Abstract
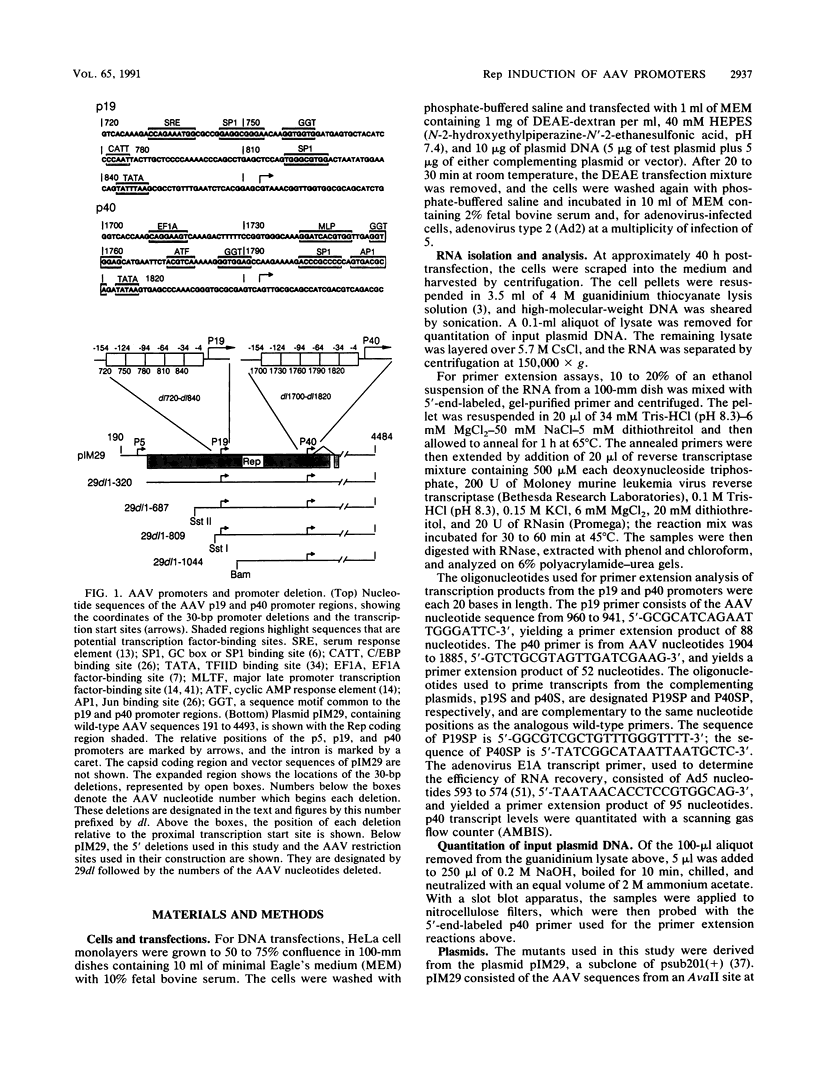
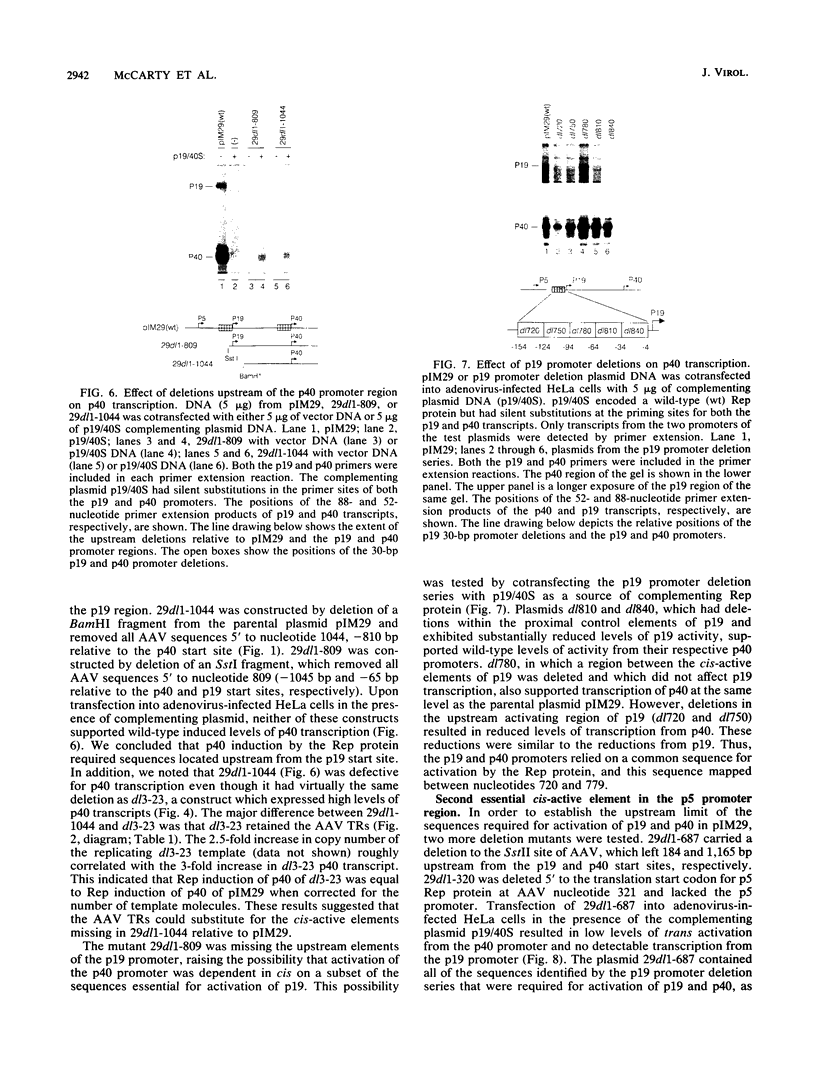
A series of contiguous 30-bp deletions were introduced into the regions upstream of the p19 and p40 promoters of adeno-associated virus (AAV), and the effects of these deletions on induction of AAV transcription by the rep gene products was evaluated. A novel complementation system was devised for supplying wild-type Rep protein when mutations disrupted the trans activation activity of the Rep protein. Transcription from the p40 promoter was eliminated upon deletion of the TATA sequence located between -4 and -33 from the cap site. Deletions which removed sequences from -34 to -123 bp from the p40 mRNA start site substantially reduced Rep induction of p40 transcription. p19 transcription was also undetectable when the p19 TATA sequence between -4 and -33 was deleted. In contrast to the p40 region, two types of cis-active sequences were found associated with the p19 promoter. Sequences between -4 and -63 bp relative to the p19 cap site were essential for Rep induction only from the p19 promoter. Deletions between -94 and -153 bp relative to the p19 cap site reduced Rep induction of both the p19 and p40 promoters coordinately. These two noncontiguous regions were separated by a 30-bp sequence that was not essential for transcription control. Further deletion analysis delineated a second cis-active element, associated with the p5 promoter (AAV nucleotides 191 to 320), which was also necessary for coordinate Rep activation of both the p19 and p40 promoters. Finally, the dependence of p40 transcription on the Rep-responsive elements within the p5 and p19 regions could be overcome by the presence of the AAV terminal repeats, suggesting that the terminal repeats contained redundant Rep-responsive elements. These results implied an interdependence in cis between the three AAV promoters and suggested a novel mechanism for coordinate regulation of gene expression in response to the trans-activating Rep protein. Coordinate induction appeared to be the result of a simultaneous interaction between the Rep protein and sequence elements associated with two or all three of the AAV promoters.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn J. K., Gavin B. J., Kumar G., Ward D. C. Transcriptional analysis of minute virus of mice P4 promoter mutants. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5425–5439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5425-5439.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashktorab H., Srivastava A. Identification of nuclear proteins that specifically interact with adeno-associated virus type 2 inverted terminal repeat hairpin DNA. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3034–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3034-3039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaton A., Palumbo P., Berns K. I. Expression from the adeno-associated virus p5 and p19 promoters is negatively regulated in trans by the rep protein. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4450–4454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4450-4454.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becerra S. P., Koczot F., Fabisch P., Rose J. A. Synthesis of adeno-associated virus structural proteins requires both alternative mRNA splicing and alternative initiations from a single transcript. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2745–2754. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2745-2754.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder J. T., Hearing P. Nuclear factor EF-1A binds to the adenovirus E1A core enhancer element and to other transcriptional control regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5143–5153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. J., Marcus-Sekura C. J., Laughlin C. A., Ketner G. Properties of an adenovirus type 2 mutant, Ad2dl807, having a deletion near the right-hand genome terminus: failure to help AAV replication. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):505–516. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. S., Shenk T. The adenovirus DNA-binding protein stimulates the rate of transcription directed by adenovirus and adeno-associated virus promoters. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2103–2109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2103-2109.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. S., Shi Y., Shenk T. Adeno-associated virus P5 promoter contains an adenovirus E1A-inducible element and a binding site for the major late transcription factor. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3479–3488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3479-3488.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chejanovsky N., Carter B. J. Mutagenesis of an AUG codon in the adeno-associated virus rep gene: effects on viral DNA replication. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chejanovsky N., Carter B. J. Mutation of a consensus purine nucleotide binding site in the adeno-associated virus rep gene generates a dominant negative phenotype for DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1764–1770. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1764-1770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Nathans D. Functional serum response elements upstream of the growth factor-inducible gene zif268. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4889–4895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint J., Shenk T. Adenovirus E1A protein paradigm viral transactivator. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:141–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin B. J., Ward D. C. Positive and negative regulation of the minute virus of mice P38 promoter. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2057–2063. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2057-2063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Definition of a novel promoter for the major adenovirus-associated virus mRNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcripts of the adeno-associated virus genome: mapping of the major RNAs. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):79–92. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.79-92.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauswirth W. W., Berns K. I. Origin and termination of adeno-associated virus DNA replication. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):488–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Labow M. A., Wright R., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Genetics of adeno-associated virus: isolation and preliminary characterization of adeno-associated virus type 2 mutants. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):329–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.329-339.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Hearing P. Adenovirus early region 4 encodes two gene products with redundant effects in lytic infection. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2605–2615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2605-2615.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. Factors that bind to adeno-associated virus terminal repeats. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3095–3104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3095-3104.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. The AAV origin binding protein Rep68 is an ATP-dependent site-specific endonuclease with DNA helicase activity. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90526-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janik J. E., Huston M. M., Cho K., Rose J. A. Efficient synthesis of adeno-associated virus structural proteins requires both adenovirus DNA binding protein and VA I RNA. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):320–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janik J. E., Huston M. M., Rose J. A. Adeno-associated virus proteins: origin of the capsid components. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):591–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.591-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay F. T., Laughlin C. A., Carter B. J. Eukaryotic translational control: adeno-associated virus protein synthesis is affected by a mutation in the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2927–2931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Berns K. I. The adeno-associated virus rep gene inhibits replication of an adeno-associated virus/simian virus 40 hybrid genome in cos-7 cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1705–1712. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1705-1712.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Hermonat P. L., Berns K. I. Positive and negative autoregulation of the adeno-associated virus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):251–258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.251-258.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin C. A., Jones N., Carter B. J. Effect of deletions in adenovirus early region 1 genes upon replication of adeno-associated virus. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):868–876. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.868-876.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin C. A., Westphal H., Carter B. J. Spliced adenovirus-associated virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5567–5571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusby E. W., Berns K. I. Mapping of the 5' termini of two adeno-associated virus 2 RNAs in the left half of the genome. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):518–526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.518-526.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson E., Trempe J. P., Carter B. J. Identification of the trans-acting Rep proteins of adeno-associated virus by antibodies to a synthetic oligopeptide. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):823–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.823-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redemann B. E., Mendelson E., Carter B. J. Adeno-associated virus rep protein synthesis during productive infection. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):873–882. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.873-882.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Berns K. I., Tan M., Muzyczka N. Cloning of adeno-associated virus into pBR322: rescue of intact virus from the recombinant plasmid in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2077–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Chang L. S., Shenk T. A recombinant plasmid from which an infectious adeno-associated virus genome can be excised in vitro and its use to study viral replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3096–3101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3096-3101.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Helper-free stocks of recombinant adeno-associated viruses: normal integration does not require viral gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3822–3828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3822-3828.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus E1B 55-Mr polypeptide facilitates timely cytoplasmic accumulation of adeno-associated virus mRNAs. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):206–210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.206-210.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Srivastava A., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Rescue of adeno-associated virus from recombinant plasmids: gene correction within the terminal repeats of AAV. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler A. B., Ketner G. Adenovirus early region 4 is essential for normal stability of late nuclear RNAs. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):624–630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.624-630.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Van Dyke M. W., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. I. Complete purification and identification of USF from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11985–11993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senapathy P., Tratschin J. D., Carter B. J. Replication of adeno-associated virus DNA. Complementation of naturally occurring rep- mutants by a wild-type genome or an ori- mutant and correction of terminal palindrome deletions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. O., Im D. S., Muzyczka N. Evidence for covalent attachment of the adeno-associated virus (AAV) rep protein to the ends of the AAV genome. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6204–6213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6204-6213.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. O., Samulski R. J., Muzyczka N. In vitro resolution of covalently joined AAV chromosome ends. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90720-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A., Lusby E. W., Berns K. I. Nucleotide sequence and organization of the adeno-associated virus 2 genome. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.555-564.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Tal J., Carter B. J. Negative and positive regulation in trans of gene expression from adeno-associated virus vectors in mammalian cells by a viral rep gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2884–2894. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., West M. H., Sandbank T., Carter B. J. A human parvovirus, adeno-associated virus, as a eucaryotic vector: transient expression and encapsidation of the procaryotic gene for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2072–2081. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempe J. P., Carter B. J. Alternate mRNA splicing is required for synthesis of adeno-associated virus VP1 capsid protein. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3356–3363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3356-3363.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempe J. P., Carter B. J. Regulation of adeno-associated virus gene expression in 293 cells: control of mRNA abundance and translation. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.68-74.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempe J. P., Mendelson E., Carter B. J. Characterization of adeno-associated virus rep proteins in human cells by antibodies raised against rep expressed in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):18–28. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ormondt H., Maat J., De Waard A., Van der Eb A. J. The nucleotide sequence of the transforming HpaI-E fragment of adenovirus type 5 DNA. Gene. 1978 Dec;4(4):309–328. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. H., Trempe J. P., Tratschin J. D., Carter B. J. Gene expression in adeno-associated virus vectors: the effects of chimeric mRNA structure, helper virus, and adenovirus VA1 RNA. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):38–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]