Abstract
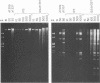
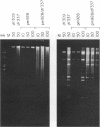
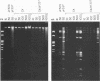
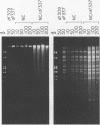
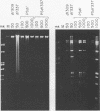
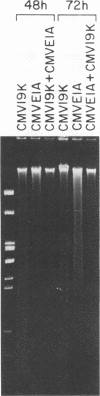
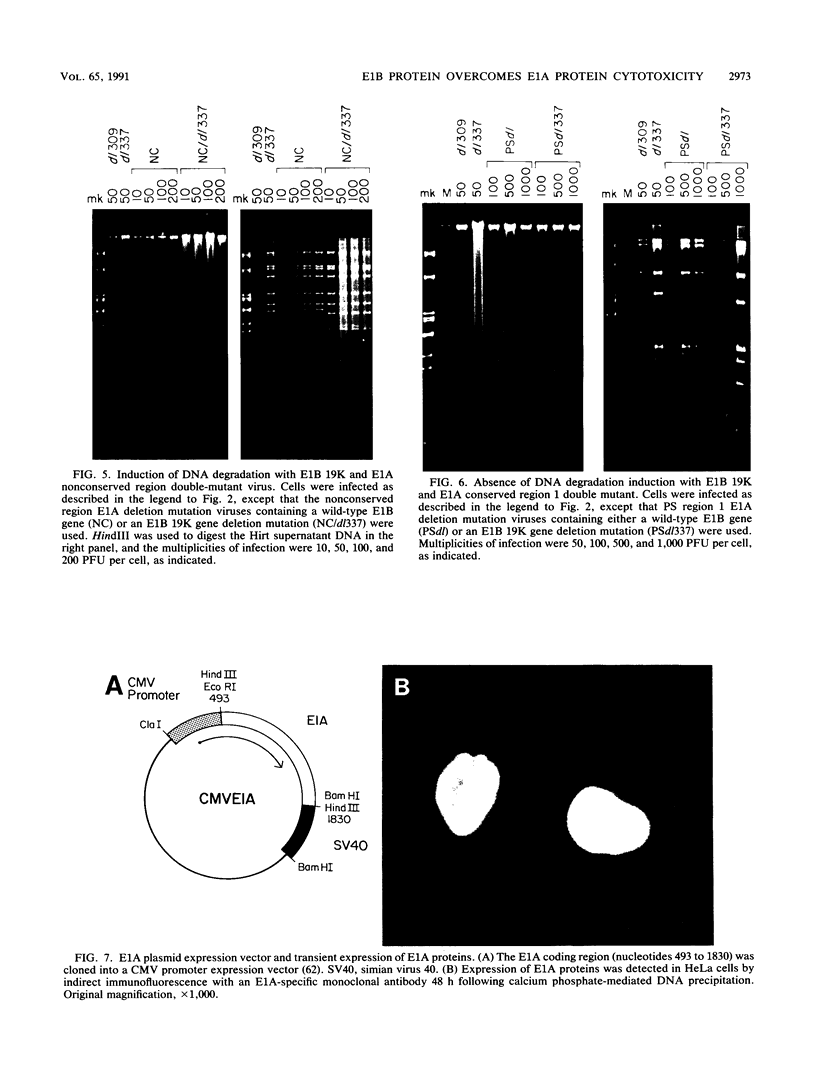
Infection with adenovirus mutants carrying either point mutations or deletions in the coding region for the 19-kDa E1B gene product (19K protein) causes degradation of host cell and viral DNAs (deg phenotype) and enhanced cytopathic effect (cyt phenotype). Therefore, one function of the E1B 19K protein is to protect nuclear DNA integrity and preserve cytoplasmic architecture during productive adenovirus infection. When placed in the background of a virus incapable of expressing a functional E1A gene product, however, E1B 19K gene mutations do not result in the appearance of the cyt and deg phenotypes. This demonstrated that expression of the E1A proteins was responsible for inducing the appearance of the cyt and deg phenotypes. By constructing a panel of viruses possessing E1A mutations spanning each of the three E1A conserved regions in conjunction with E1B 19K gene mutations, we mapped the induction of the cyt and deg phenotypes to the amino-terminal region of E1A. Viruses that fail to express conserved region 3 (amino acids 140 to 185) and/or 2, (amino acids 121 to 185) or nonconserved sequences between conserved regions 2 and 1 of E1A (amino acids 86 to 120) were still capable of inducing cyt and deg. This indicated that activities associated with these regions, such as transactivation and binding to the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene, were dispensable for induction of E1A-dependent cytotoxic effects. In contrast, deletion of sequences in the amino terminus of E1A (amino acids 22 to 107) resulted in extragenic suppression of the cyt and deg phenotypes. Therefore, a function affected by deletion of amino acids 22 to 86 of E1A is responsible for exerting cytotoxic effects in virally infected cells. Furthermore, transient high-level expression of the E1A region using a cytomegalovirus promoter plasmid expression vector was sufficient to induce the cyt and deg phenotypes, demonstrating that E1A expression alone is sufficient to exert these cytotoxic effects and that other viral gene products are not involved. Finally, placing E1A expression under the control of a strong promoter did not alter the requirement for E1B in the transformation of primary cells. One possibility is that the E1B 19K protein is required to overcome the cytotoxic effects of E1A protein expression and thereby enable primary cells to become transformed.
