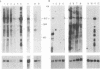
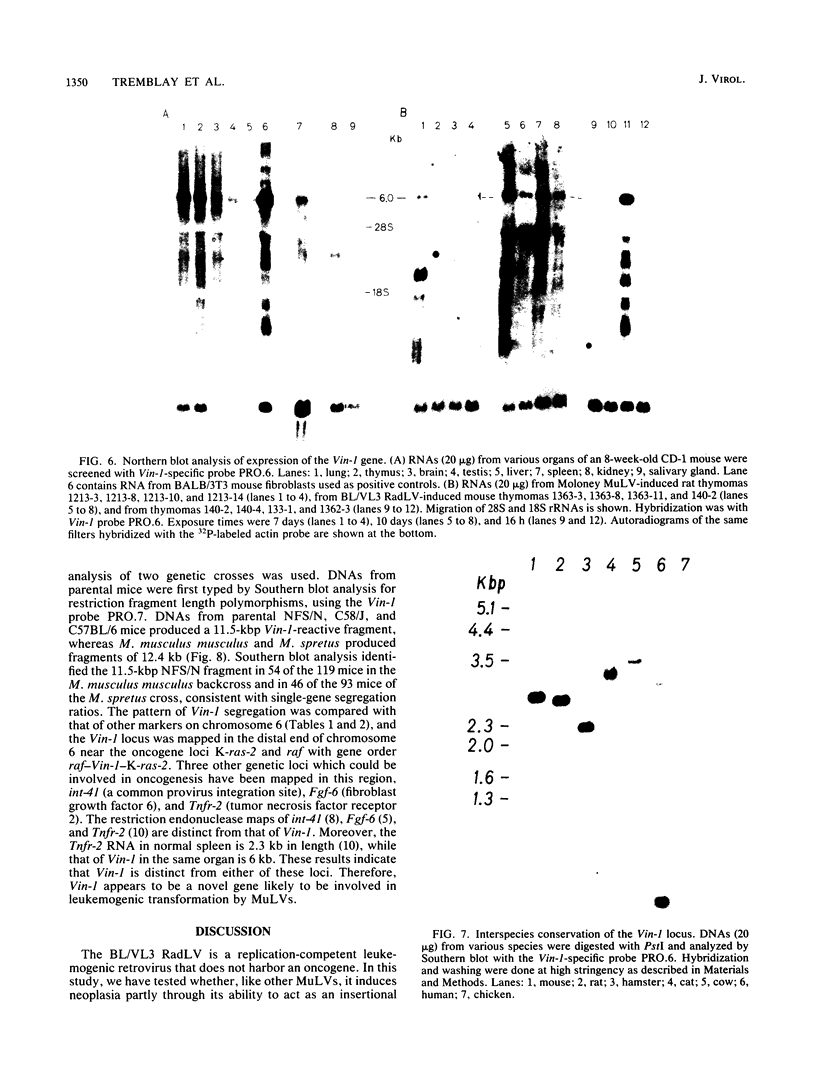
Abstract
The BL/VL3 radiation leukemia virus is a nondefective retrovirus which induces clonal or oligoclonal T-cell leukemia in mice. To study the role of provirus insertional mutagenesis in the development of these neoplasias, we searched for common provirus integration sites in BL/VL3 radiation leukemia virus-induced tumors. Using cellular sequences flanking a provirus cloned from one of these thymomas, we found that the viral genome was integrated into a common region, designated Vin-1, in a low percentage (5%) of these tumors. The proviruses found in this locus were integrated in the same orientation, close to a CpG-rich island, at proximity of a transcriptional unit encoding a 6-kb RNA. Vin-1 RNA was detected in several organs of the adult mouse. Vin-1 RNA levels were high in tumors having a provirus inserted within the Vin-1 region but were also high in some other tumors whose Vin-1 region was not found to be rearranged. Vin-1 was found to be well conserved among mammalian species and was mapped to mouse chromosome 6, between raf and K-ras-2. Vin-1 appears to be a novel gene which may be involved in tumor development.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declève A., Sato C., Lieberman M., Kaplan H. S. Selective thymic localization of murine leukemia virus-related antigens in C57BL-Ka mice after inoculation with radiation virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3124–3128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulari N. G. Murine leukemia viruses with recombinant env genes: a discussion of their role in leukemogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;103:75–108. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68943-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M., Wellinger R., Vessaz A., Diggelmann H. A new site of integration for mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA common to BALB/cf(C3H) mammary and kidney adenocarcinomas. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):127–134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Anderson D., Jerzy R., Davis T., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Smith C. A. Molecular cloning and expression of the type 1 and type 2 murine receptors for tumor necrosis factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3020–3026. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Schwartz D., Gilbert W. Isolation and mapping of cDNA hybridization probes specific for ecotropic and nonecotropic murine leukemia proviruses. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):139–154. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN H. S. THE ROLE OF RADIATION ON EXPERIMENTAL LEUKEMOGENESIS. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1964 May;14:207–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S. On the natural history of the murine leukemias: presidential address. Cancer Res. 1967 Aug;27(8):1325–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Rowe W. P. Genetic mapping of the ecotropic murine leukemia virus-inducing locus of BALB/c mouse to chromosome 5. Science. 1979 Apr 6;204(4388):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.219475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Rowe W. P. Genetic mapping of the ecotropic virus-inducing locus Akv-2 of the AKR mouse. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1419–1423. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C., Nichols E., Ruddle F. H. Gene linkage analysis in the mouse by somatic cell hybridization: assignment of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase to chromosome 8 and alpha-galactosidase to the X chromosome. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):371–382. doi: 10.1007/BF01538668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemay G., Jolicoeur P. Rearrangement of a DNA sequence homologous to a cell-virus junction fragment in several Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced rat thymomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):38–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M., Declève A., Kaplan H. S. Rapid in vitro assay for thymotropic, leukemogenic murine C-type RNA viruses. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):274–278. