Abstract
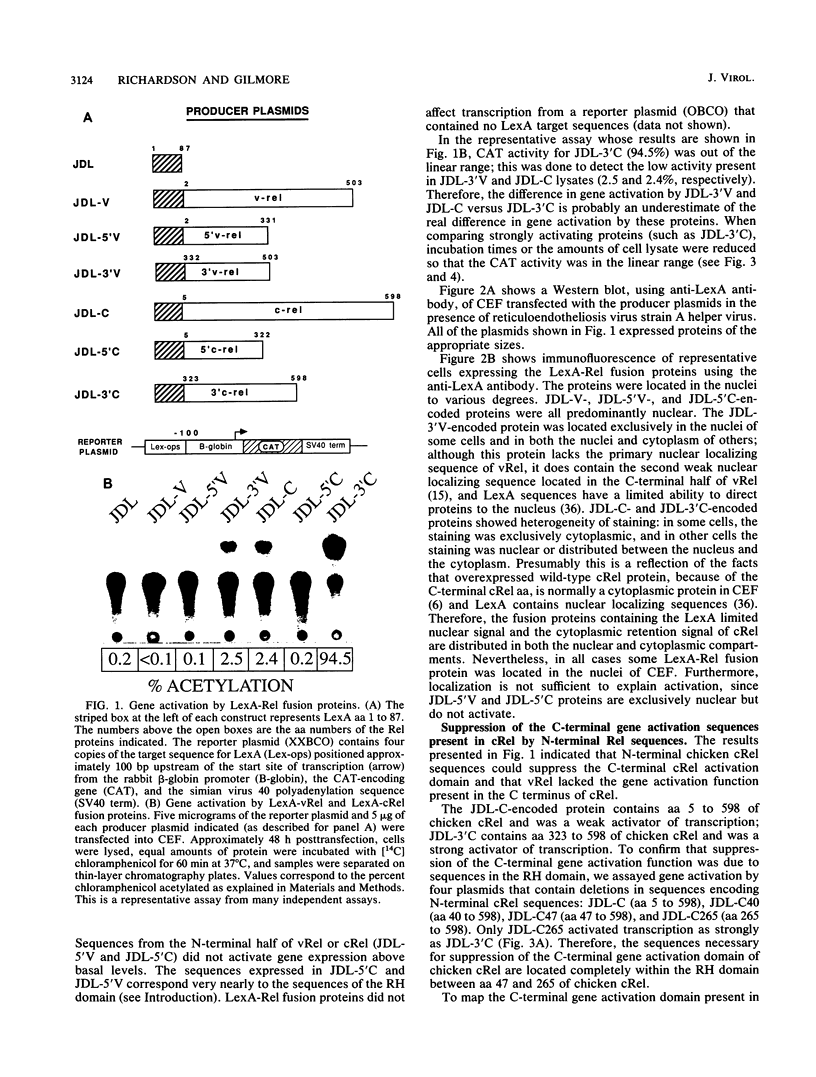
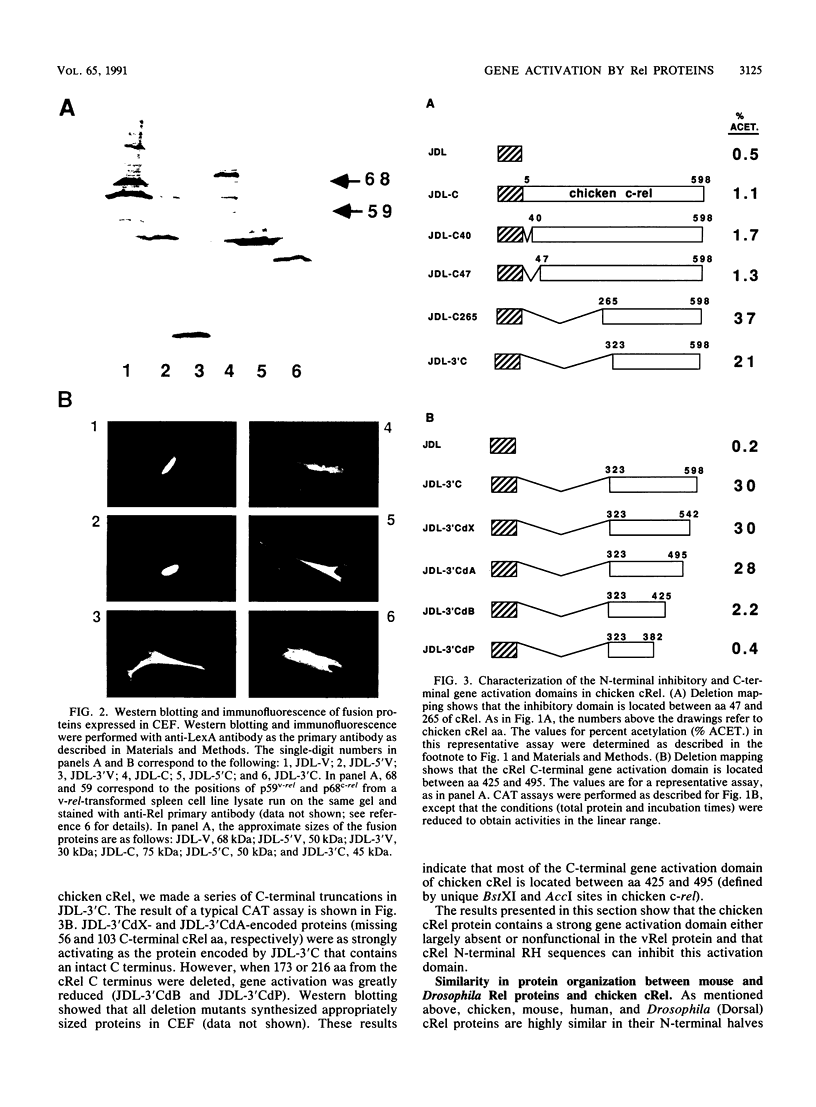
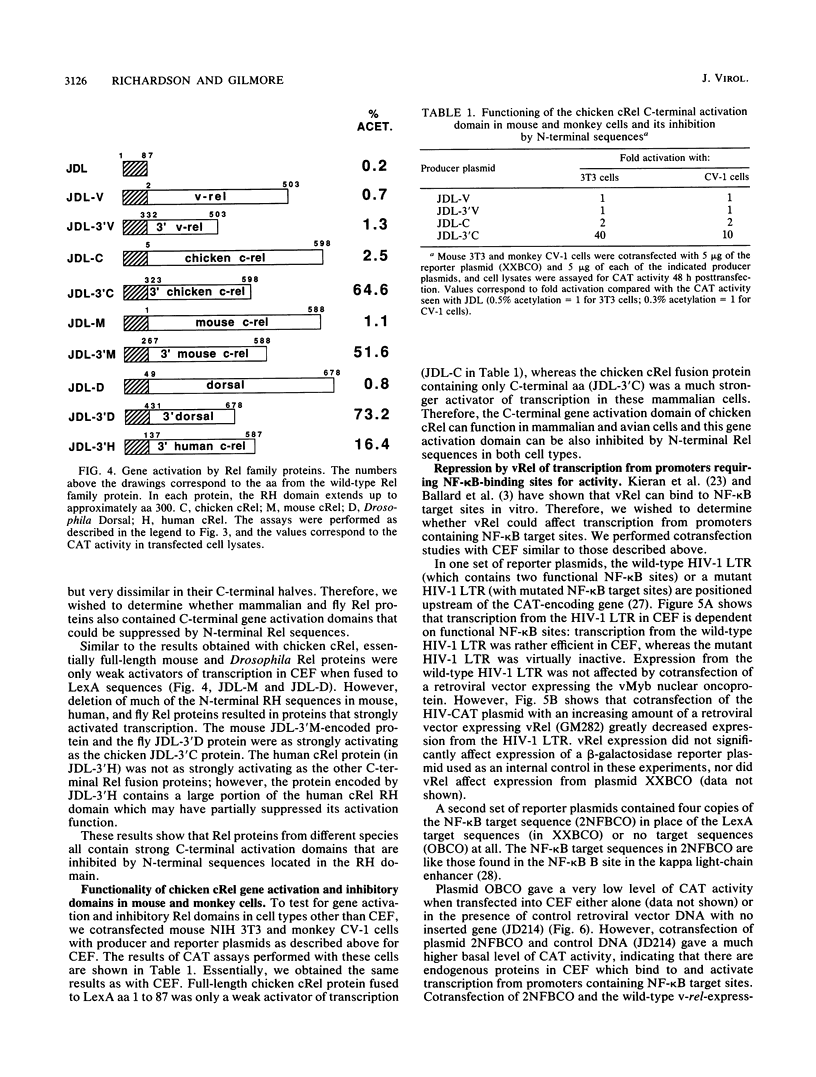
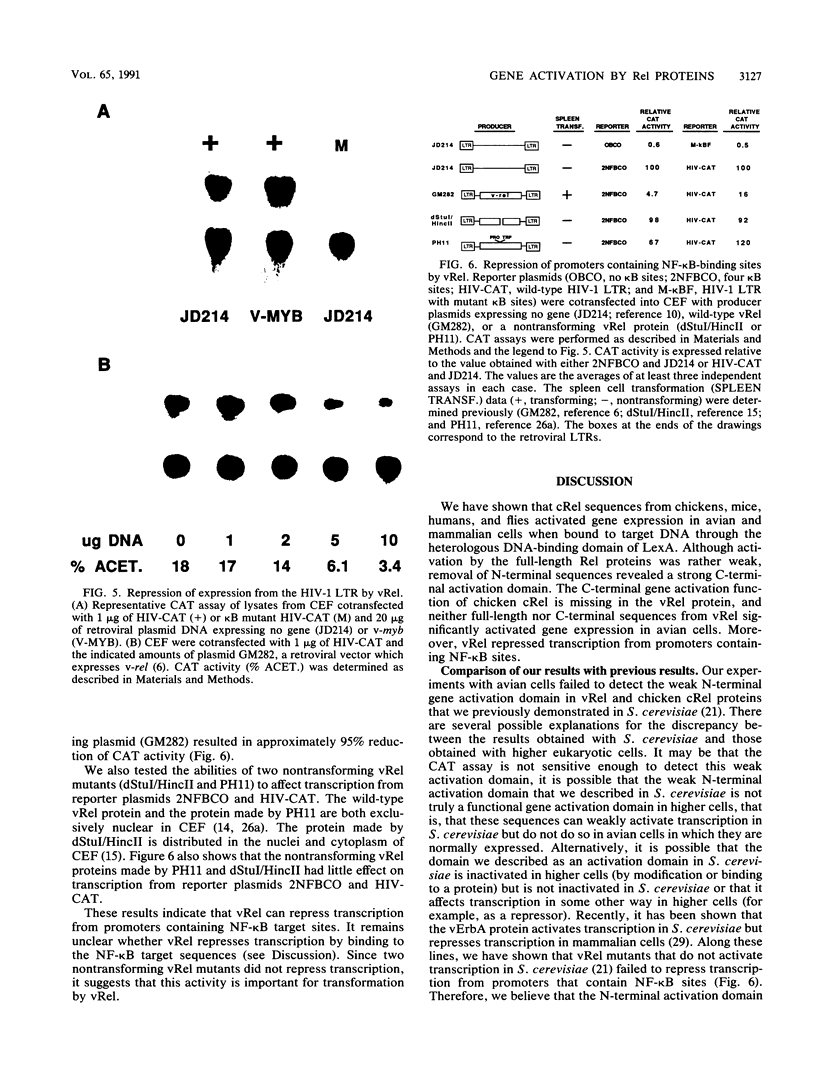
The vRel oncoprotein is member of a family of related proteins that also includes cRel, NF-kappa B, and Dorsal. We investigated the transcriptional regulatory properties of several Rel proteins in cotransfection assays with chicken embryo fibroblasts (CEF). Retroviral vectors expressing hybrid proteins that contain the DNA-binding domain of LexA fused to portions of the viral oncoprotein vRel or chicken, mouse, human, or Drosophila melanogaster (Dorsal) cRel proteins were cotransfected with a reporter plasmid that contains the DNA sequence recognized by LexA, a promoter, and the assayable gene for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. In transient assays, a LexA-vRel protein did not activate transcription in CEF. Full-length chicken cRel, mouse cRel, and Dorsal fusion proteins all activated transcription weakly; however, deletion of N-terminal Rel sequences from each of these proto-oncogene encoded proteins resulted in strong activation by LexA fusion proteins containing only C-terminal sequences. Inhibition of the C-terminal chicken cRel gene activation domain by N-terminal sequences was seen in CEF and mouse and monkey fibroblasts. These results show that cRel proteins from different species have the same general organization: an N-terminal inhibitory domain and a C-terminal activation domain. Sequence comparison suggests that the inhibitory domain is conserved but the activation domain is species specific. In contrast, vRel lacks a strong C-terminal gene activation function, since a LexA fusion protein containing C-terminal vRel sequences alone only weakly activated transcription. In addition, the wild-type vRel protein (lacking LexA sequences) repressed transcription from reporter plasmids containing NF-kappa B target sequences; nontransforming vRel mutants did not repress transcription from these plasmids. Our results suggest that vRel transforms cells by interfering with transcriptional activation by cellular Rel proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1689–1698. