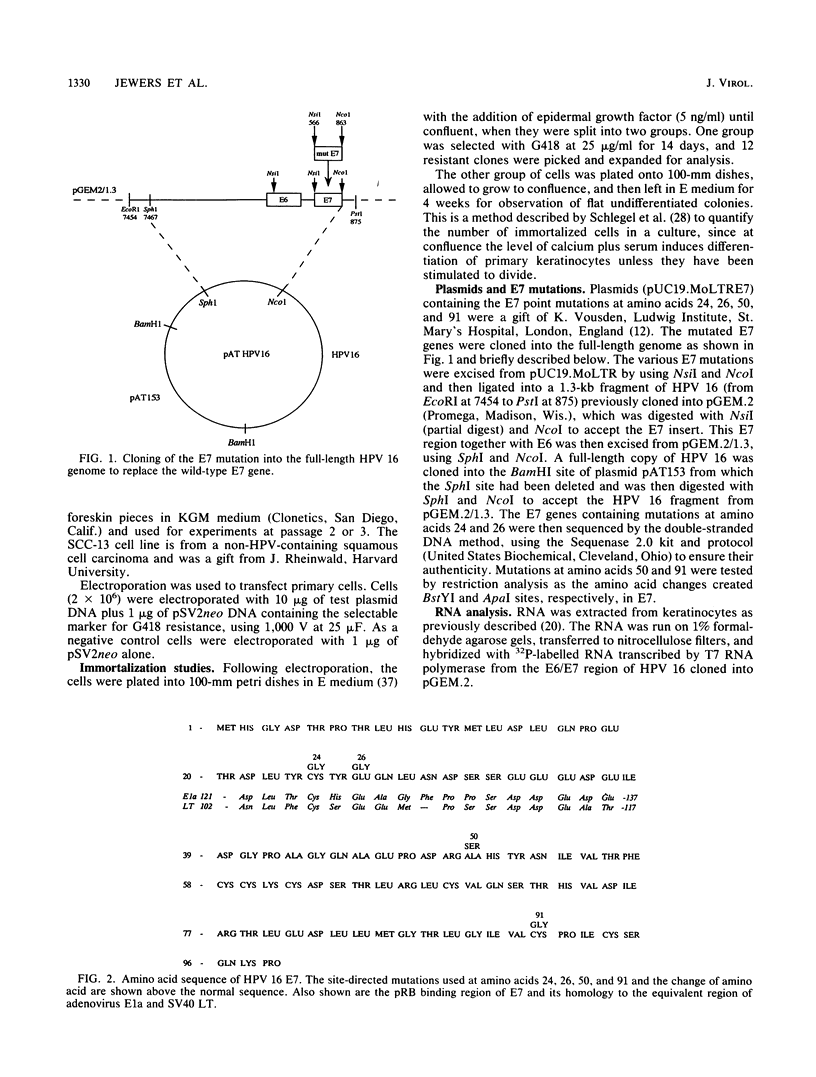
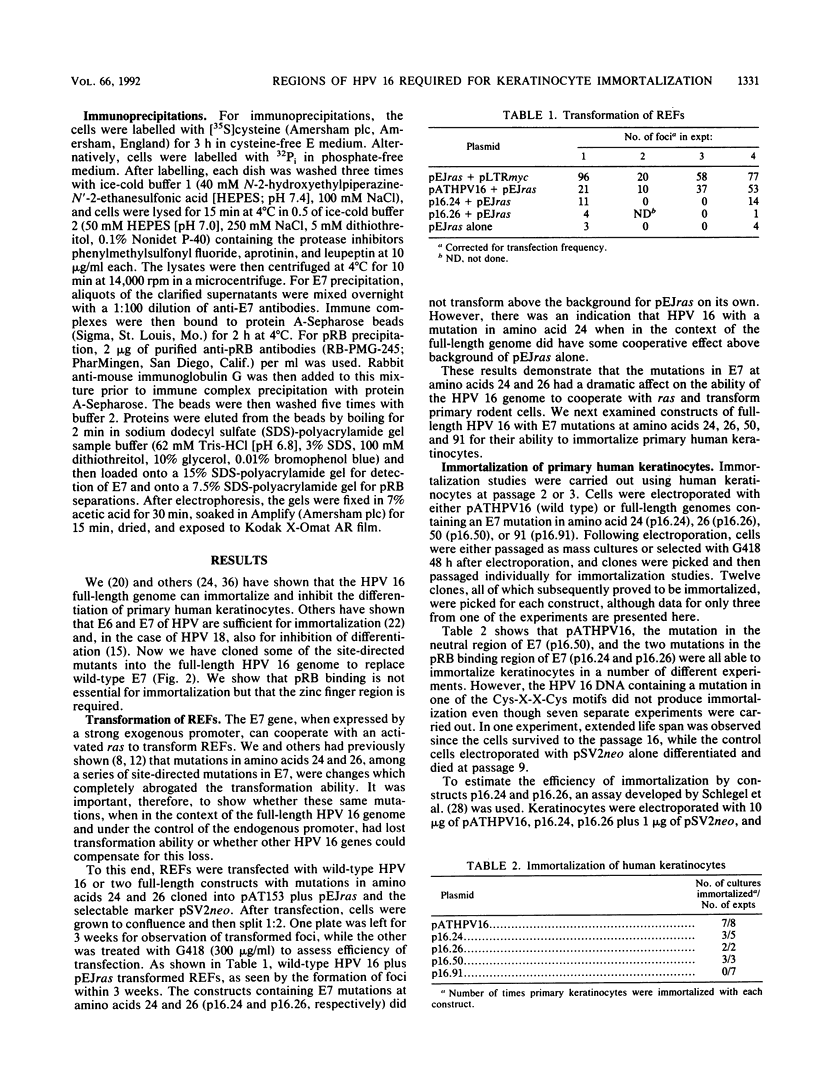
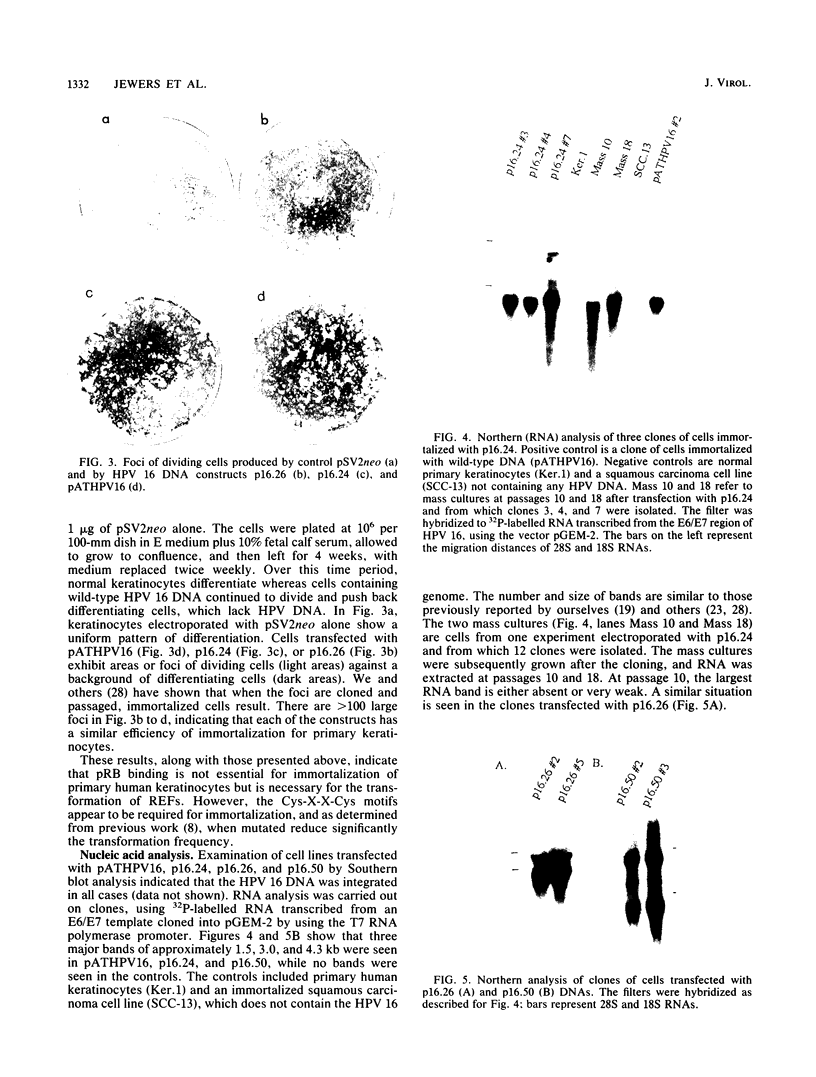
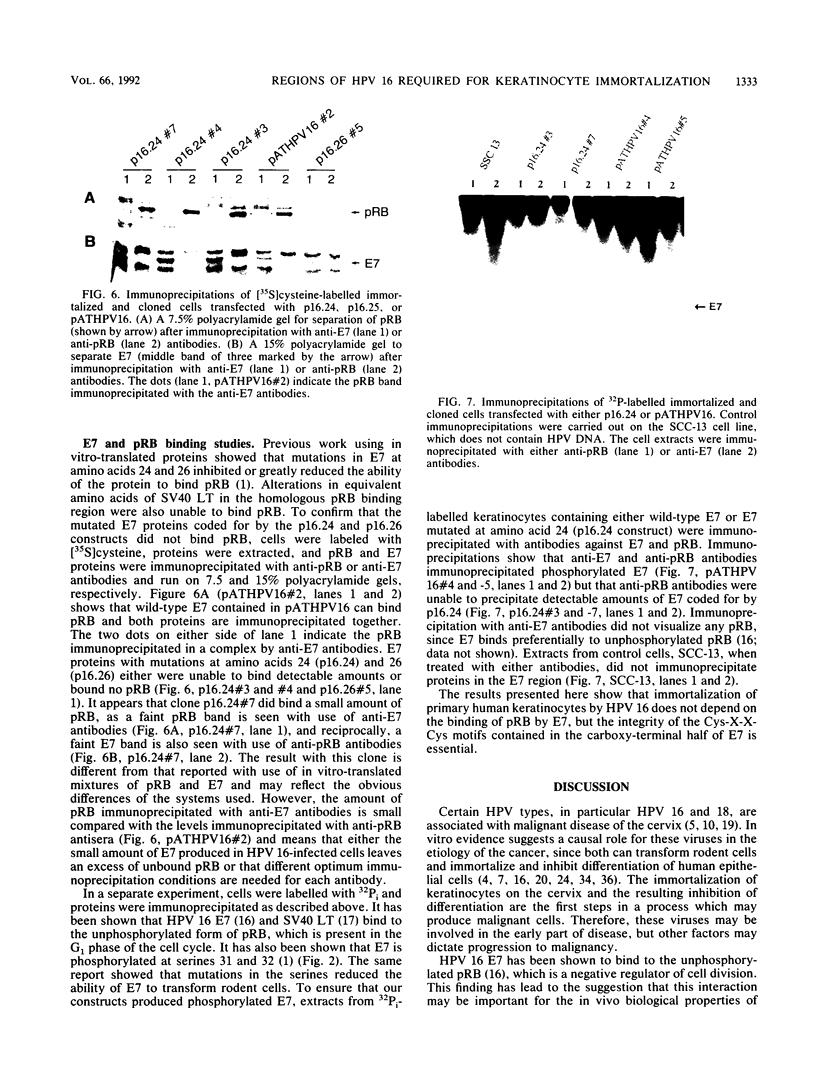
Binding of the retinoblastoma gene product (pRB) by viral oncoproteins, including the E7 of human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV 16), is thought to be important in transformation of cells. One of the steps in transformation is the immortalization process. Here we show that mutations in E7 within the full-length genome which inhibit binding of pRB do not abrogate the ability of the HPV 16 DNA to immortalize primary human epithelial (keratinocyte) cells. A mutation in one of the cysteines of a Cys-X-X-Cys motif which is contained in the carboxy half of the E7 and is part of a zinc finger arrangement completely eliminates the ability of HPV 16 DNA to immortalize cells. The results indicate the importance of E7 in the immortalization of primary keratinocytes but suggest that the binding of pRB is not essential.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbosa M. S., Edmonds C., Fisher C., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Vousden K. H. The region of the HPV E7 oncoprotein homologous to adenovirus E1a and Sv40 large T antigen contains separate domains for Rb binding and casein kinase II phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):153–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08091.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Papillomavirus polypeptides E6 and E7 are zinc-binding proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1404–1407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1404-1407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 transforming genes in immortalized and primary cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1247–1255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1247-1255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Laimins L. A. The E6-E7 region of human papillomavirus type 18 is sufficient for transformation of NIH 3T3 and rat-1 cells. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3635–3640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3635-3640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Paucha E. Identification of a region of simian virus 40 large T antigen required for cell transformation. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3350–3357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3350-3357.