Abstract
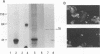
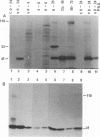
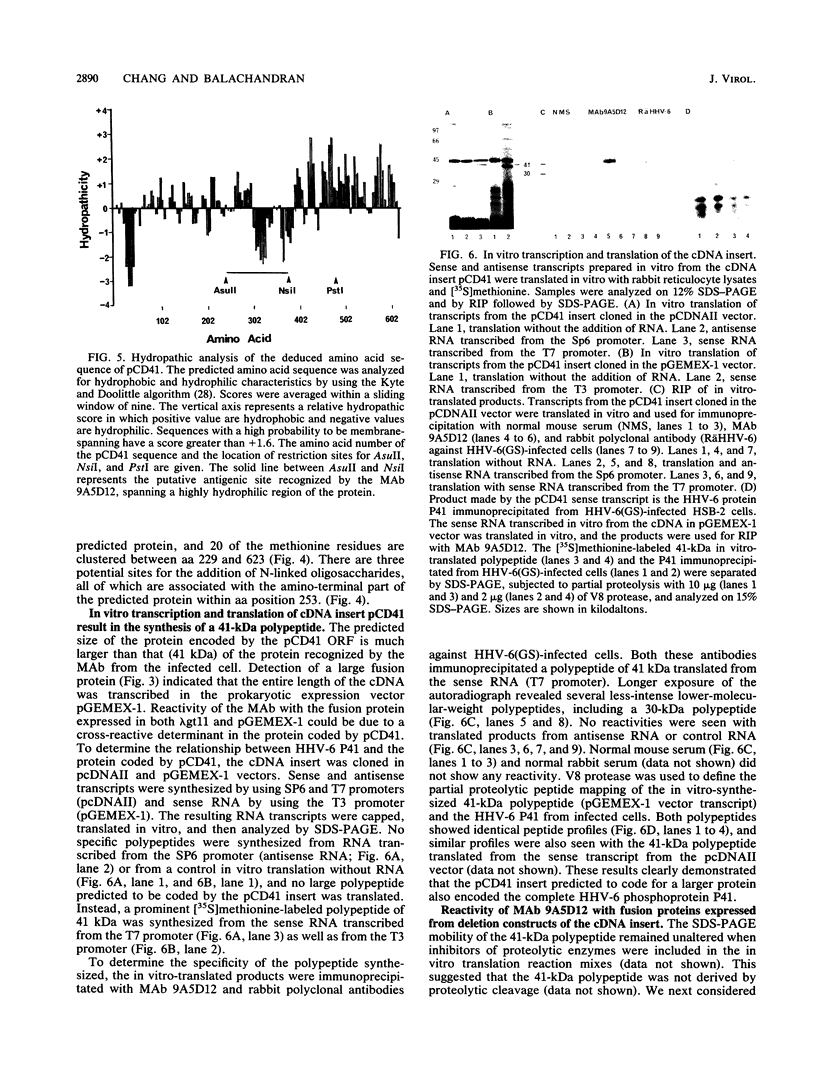
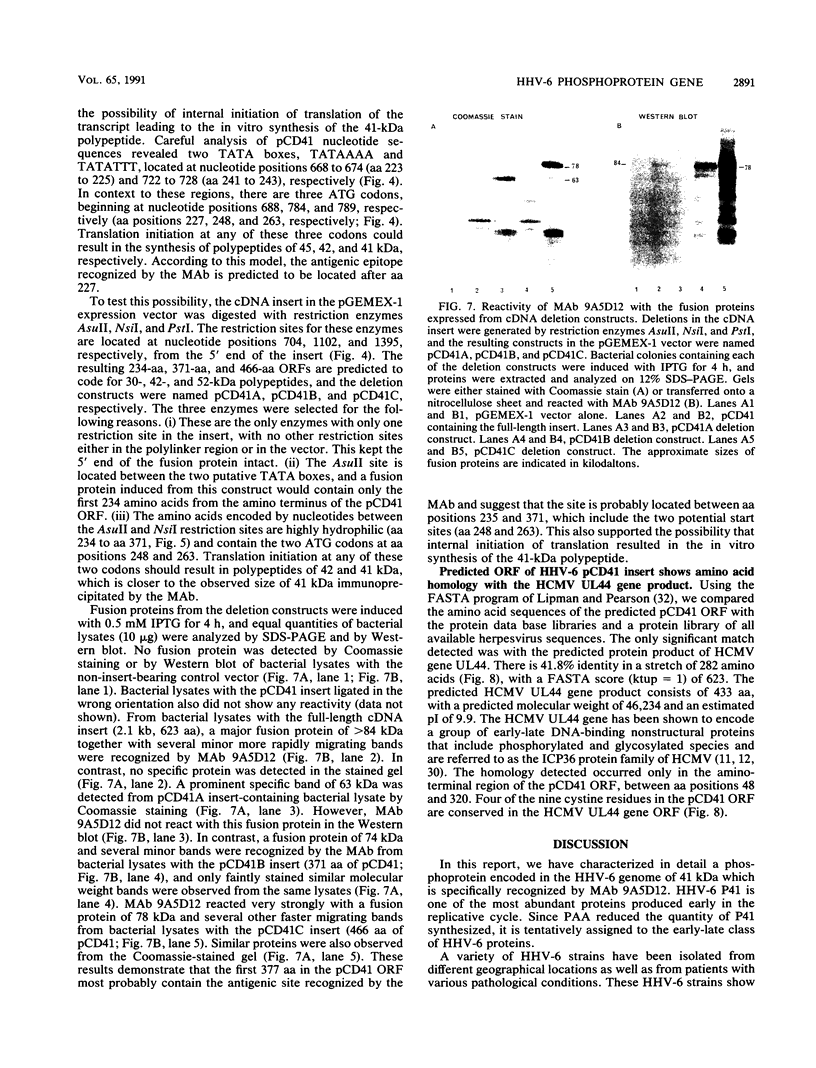
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6)-specific monoclonal antibody (Mab) 9A5D12 reacted with the nucleus of HHV-6 strain GS-infected cells and immunoprecipitated a phosphorylated polypeptide with an approximate size of 41 kDa, designated HHV-6 P41. A 110-kDa polypeptide was also immunoprecipitated by the MAb. These polypeptides were synthesized early in infection, and the synthesis was greatly reduced by phosphonoacetic acid. Polypeptides with identical sizes were recognized by the MAb from cells infected with an additional eight HHV-6 strains. A 2.1-kb cDNA insert was identified from an HHV-6(GS) cDNA library constructed in the lambda gt11 expression system by using MAb 9A5D12. This cDNA insert hybridized specifically with viral DNA from HHV-6 strains GS and Z-29 and with two predominant transcripts with approximate sizes of 2.5 and 1.2 kb from infected cells. The reactivity of the MAb with a fusion protein expressed in the prokaryotic vector suggested that the cDNA encodes a 62- to 66-kDa protein. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA insert revealed a 623-amino-acid-residue single open reading frame of 1,871 nucleotides, with an open 5' end. The predicted polypeptide is highly basic and contains a long stretch of highly hydrophobic residues localized to the carboxy terminus. The amino-terminal half of the predicted HHV-6 protein from the cDNA shows significant homology with the UL44 gene product of human cytomegalovirus, coding for the ICP36 family of early-late-class phosphoproteins. Two TATA boxes are located at nucleotide positions 668 and 722 of the cDNA. In vitro translation of RNA transcribed in vitro from the cDNA resulted in the synthesis of a 41-kDa polypeptide only. This polypeptide was readily immunoprecipitated by MAb 9A5D12, and its partial peptide map was identical to that of the 41-kDa polypeptide detected in infected cells. Together, these results indicate that the HHV-6 P41 is encoded within a gene coding for a larger protein.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ablashi D. V., Josephs S. F., Buchbinder A., Hellman K., Nakamura S., Llana T., Lusso P., Kaplan M., Dahlberg J., Memon S. Human B-lymphotropic virus (human herpesvirus-6). J Virol Methods. 1988 Sep;21(1-4):29–48. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ablashi D. V., Lusso P., Hung C. L., Salahuddin S. Z., Josephs S. F., Llana T., Kramarsky B., Biberfeld P., Markham P. D., Gallo R. C. Utilization of human hematopoietic cell lines for the propagation and characterization of HBLV (human herpesvirus 6). Int J Cancer. 1988 Nov 15;42(5):787–791. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agut H., Guetard D., Collandre H., Dauguet C., Montagnier L., Miclea J. M., Baurmann H., Gessain A. Concomitant infection by human herpesvirus 6, HTLV-I, and HIV-2. Lancet. 1988 Mar 26;1(8587):712–712. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91520-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano Y., Yoshikawa T., Suga S., Yazaki T., Hirabayashi S., Ono Y., Tsuzuki K., Oshima S. Human herpesvirus 6 harbouring in kidney. Lancet. 1989 Dec 9;2(8676):1391–1391. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91993-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano Y., Yoshikawa T., Suga S., Yazaki T., Kondo K., Yamanishi K. Fatal fulminant hepatitis in an infant with human herpesvirus-6 infection. Lancet. 1990 Apr 7;335(8693):862–863. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90983-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Amelse R. E., Zhou W. W., Chang C. K. Identification of proteins specific for human herpesvirus 6-infected human T cells. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2835–2840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2835-2840.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Oba D. E., Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Antigenic cross-reactions among herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1125–1135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1125-1135.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Tirawatnapong S., Pfeiffer B., Ablashi D. V., Salahuddin S. Z. Electrophoretic analysis of human herpesvirus 6 polypeptides immunoprecipitated from infected cells with human sera. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):29–34. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. A human cytomegalovirus early gene has three inducible promoters that are regulated differentially at various times after infection. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.281-290.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Luca D., Katsafanas G., Schirmer E. C., Balachandran N., Frenkel N. The replication of viral and cellular DNA in human herpesvirus 6-infected cells. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):199–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90200-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing R. G., Sewankambo N., Serwadda D., Honess R., Crawford D., Jarrett R., Griffin B. E. Isolation of human lymphotropic herpesviruses from Uganda. Lancet. 1987 Aug 15;2(8555):390–390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gretch D. R., Kari B., Gehrz R. C., Stinski M. F. A multigene family encodes the human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein complex gcII (gp47-52 complex). J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1956–1962. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1956-1962.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett G. B., Farr T. J., Pietroboni G. R., Bucens M. R. Frequent shedding of human herpesvirus 6 in saliva. J Med Virol. 1990 Feb;30(2):128–130. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890300209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving W. L., Cunningham A. L. Serological diagnosis of infection with human herpesvirus type 6. BMJ. 1990 Jan 20;300(6718):156–159. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6718.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs S. F., Ablashi D. V., Salahuddin S. Z., Kramarsky B., Franza B. R., Jr, Pellett P., Buchbinder A., Memon S., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Molecular studies of HHV-6. J Virol Methods. 1988 Sep;21(1-4):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuta H., Lu H., Matsumoto S., Josephs S. F., Gallo R. C. Polymorphism of human herpesvirus 6 DNA from five Japanese patients with exanthem subitum. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):550–551. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchesch H., Mertens T., Burkhardt U., Kruppenbacher J. P., Höffken A., Eggers H. J. Seroconversion against human herpesvirus-6 (and other herpesviruses) and clinical illness. Lancet. 1988 Jul 30;2(8605):273–274. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92557-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles W. A., Gardner S. D. High prevalence of antibody to human herpesvirus-6 and seroconversion associated with rash in two infants. Lancet. 1988 Oct 15;2(8616):912–913. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92522-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger G. R., Wassermann K., De Clerck L. S., Stevens W. J., Bourgeois N., Ablashi D. V., Josephs S. F., Balachandran N. Latent herpesvirus-6 in salivary and bronchial glands. Lancet. 1990 Nov 17;336(8725):1255–1256. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92874-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence G. L., Chee M., Craxton M. A., Gompels U. A., Honess R. W., Barrell B. G. Human herpesvirus 6 is closely related to human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):287–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.287-299.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach F. S., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus late-gene expression: differential use of three start sites in the transcriptional activation of ICP36 gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1783–1791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1783-1791.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Ferro F., Greenspan D., Lennette E. T. Frequent isolation of HHV-6 from saliva and high seroprevalence of the virus in the population. Lancet. 1990 May 5;335(8697):1047–1050. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92628-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler E., Lawrence G., Liu M. Y., Barrell B. G., Arrand J. R. Identification, cloning, and expression of the major capsid protein gene of human herpesvirus 6. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):714–722. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.714-722.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Pellett P., Stewart J., Goldsmith C., Sanderlin K., Black J., Warfield D., Feorino P. Characteristics of human herpesvirus-6. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1271–1273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. J., Littler E., Arrand J. R., Jordan D., Mallick N. P., Johnson R. W. Human herpesvirus 6 infection in renal-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 8;320(23):1560–1561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman J. C., Liu C. R., Kaplan M. H., Brown N. A. Clinical and serological features of human herpesvirus-6 infection in three adults. Lancet. 1988 Oct 8;2(8615):817–819. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92783-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno T., Takahashi K., Balachandra K., Shiraki K., Yamanishi K., Takahashi M., Baba K. Seroepidemiology of human herpesvirus 6 infection in normal children and adults. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):651–653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.651-653.