Abstract
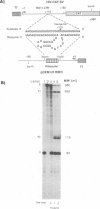
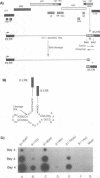
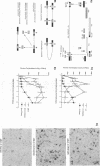
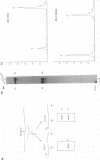
We have designed a ribozyme that cleaves human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA in U5 (at nucleotide +115). This ribozyme was tested in vitro and was found to give efficient and specific digestion of RNA containing the HIV-1 U5 sequence. When the U5 ribozyme was placed into the HIV-1 genome, virus replication was suppressed in tissue culture. Introduction of this ribozyme into cells by using an amphotropic retrovirus vector significantly reduced expression of U5-containing RNA in cells chronically infected with HIV-1. Naive T cells were cocultivated with packaging cells that produce defective amphotropic retroviruses containing the U5 ribozyme. These lymphocytes were found to be partially protected from HIV-1 infection.
Full text
PDF

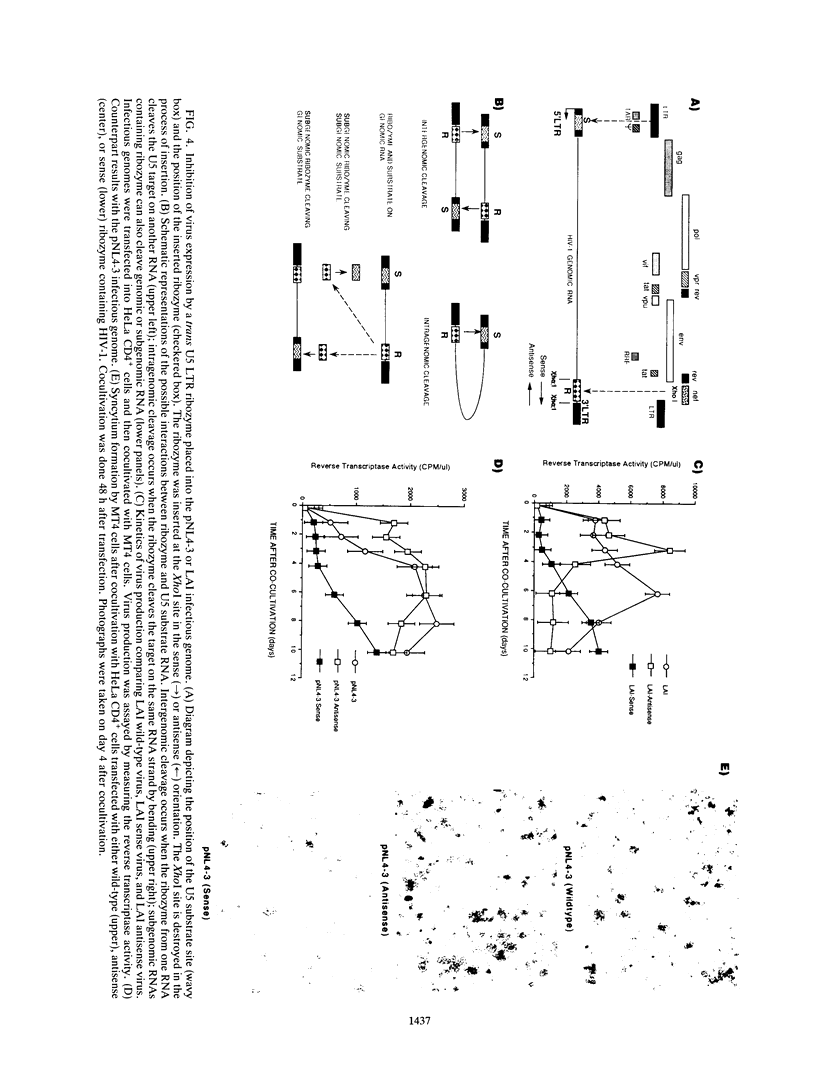
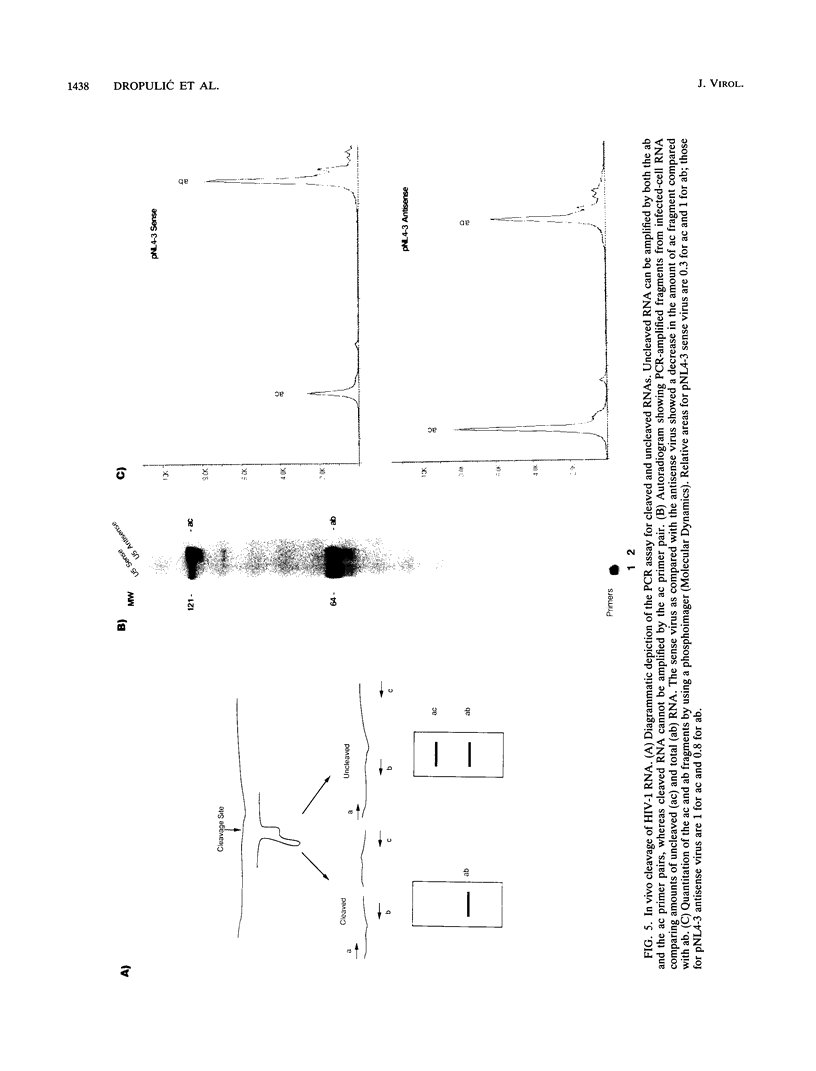
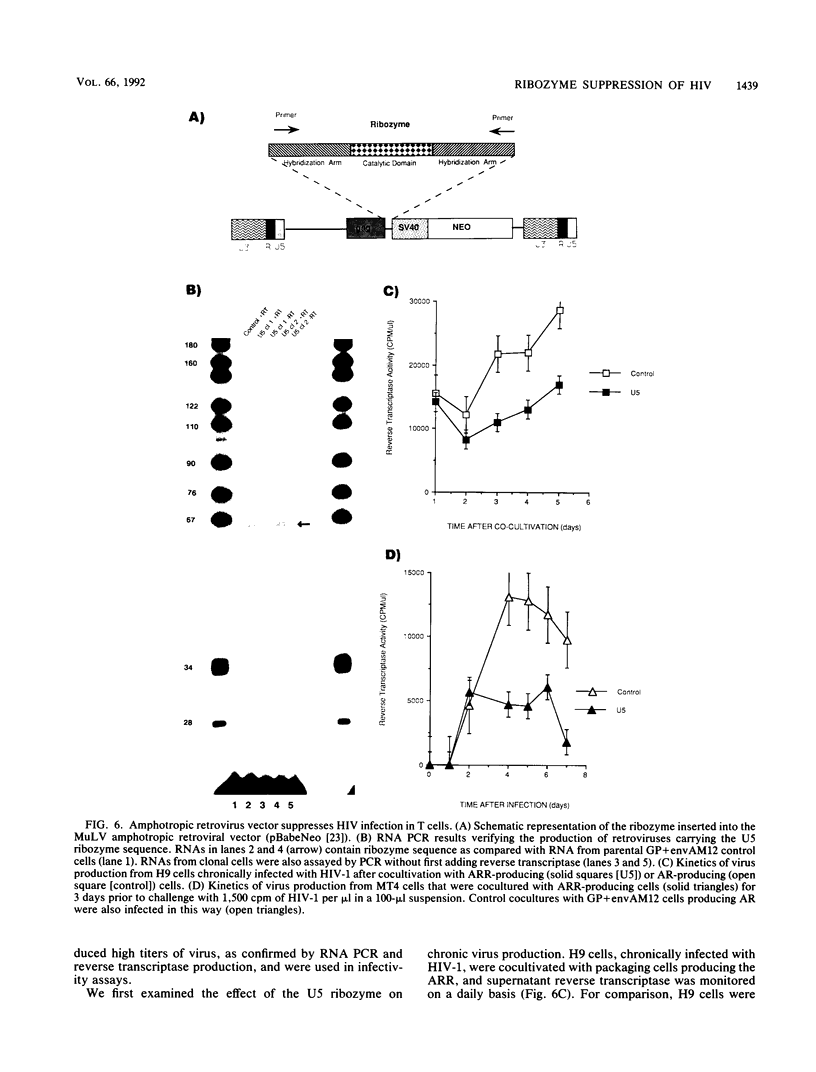


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal S., Ikeuchi T., Sun D., Sarin P. S., Konopka A., Maizel J., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus in early infected and chronically infected cells by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides and their phosphorothioate analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7790–7794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad N., Maitra R. K., Venkatesan S. Rev-induced modulation of Nef protein underlies temporal regulation of human immunodeficiency virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6111–6115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzayan J. M., Gerlach W. L., Bruening G. Satellite tobacco ringspot virus RNA: A subset of the RNA sequence is sufficient for autolytic processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8859–8862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron F. H., Jennings P. A. Specific gene suppression by engineered ribozymes in monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K. Development of a sensitive quantitative focal assay for human immunodeficiency virus infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3779–3788. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3779-3788.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuat J. C., Galibert F. Can ribozymes be used to regulate procaryote gene expression? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1025–1029. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90776-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correll P. H., Kew Y., Perry L. K., Brady R. O., Fink J. K., Karlsson S. Expression of human glucocerebrosidase in long-term reconstituted mice following retroviral-mediated gene transfer into hematopoietic stem cells. Hum Gene Ther. 1990 Fall;1(3):277–287. doi: 10.1089/hum.1990.1.3-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Birnstiel M. L. Ribozyme mediated destruction of RNA in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3861–3866. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Schaffner G., Birnstiel M. L. Ribozyme, antisense RNA, and antisense DNA inhibition of U7 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein-mediated histone pre-mRNA processing in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4479–4487. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of plus and minus RNAs of a virusoid and a structural model for the active sites. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of virusoid RNA is performed by the proposed 55-nucleotide active site. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90657-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild J., Agrawal S., Civeira M. P., Sarin P. S., Sun D., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus replication by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5507–5511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J., Gerlach W. L. Simple RNA enzymes with new and highly specific endoribonuclease activities. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):585–591. doi: 10.1038/334585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchins C. J., Rathjen P. D., Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of plus and minus RNA transcripts of avocado sunblotch viroid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3627–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang L. H., Gilboa E. Expression of genes introduced into cells by retroviral infection is more efficient than that of genes introduced into cells by DNA transfection. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):417–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.417-424.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H. W., 3rd, Ringler D. J., Mori K., Panicali D. L., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Importance of the nef gene for maintenance of high virus loads and for development of AIDS. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):651–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90097-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. A safe packaging line for gene transfer: separating viral genes on two different plasmids. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1120-1124.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. Construction and use of a safe and efficient amphotropic packaging cell line. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. Advanced mammalian gene transfer: high titre retroviral vectors with multiple drug selection markers and a complementary helper-free packaging cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3587–3596. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterlin B. M., Luciw P. A., Barr P. J., Walker M. D. Elevated levels of mRNA can account for the trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9734–9738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston B. D., Poiesz B. J., Loeb L. A. Fidelity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1168–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.2460924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prody G. A., Bakos J. T., Buzayan J. M., Schneider I. R., Bruening G. Autolytic processing of dimeric plant virus satellite RNA. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1577–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4745.1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Bebenek K., Kunkel T. A. The accuracy of reverse transcriptase from HIV-1. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1171–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.2460925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy-Burman P., Dougherty M., Pal B. K., Charman H. P., Klement V., Gardner M. B. Assay for type C virus in mouse sera based on particulate reverse transcriptase activity. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):1107–1110. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.1107-1110.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Cantin E. M., Chang P. S., Zaia J. A., Ladne P. A., Stephens D. A., Rossi J. J. Ribozymes as potential anti-HIV-1 therapeutic agents. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1222–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.2107573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sczakiel G., Pawlita M. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in human T cells stably expressing antisense RNA. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):468–472. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.468-472.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sczakiel G., Pawlita M., Kleinheinz A. Specific inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by RNA transcribed in sense and antisense orientation from the 5'-leader/gag region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90379-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of RNA in the replication of small pathogens of plants and animals. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Nov;14(11):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tersmette M., Gruters R. A., de Wolf F., de Goede R. E., Lange J. M., Schellekens P. T., Goudsmit J., Huisman H. G., Miedema F. Evidence for a role of virulent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) variants in the pathogenesis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: studies on sequential HIV isolates. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2118–2125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2118-2125.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C. A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):596–600. doi: 10.1038/328596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Vartanian J. P., Henry M., Chenciner N., Cheynier R., Delassus S., Martins L. P., Sala M., Nugeyre M. T., Guétard D. LAV revisited: origins of the early HIV-1 isolates from Institut Pasteur. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):961–965. doi: 10.1126/science.2035026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Smith D. H., Lasky L. A., Theodore T. S., Earl P. L., Moss B., Capon D. J., Martin M. A. In vitro mutagenesis identifies a region within the envelope gene of the human immunodeficiency virus that is critical for infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):139–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.139-147.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]