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M., Declève A., Ricciardi-Castagnoli P., Boniver J., Finn O. J., Kaplan H. S. Establishment, characterization and virus expression of cell lines derived from radiation- and virus-induced lymphomas of C57BL/Ka mice. Int J Cancer. 1979 Aug;24(2):168–177. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M., Niwa O., Declève A., Kaplan H. S. Continuous propagation of radiation leukemia virus on a C57BL mouse-embryo fibroblast line, with attenuation of leukemogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1250–1253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Fleissner E., Lonial H., Koehne C. F., Reicin A. Early clonality and high-frequency proviral integration into the c-myc locus in AKR leukemias. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):500–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.500-503.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G. Oncogenes at viral integration sites. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Oct;1(10):503–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier Y., Jolicoeur P. Distinct helper virus requirements for Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced pre-B- and T-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2088–2098. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2088-2098.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier Y., Kozak C., Jolicoeur P. Identification of a common helper provirus integration site in Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced lymphoma DNA. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3985–3992. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3985-3992.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappold G. A., Stubbs L., Labeit S., Crkvenjakov R. B., Lehrach H. Identification of a testis-specific gene from the mouse t-complex next to a CpG-rich island. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1975–1980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassart E., Shang M., Boie Y., Jolicoeur P. Studies on emerging radiation leukemia virus variants in C57BL/Ka mice. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):96–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.96-106.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savard P., DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Poirier Y., Jolicoeur P. Important role of the long terminal repeat of the helper Moloney murine leukemia virus in Abelson virus-induced lymphoma. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3266–3275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3266-3275.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherdin U., Rhodes K., Breindl M. Transcriptionally active genome regions are preferred targets for retrovirus integration. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):907–912. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.907-912.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Kozak C. Common proviral integration region on mouse chromosome 7 in lymphomas and myelogenous leukemias induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):526–533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.526-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villemur R., Monczak Y., Rassart E., Kozak C., Jolicoeur P. Identification of a new common provirus integration site in gross passage A murine leukemia virus-induced mouse thymoma DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):512–522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P., Graham M., Adams J. M. Proviral integration site Mis-1 in rat thymomas corresponds to the pvt-1 translocation breakpoint in murine plasmacytomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1834–1837. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lapeyriere O., Rosnet O., Benharroch D., Raybaud F., Marchetto S., Planche J., Galland F., Mattei M. G., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Structure, chromosome mapping and expression of the murine Fgf-6 gene. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):823–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lohuizen M., Verbeek S., Krimpenfort P., Domen J., Saris C., Radaszkiewicz T., Berns A. Predisposition to lymphomagenesis in pim-1 transgenic mice: cooperation with c-myc and N-myc in murine leukemia virus-induced tumors. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90589-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]