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzner A. J., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Characterization of a cDNA clone corresponding to a transcript from the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI M fragment: evidence for overlapping mRNAs. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2943–2946. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2943-2946.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L., Gibson W. Primate cytomegalovirus assembly protein: genome location and nucleotide sequence. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):669–676. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.669-676.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüger B., Klages S., Walla B., Albrecht J., Fleckenstein B., Tomlinson P., Barrell B. Primary structure and transcription of the genes coding for the two virion phosphoproteins pp65 and pp71 of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):446–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.446-453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Ablashi D. V., Markham P. D., Josephs S. F., Sturzenegger S., Kaplan M., Halligan G., Biberfeld P., Wong-Staal F., Kramarsky B. Isolation of a new virus, HBLV, in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):596–601. doi: 10.1126/science.2876520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suga S., Yoshikawa T., Asano Y., Yazaki T., Hirata S. Human herpesvirus-6 infection (exanthem subitum) without rash. Pediatrics. 1989 Jun;83(6):1003–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder R. S., Briggs M., Cameron C. H., Honess R., Robertson D., Whittle H. A novel lymphotropic herpesvirus. Lancet. 1987 Aug 15;2(8555):390–392. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92404-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Petti L., Braun D., Seung S., Kieff E. A bicistronic Epstein-Barr virus mRNA encodes two nuclear proteins in latently infected, growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):945–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.945-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward K. N., Gray J. J., Efstathiou S. Brief report: primary human herpesvirus 6 infection in a patient following liver transplantation from a seropositive donor. J Med Virol. 1989 Jun;28(2):69–72. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890280203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrzos H., Gibbons J., Abt P. L., Gifford R. R., Yang H. C. Human herpesvirus 6 in monocytes of transplant patients. Lancet. 1990 Feb 24;335(8687):486–487. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90729-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt L. S., Balachandran N., Frenkel N. Variations in the replication and antigenic properties of human herpesvirus 6 strains. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):852–857. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Okuno T., Shiraki K., Takahashi M., Kondo T., Asano Y., Kurata T. Identification of human herpesvirus-6 as a causal agent for exanthem subitum. Lancet. 1988 May 14;1(8594):1065–1067. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91893-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]