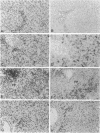
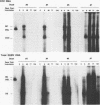
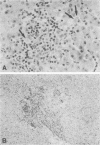
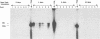Abstract
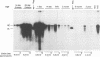
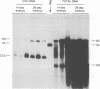
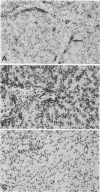
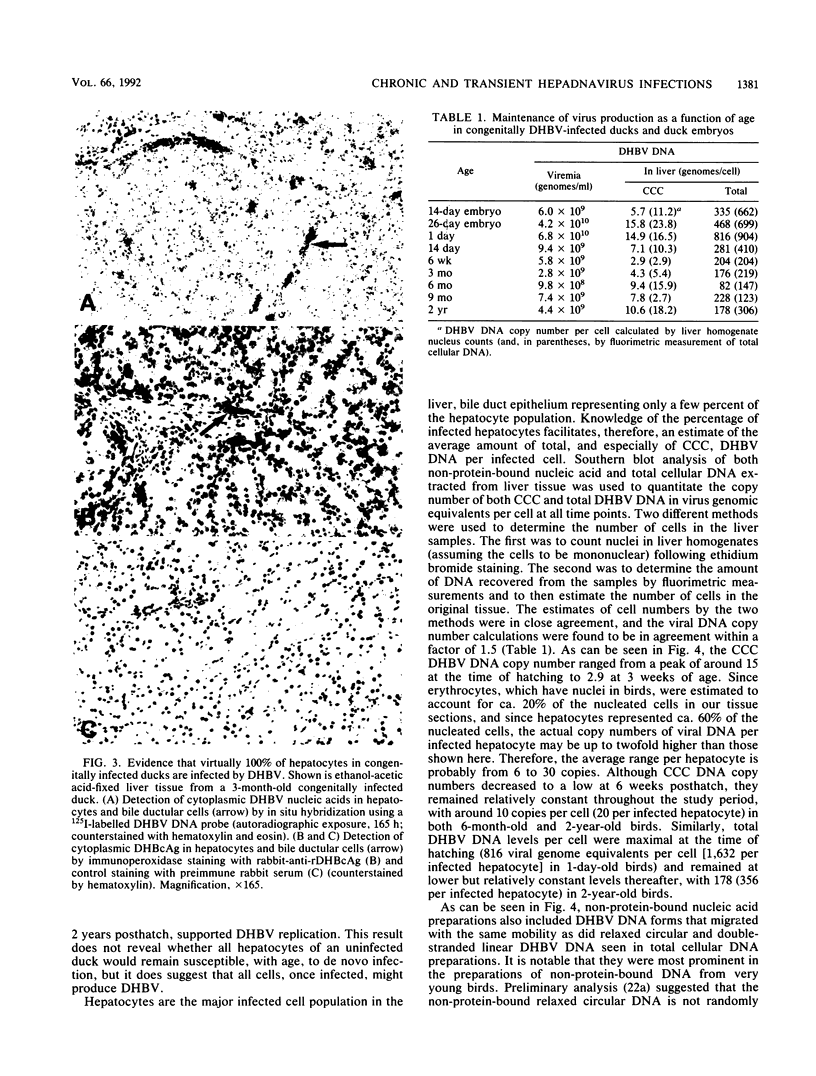
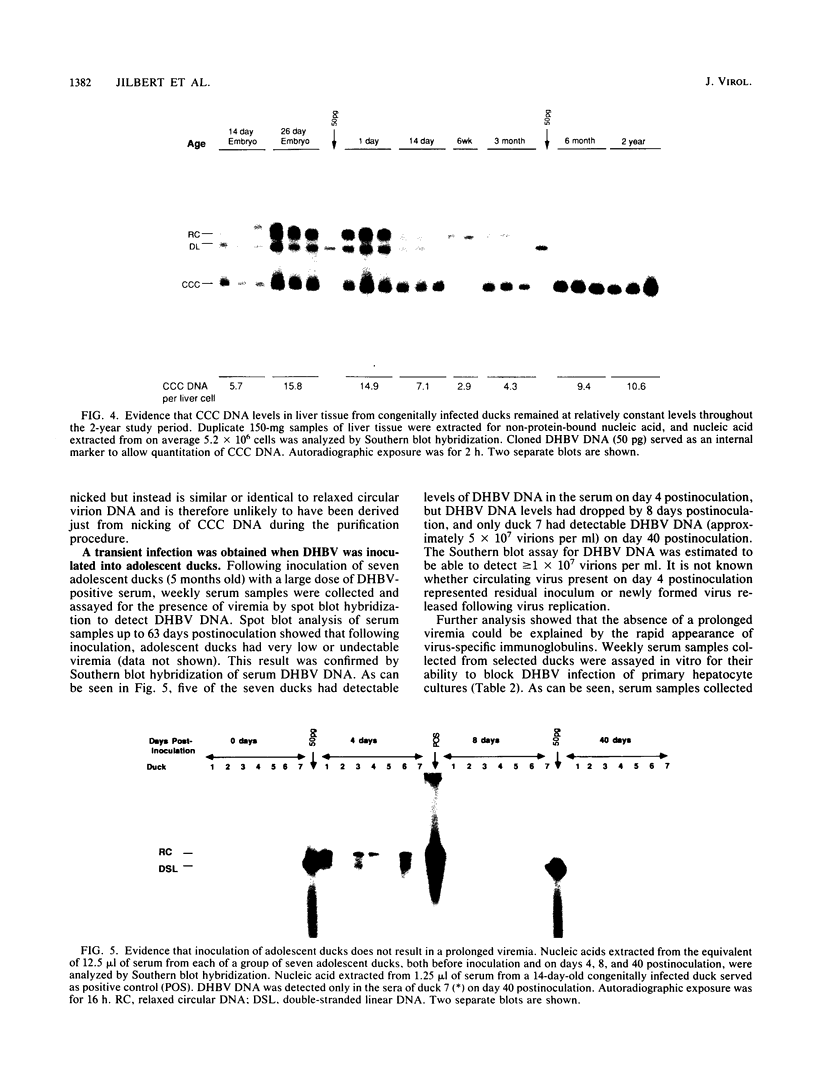
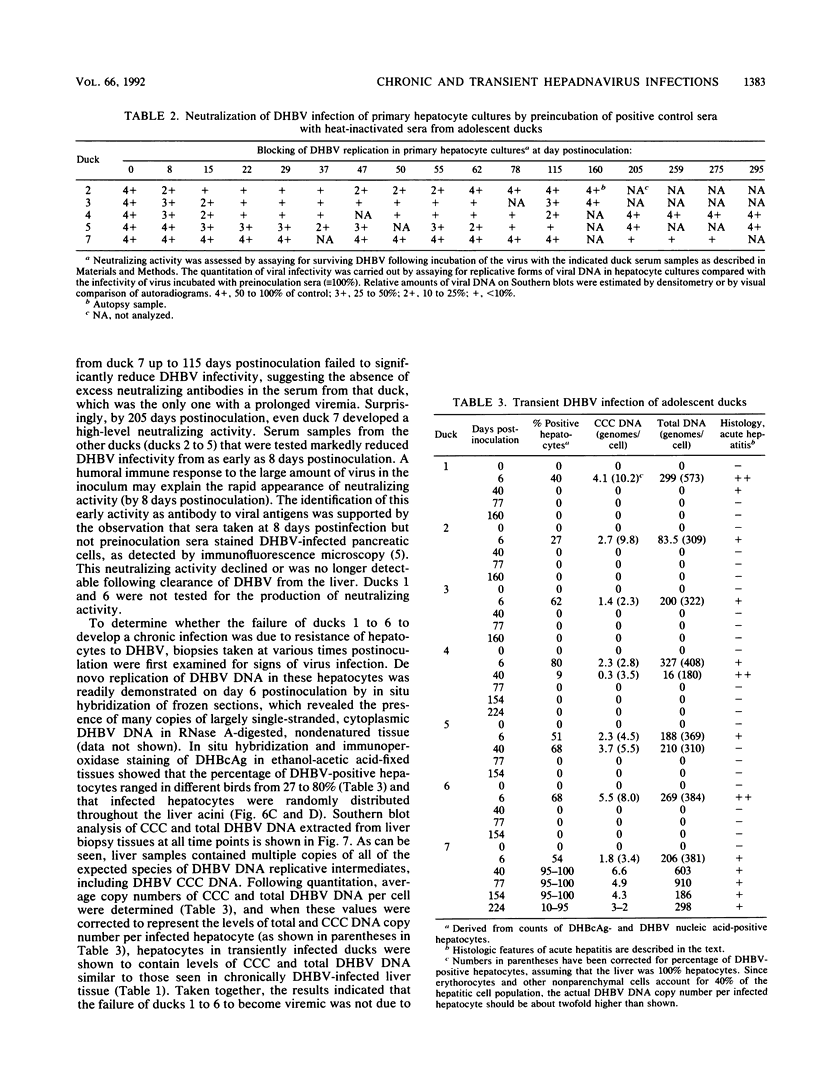
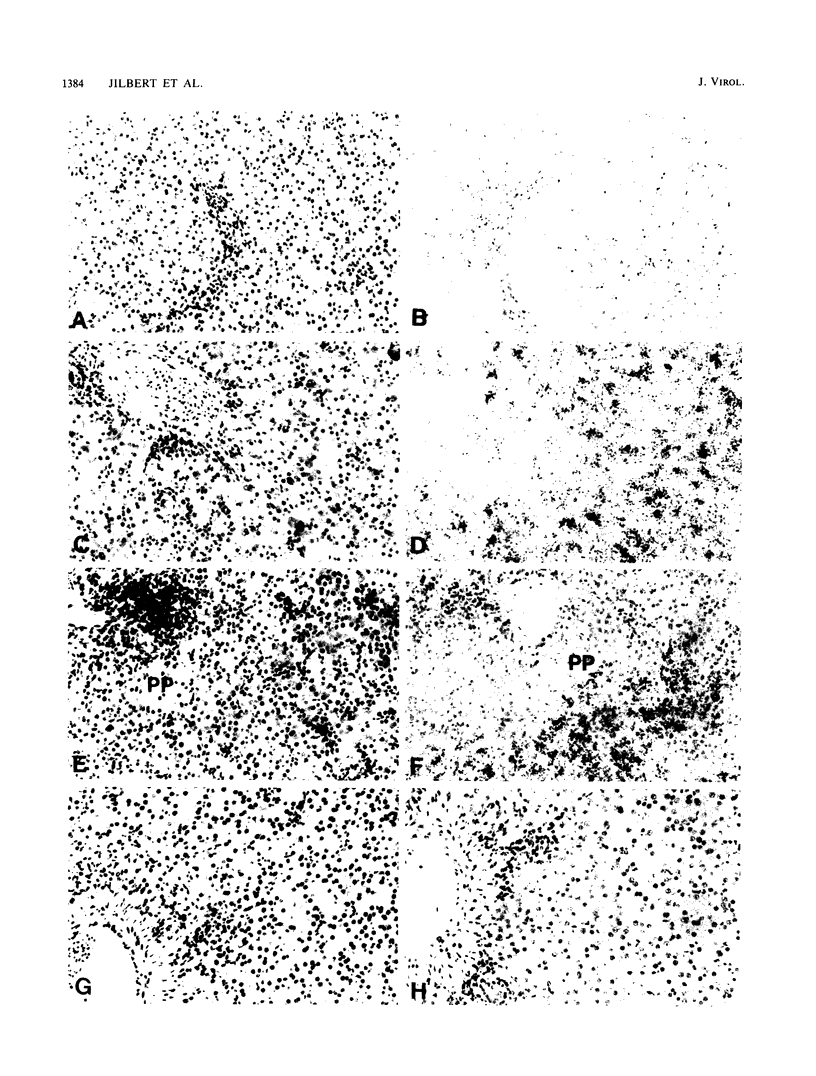
A study was carried out to determine some of the factors that might distinguish transient from chronic hepadnavirus infection. First, to better characterize chronic infection, Pekin ducks, congenitally infected with the duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV), were used to assess age-dependent variations in viremia, percentage of DHBV-infected hepatocytes, and average levels of DNA replication intermediates in the cytoplasm and of covalently closed circular DNA in the nuclei of infected hepatocytes. Levels of viremia and viral DNA were found to peak at about the time of hatching but persisted at relatively constant levels in chronically infected birds up to 2 years of age. The percentage of infected hepatocytes was also constant, with DHBV replication in virtually 100% of hepatocytes in all birds. Next, we found that adolescent ducks inoculated intravenously with a large dose of DHBV also developed massive infection of hepatocytes