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters P. M., McCance D. J. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 16 in cooperation with Ha-ras transform secondary rat embryo fibroblasts. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):353–365. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters P. M., Vousden K. H., Edmonds C., McCance D. J. Analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 open reading frame E7 immortalizing function in rat embryo fibroblast cells. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):449–453. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C., Vousden K. H. A point mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2650–2656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2650-2656.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissmann L., Wolnik L., Ikenberg H., Koldovsky U., Schnürch H. G., zur Hausen H. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 DNA sequences in genital and laryngeal papillomas and in some cervical cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):560–563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert C. L., Demers G. W., Galloway D. A. The E7 gene of human papillomavirus type 16 is sufficient for immortalization of human epithelial cells. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):473–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.473-478.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B., Bedell M. A., McCance D. J., Laiminis L. A. Immortalization and altered differentiation of human keratinocytes in vitro by the E6 and E7 open reading frames of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):519–526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.519-526.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y., Matsushima Y., Sugimura T., Terada M. Purification and characterization of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein with preferential binding capacity to the underphosphorylated form of retinoblastoma gene product. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4966–4972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4966-4972.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., DeCaprio J. A., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large T antigen binds preferentially to an underphosphorylated member of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product family. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90983-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., Shon J., Pipas J. M., Livingston D. M., DeCaprio J. A. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product undergoes cell cycle-dependent dephosphorylation and binding to and release from SV40 large T. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90590-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J., Campion M. J., Clarkson P. K., Chesters P. M., Jenkins D., Singer A. Prevalence of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequences in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive carcinoma of the cervix. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985 Nov;92(11):1101–1105. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1985.tb03019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J., Kopan R., Fuchs E., Laimins L. A. Human papillomavirus type 16 alters human epithelial cell differentiation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7169–7173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J., Lowe D., Simmons P., Thomson J. P. Human papilloma virus in condyloma acuminata of the anus. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;39(8):927–927. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.8.927-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei X. F., Gorman P. A., Watt F. M. Two strains of human keratinocytes transfected with HPV16 DNA: comparison with the normal parental cells. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Feb;12(2):277–284. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Yasumoto S., Feller M., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Transformation of human fibroblasts and keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1061-1066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick-Silverman L., Pang Z., Li G., Jha K. K., Ozer H. L. Retinoblastoma protein and simian virus 40-dependent immortalization of human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2845–2852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2845-2852.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanczuk H., Villa L. L., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. The viral transcriptional regulatory region upstream of the E6 and E7 genes is a major determinant of the differential immortalization activities of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2739–2744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2739-2744.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Phelps W. C., Zhang Y. L., Barbosa M. Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3181–3187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. The major human papillomavirus protein in cervical cancers is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1686–1689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1686-1689.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey A., Almond N., Osborn K., Crawford L. Mutations of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene that affect transformation, transactivation and phosphorylation by the E7 protein. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):965–970. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey A., Pim D., Murray A., Osborn K., Banks L., Crawford L. Comparison of the in vitro transforming activities of human papillomavirus types. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1815–1820. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. L., Kalderon D., Smith A. E., Tevethia M. J. Dissociation of Rb-binding and anchorage-independent growth from immortalization and tumorigenicity using SV40 mutants producing N-terminally truncated large T antigens. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):15–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A., Lowy D. R. The E7 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 16 encodes a transforming gene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):167–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werness B. A., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Immortalization of human foreskin keratinocytes by various human papillomavirus DNAs corresponds to their association with cervical carcinoma. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):159–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.159-164.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Parker L. M., Binder N. E., Beckett M. A., Sinard J. H., Griffiths C. T., Rheinwald J. G. The mesothelial keratins: a new family of cytoskeletal proteins identified in cultured mesothelial cells and nonkeratinizing epithelia. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):693–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]