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Tjian R. Control of c-Jun activity by interaction of a cell-specific inhibitor with regulatory domain delta: differences between v- and c-Jun. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell E., Mittereder N., Rice N. R. A human rel proto-oncogene cDNA containing an Alu fragment as a potential coding exon. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):935–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Morley K. L., Hoekstra M. F., Hunter T., Verma I. M. The mouse c-rel protein has an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal transcriptional transactivation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5473–5485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco A. J., Simmons D. L., Gilmore T. D. Cloning and expression of a chicken c-rel cDNA: unlike p59v-rel, p68c-rel is a cytoplasmic protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. R., Yeh L. S., Barker W. C. Similarity between oncogenic v-rel protein and regulatory fnr protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3977–3977. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
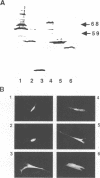
- Davis N., Bargmann W., Lim M. Y., Bose H., Jr Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus-transformed lymphoid cells contain multiple pp59v-rel complexes. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.584-591.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Temin H. M. High mutation rate of a spleen necrosis virus-based retrovirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4387–4395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. NF-kappa B, KBF1, dorsal, and related matters. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):841–843. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90257-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. Different localization of the product of the v-rel oncogene in chicken fibroblasts and spleen cells correlates with transformation by REV-T. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):791–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90845-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. v-rel oncoproteins in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm transform chicken spleen cells. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):703–714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.703-714.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Signal transduction and transcriptional regulation by glucocorticoid receptor-LexA fusion proteins. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):812–816. doi: 10.1126/science.3043662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumont R. J., Gerondakis S. Structure of a mammalian c-rel protein deduced from the nucleotide sequence of murine cDNA clones. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gélinas C., Temin H. M. The v-rel oncogene encodes a cell-specific transcriptional activator of certain promoters. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Temin H. M. Transactivation of gene expression by nuclear and cytoplasmic rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4323–4336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog N. K., Bose H. R., Jr Expression of the oncogene of avian reticuloendotheliosis virus in Escherichia coli and identification of the transforming protein in reticuloendotheliosis virus T-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):812–816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamens J., Richardson P., Mosialos G., Brent R., Gilmore T. Oncogenic transformation by vrel requires an amino-terminal activation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2840–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Kabrun N., Mudri S., Hayman M. J., Enrietto P. J. Viral rel and cellular rel associate with cellular proteins in transformed and normal cells. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):677–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Oligonucleotide that binds nuclear factor NF-kappa B acts as a lymphoid-specific and inducible enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1482–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Sharif M., Yamamoto K. R. The viral erbA oncogene protein, a constitutive repressor in animal cells, is a hormone-regulated activator in yeast. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90423-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Copeland T. D., Simek S., Oroszlan S., Gilden R. V. Detection and characterization of the protein encoded by the v-rel oncogene. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Brent R., Ptashne M. DNA binding is not sufficient for nuclear localization of regulatory proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4763–4766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S., Rice N. R. Detection and characterization of the protein encoded by the chicken c-rel protooncogene. Oncogene Res. 1988;2(2):103–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S., Rice N. R. p59v-rel, the transforming protein of reticuloendotheliosis virus, is complexed with at least four other proteins in transformed chicken lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4730–4736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4730-4736.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Rice N. R., Hiebsch R. R., Bose H. R., Jr, Gilden R. V. Nucleotide sequence of v-rel: the oncogene of reticuloendotheliosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6229–6233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Relocalization of the dorsal protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus correlates with its function. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Encapsidation sequences for spleen necrosis virus, an avian retrovirus, are between the 5' long terminal repeat and the start of the gag gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5986–5990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]