with an early but low-level viremia, followed by rapid development of a neutralizing antibody response. No obvious quantitative or qualitative differences between transiently and chronically infected liver tissue were detected in the intracellular markers of viral replication examined. However, in the adolescent duck experiment, DHBV infection was rapidly cleared from the liver even when up to 80% of hepatocytes were initially infected. In all of these ducks, clearance of infection was accompanied by only a mild hepatitis, with no evidence that massive cell death contributed to the clearance. This finding suggested that mechanisms in addition to immune-mediated destruction of hepatocytes might make major contributions to clearance of infections, including physiological turnover of hepatocytes in the presence of a neutralizing antibody response and/or spontaneous loss of the capacity of hepatocytes to support virus replication.
Full text
PDF


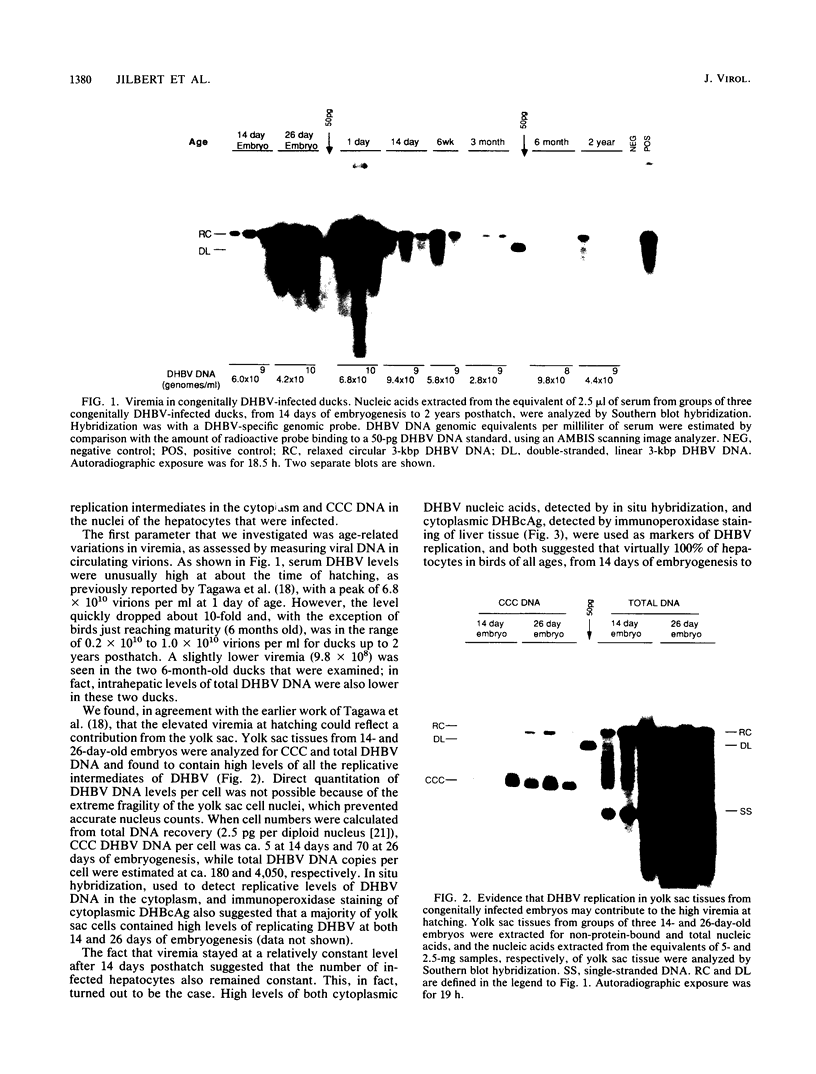



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber N., Zajicek G., Ariel I. The streaming liver. II. Hepatocyte life history. Liver. 1988 Apr;8(2):80–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1988.tb00972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker L. F., Chisari F. V., McGrath P. P., Dalgard D. W., Kirschstein R. L., Almeida J. D., Edington T. S., Sharp D. G., Peterson M. R. Transmission of type B viral hepatitis to chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):648–662. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berquist K. R., Peterson J. M., Murphy B. L., Ebert J. W., Maynard J. E., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis B antigens in serum and liver of chimpanzees acutely infected with hepatitis B virus. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):602–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.602-605.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. S., Mason W. S., Coates L., O'Connell A. P., England J. M. Humoral immune responsiveness in duck hepatitis B virus-infected ducks. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):916–920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.916-920.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Michalak T., Nowoslawski A., Gerety R. J., Barker L. F. Immunofluorescence microscopy in experimentally induced, type B hepatitis in the chimpanzee. Gastroenterology. 1978 Feb;74(2 Pt 1):182–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilbert A. R., Freiman J. S., Burrell C. J., Holmes M., Gowans E. J., Rowland R., Hall P., Cossart Y. E. Virus-liver cell interactions in duck hepatitis B virus infection. A study of virus dissemination within the liver. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1375–1382. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilbert A. R., Freiman J. S., Gowans E. J., Holmes M., Cossart Y. E., Burrell C. J. Duck hepatitis B virus DNA in liver, spleen, and pancreas: analysis by in situ and Southern blot hybridization. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q. X., Fan H. Combined infection by Moloney murine leukemia virus and a mink cell focus-forming virus recombinant induces cytopathic effects in fibroblasts or in long-term bone marrow cultures from preleukemic mice. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3701–3711. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3701-3711.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandart E., Kay A., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):782–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.782-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto A., Cote P. J., Ford E. C., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Core antigen and antibody in woodchucks after infection with woodchuck hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):70–76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.70-76.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. Infection and uptake of duck hepatitis B virus by duck hepatocytes maintained in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):564–572. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. Is there a liver stem cell? Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 1;50(13):3811–3815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Huang M. J., Yu M. S. Morphogenetic and regulatory effects of mutations in the envelope proteins of an avian hepadnavirus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1310-1317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa M., Robinson W. S., Marion P. L. Duck hepatitis B virus replicates in the yolk sac of developing embryos. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2273–2279. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2273-2279.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pourcel C., Summers J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90602-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. K., O'Connell A. P., London W. T. Sequence of events in natural infection of Pekin duck embryos with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.16-22.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENDRELY R. La notion d'espèce à travers quelques données biochimiques récentes et le cycle L. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Feb;94(2):142–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Coates L., Aldrich C. E., Summers J., Mason W. S. In hepatocytes infected with duck hepatitis B virus, the template for viral RNA synthesis is amplified by an intracellular pathway. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]