Full text
PDF
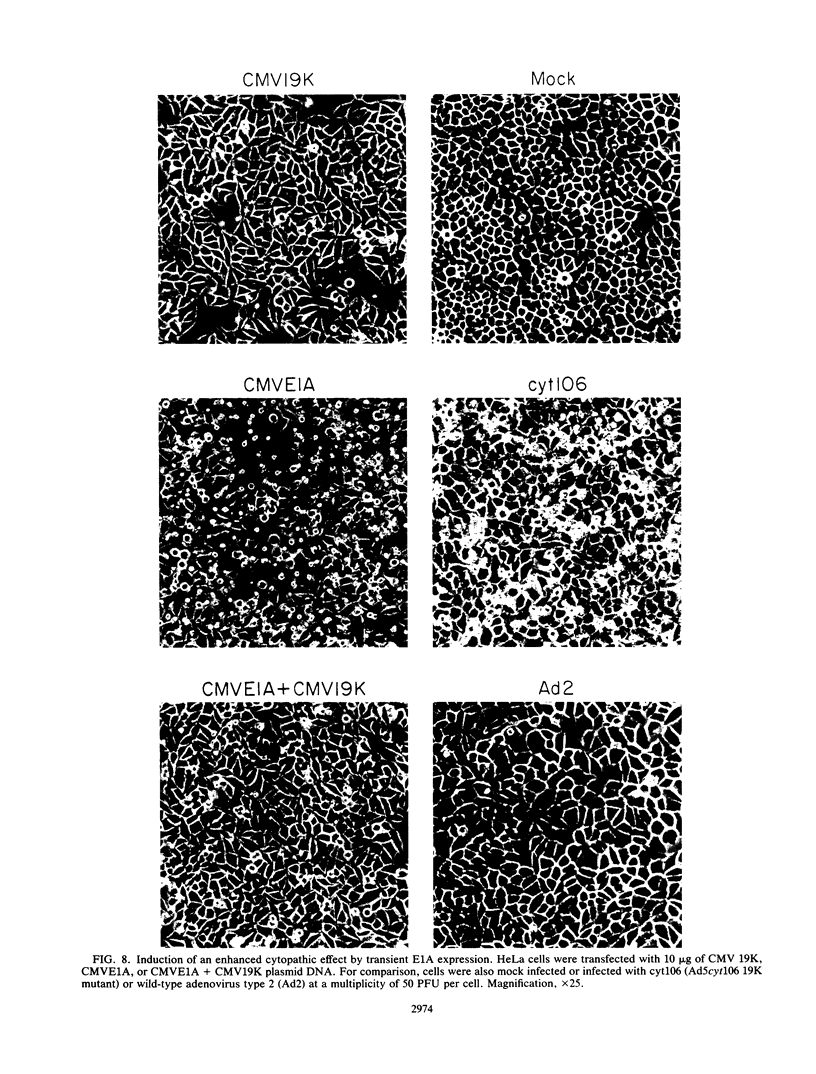









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami G. R., Babiss L. E. The efficiency of adenovirus transformation of rodent cells is inversely related to the rate of viral E1A gene expression. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3427–3436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3427-3436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames R. S., Holskin B., Mitcho M., Shalloway D., Chen M. J. Induction of sensitivity to the cytotoxic action of tumor necrosis factor alpha by adenovirus E1A is independent of transformation and transcriptional activation. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4115–4122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4115-4122.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J. Adenovirus promoters and E1A transactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:45–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton P. E., Bayley S. T., Graham F. L. Transformation by human adenoviruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;780(1):67–94. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(84)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. J., Holskin B., Strickler J., Gorniak J., Clark M. A., Johnson P. J., Mitcho M., Shalloway D. Induction by E1A oncogene expression of cellular susceptibility to lysis by TNF. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):581–583. doi: 10.1038/330581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus 2 Ip+ locus codes for a 19 kd tumor antigen that plays an essential role in cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. L., May D. L., Wilson B. A., Holskin B., Chen M. J., Shalloway D., Walker T. A. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in E1A oncogene-induced susceptibility of neoplastic cells to lysis by natural killer cells and activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4527–4534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dealtry G. B., Naylor M. S., Fiers W., Balkwill F. R. DNA fragmentation and cytotoxicity caused by tumor necrosis factor is enhanced by interferon-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):689–693. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerksen-Hughes P. J., Hermiston T. W., Wold W. S., Gooding L. R. The amino-terminal portion of CD1 of the adenovirus E1A proteins is required to induce susceptibility to tumor necrosis factor cytolysis in adenovirus-infected mouse cells. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1236–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1236-1244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerksen-Hughes P., Wold W. S., Gooding L. R. Adenovirus E1A renders infected cells sensitive to cytolysis by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4193–4200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Chervenak R., Cohen J. J. Endogenous endonuclease-induced DNA fragmentation: an early event in cell-mediated cytolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan C., Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Bayley S. T., Ferguson B., Branton P. E. Mapping of cellular protein-binding sites on the products of early-region 1A of human adenovirus type 5. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3955–3959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J. Cellular transformation by adenoviruses. Pharmacol Ther. 1984;26(1):59–88. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(84)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Whyte P., Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Beach D., Draetta G. A 60 kd cdc2-associated polypeptide complexes with the E1A proteins in adenovirus-infected cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooding L. R., Aquino L., Duerksen-Hughes P. J., Day D., Horton T. M., Yei S. P., Wold W. S. The E1B 19,000-molecular-weight protein of group C adenoviruses prevents tumor necrosis factor cytolysis of human cells but not of mouse cells. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3083–3094. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3083-3094.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L. THE LIMITED IN VITRO LIFETIME OF HUMAN DIPLOID CELL STRAINS. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Mar;37:614–636. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley K. P., Overhauser J., Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Jones N. C. Transformation properties of type 5 adenovirus mutants that differentially express the E1A gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Whyte P., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Association of adenovirus early-region 1A proteins with cellular polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1579–1589. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. A., Mymryk J. S., Egan C., Branton P. E., Bayley S. T. Retinoblastoma growth suppressor and a 300-kDa protein appear to regulate cellular DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5883–5887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Mymryk J. S., Evelegh C. M., Cunniff N. F., Bayley S. T. Sequences in E1A proteins of human adenovirus 5 required for cell transformation, repression of a transcriptional enhancer, and induction of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):120–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90518-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochemsen A. G., Peltenburg L. T., te Pas M. F., de Wit C. M., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Activation of adenovirus 5 E1A transcription by region E1B in transformed primary rat cells. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3399–3405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Ferguson B., Rosenberg M., Baserga R. Induction of cellular DNA synthesis by purified adenovirus E1A proteins. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Westphal H. The structure of adenovirus 2 early nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):23–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy M. N., Chinnadurai G. Relationship between the transforming and transcriptional regulatory functions of adenovirus 2 E1a oncogene. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90344-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Fatt R. B., Mak S. Mapping of an adenovirus function involved in the inhibition of DNA degradation. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):969–977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.969-977.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Philipson L. Early events of virus-cell interaction in an adenovirus system. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):323–338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.323-338.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran B., Zerler B. Interactions between cell growth-regulating domains in the products of the adenovirus E1A oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1756–1764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E. A region of SV40 large T antigen can substitute for a transforming domain of the adenovirus E1A products. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):168–170. doi: 10.1038/334168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Grodzicker T., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Zerler B. Lytic and transforming functions of individual products of the adenovirus E1A gene. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.765-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Mathews M. B. Multiple functional domains in the adenovirus E1A gene. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilder S., Logan J., Shenk T. Deletion of the gene encoding the adenovirus 5 early region 1b 21,000-molecular-weight polypeptide leads to degradation of viral and host cell DNA. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.664-671.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid D. S., Tite J. P., Ruddle N. H. DNA fragmentation: manifestation of target cell destruction mediated by cytotoxic T-cell lines, lymphotoxin-secreting helper T-cell clones, and cell-free lymphotoxin-containing supernatant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1881–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. F., Fisher F., Goding C. R., Jones N. C. Mutational analysis of the adenovirus E1a gene: the role of transcriptional regulation in transformation. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2053–2060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Ziff E. B. The amino-terminal region of the adenovirus serotype 5 E1a protein performs two separate functions when expressed in primary baby rat kidney cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3882–3890. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Argos P., Philipson L. The release of growth arrest by microinjection of adenovirus E1A DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2329–2336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. W., Corrigan M., Yaciuk P., Whelan J., Moran E. Analysis of E1A-mediated growth regulation functions: binding of the 300-kilodalton cellular product correlates with E1A enhancer repression function and DNA synthesis-inducing activity. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4421–4427. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4421-4427.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens C., Harlow E. Differential splicing yields novel adenovirus 5 E1A mRNAs that encode 30 kd and 35 kd proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2027–2035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Chinnadurai G. Separation of the functions controlled by adenovirus 2 lp+ locus. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Kuppuswamy M., Nasr R. J., Chinnadurai G. An N-terminal region of adenovirus E1a essential for cell transformation and induction of an epithelial cell growth factor. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori N., Cladaras C., Bhat B., Conley A. J., Wold W. S. cyt gene of adenoviruses 2 and 5 is an oncogene for transforming function in early region E1B and encodes the E1B 19,000-molecular-weight polypeptide. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):793–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.793-805.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfendahl P. J., Linder S., Kreivi J. P., Nordqvist K., Sevensson C., Hultberg H., Akusjärvi G. A novel adenovirus-2 E1A mRNA encoding a protein with transcription activation properties. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2037–2044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaesebroeck B., Timmers H. T., Pronk G. J., van Roy F., Van der Eb A. J., Fiers W. Modulation of cellular susceptibility to the cytotoxic/cytostatic action of tumor necrosis factor by adenovirus E1 gene expression is cell type-dependent. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90006-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen A., Pettersson U. The molecular structure of the 9S mRNA from early region 1A of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 15;165(3):496–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Blose S. H., Stillman B. W. Nuclear envelope localization of an adenovirus tumor antigen maintains the integrity of cellular DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2865–2875. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R. Role of adenovirus E1B proteins in transformation: altered organization of intermediate filaments in transformed cells that express the 19-kilodalton protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):120–130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R. Specific disruption of intermediate filaments and the nuclear lamina by the 19-kDa product of the adenovirus E1B oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9886–9890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Denton A., Stillman B. Role of the adenovirus E1B 19,000-dalton tumor antigen in regulating early gene expression. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3445–3454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3445-3454.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Faha B., Stillman B. Regulation of adenovirus gene expression in human WI38 cells by an E1B-encoded tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3763–3773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Grodzicker T., Stillman B. W. Mutations in the gene encoding the adenovirus early region 1B 19,000-molecular-weight tumor antigen cause the degradation of chromosomal DNA. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):410–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.410-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Stillman B. Expression of adenovirus E1B mutant phenotypes is dependent on the host cell and on synthesis of E1A proteins. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):426–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.426-435.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Ruley H. E., Harlow E. Two regions of the adenovirus early region 1A proteins are required for transformation. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):257–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.257-265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Branton P. E. Detection of cellular proteins associated with human adenovirus type 5 early region 1A polypeptides. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):142–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Venkatesh L., Kuppuswamy M., Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus transforming 19-kD T antigen has an enhancer-dependent trans-activation function and relieves enhancer repression mediated by viral and cellular genes. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):645–658. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Moran B., Maruyama K., Moomaw J., Grodzicker T., Ruley H. E. Adenovirus E1A coding sequences that enable ras and pmt oncogenes to transform cultured primary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):887–899. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Moran E. Different functional domains of the adenovirus E1A gene are involved in regulation of host cell cycle products. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):821–829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Elsen P. J., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Morphological transformation of human adenoviruses is determined to a large extent by gene products of region E1a. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):242–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90549-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]