Abstract
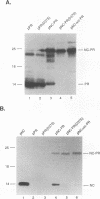
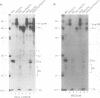
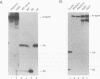
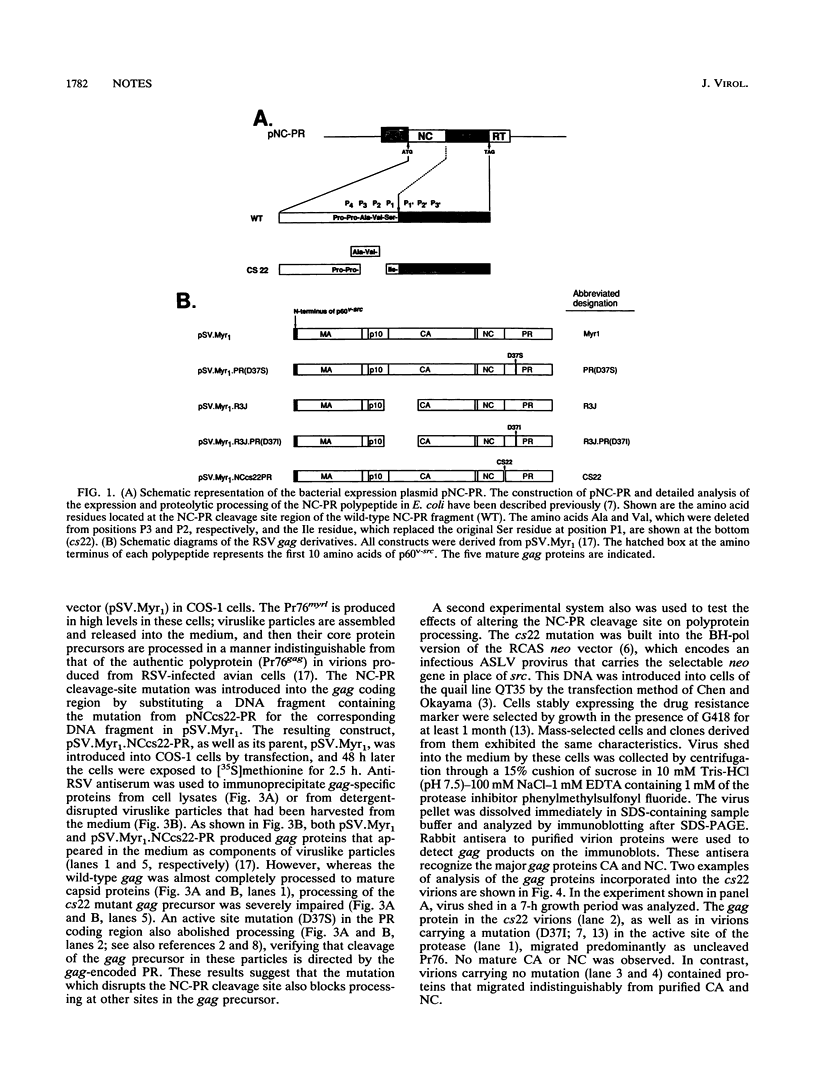
The avian sarcoma and leukosis viruses (ASLV) encode a protease (PR) at the C terminus of gag which in vivo catalyzes the processing of both gag and gag-pol precursors. The studies reported here were undertaken to determine whether PR is able to cleave these polyproteins while it is still part of the gag precursor or whether the release of its N terminus to form free PR is necessary for full proteolytic activity. To address this question, we created a mutation that disrupts the PR cleavage site between the NC and PR coding regions of the gag gene. This mutation was introduced into a eukaryotic vector that expresses only the gag precursor and into an otherwise infectious clone of ASLV that carries the neo gene as a selectable marker. These constructs were expressed in monkey COS cells or in quail QT35 cells, respectively. Processing was impaired in both systems. Mutant particles were formed, but they contained no mature processed gag proteins. We observed only the uncleaved gag precursor polypeptide Pr76 in one case or Pr76 and a cleaved product of about 60 kDa in the other. Processing of the mutant gag precursor could be complemented in trans by from a wild-type construct, suggesting that the mutation did not induce gross structural alterations in its precursor. Our results suggest that the PR first must be released from its precursor before it can attack other sites in the gag and gag-pol polyproteins and that cleavage at the NC-PR boundary is a prerequisite for the initiation of the PR-directed processing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett R. P., Rhee S., Craven R. C., Hunter E., Wills J. W. Amino acids encoded downstream of gag are not required by Rous sarcoma virus protease during gag-mediated assembly. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):272–280. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.272-280.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein H., Bizub D., Skalka A. M. Assembly and processing of avian retroviral gag polyproteins containing linked protease dimers. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6165–6172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6165-6172.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven R. C., Bennett R. P., Wills J. W. Role of the avian retroviral protease in the activation of reverse transcriptase during virion assembly. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6205–6217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6205-6217.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. Activity of avian retroviral protease expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2696–2700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2696-2700.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis J. M., McDonald R. A., Nashed N. T., Wondrak E. M., Jerina D. M., Oroszlan S., Mora P. T. Autoprocessing of the HIV-1 protease using purified wild-type and mutated fusion proteins expressed at high levels in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):361–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertle S., Spahr P. F. Role of the gag polyprotein precursor in packaging and maturation of Rous sarcoma virus genomic RNA. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5757–5763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5757-5763.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A. M. Retroviral proteases: first glimpses at the anatomy of a processing machine. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):911–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90621-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart L., Schatz G., Vogt V. M. Properties of avian retrovirus particles defective in viral protease. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5076–5092. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5076-5092.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart L., Vogt V. M. trans-acting viral protease is necessary and sufficient for activation of avian leukosis virus reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6218–6231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6218-6231.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Eisenman R., Diggelmann H. Generation of avian myeloblastosis virus structural proteins by proteolytic cleavage of a precursor polypeptide. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 15;96(3):471–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C., Achacoso J. A. Creation and expression of myristylated forms of Rous sarcoma virus gag protein in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4331–4343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4331-4343.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C. Form, function, and use of retroviral gag proteins. AIDS. 1991 Jun;5(6):639–654. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199106000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]