Abstract
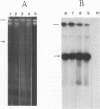
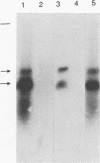
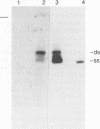
Circular double-stranded replication intermediates were identified in low-molecular-weight DNA of cells of the avian leukemia virus-induced lymphoblastoid cell line 1104-X-5 infected with chicken anemia virus (CAV). To characterize the genome of CAV, we cloned linearized CAV DNA into the vector pIC20H. Transfection of the circularized cloned insert into chicken cell lines caused a cytopathogenic effect, which was arrested when a chicken serum with neutralizing antibodies directed against CAV was added. Chickens inoculated at 1 day of age with CAV collected from cell lines transfected with cloned CAV DNA developed clinical signs of CAV. The 2,319-bp cloned CAV DNA contained all the genetic information needed for the complete replication cycle of CAV. The CAV DNA sequence has three partially overlapping major reading frames coding for putative peptides of 51.6, 24.0, and 13.6 kDa. The CAV genome probably contains only one promoter region and only one poly(A) addition signal. Southern blot analysis using oligomers derived from the CAV DNA sequence showed that infected cells contained double- and single-stranded CAV DNAs, whereas purified virus contained only the minus strand. It is the first time that the genome of one of the three known single-stranded circular DNA viruses has been completely analyzed.
Full text
PDF

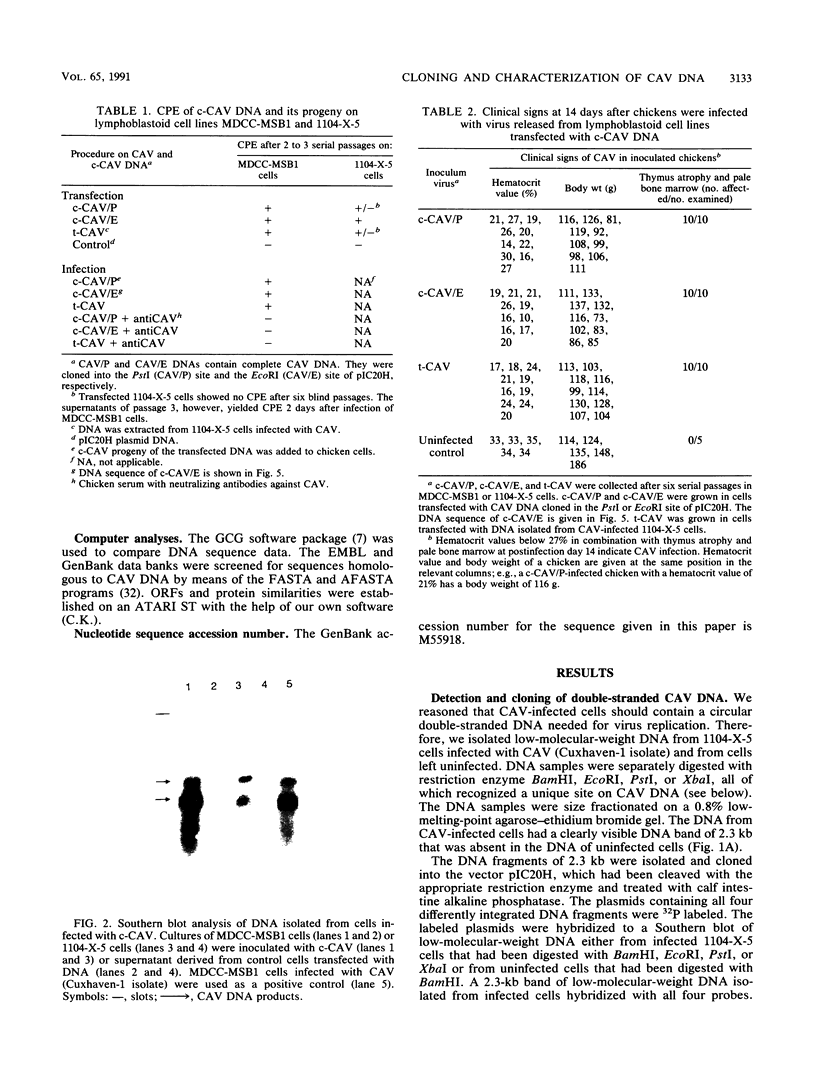





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becerra S. P., Rose J. A., Hardy M., Baroudy B. M., Anderson C. W. Direct mapping of adeno-associated virus capsid proteins B and C: a possible ACG initiation codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7919–7923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L., Polder L. J., Bernards R., Schrier P. I., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J., van Ormondt H. The 2.2 kb E1b mRNA of human Ad12 and Ad5 codes for two tumor antigens starting at different AUG triplets. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90366-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon P. J., Gupta K. C. Expression of five proteins from the Sendai virus P/C mRNA in infected cells. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):974–977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.974-977.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H., Kling S., Lurz R., Tischer I., von Bülow V. Morphological characterization of chicken anaemia agent (CAA). Arch Virol. 1989;109(1-2):115–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01310522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goryo M., Shibata Y., Suwa T., Umemura T., Itakura C. Outbreak of anemia associated with chicken anemia agent in young chicks. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1987 Oct;49(5):867–873. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.49.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hihara H., Shimizu T., Yamamoto H. Establishment of tumor cell lines cultured from chickens with avian lymphoid leukosis. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1974 Winter;14(4):163–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeurissen S. H., Janse E. M., Ekino S., Nieuwenhuis P., Koch G., De Boer G. F. Monoclonal antibodies as probes for defining cellular subsets in the bone marrow, thymus, bursa of fabricius, and spleen of the chicken. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Oct;19(3-4):225–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(88)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeurissen S. H., Pol J. M., de Boer G. F. Transient depletion of cortical thymocytes induced by chicken anaemia agent. Thymus. 1989;14(1-3):115–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Structure and function of transcription factors. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):5–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucio B., Schat K. A., Shivaprasad H. L. Identification of the chicken anemia agent, reproduction of the disease, and serological survey in the United States. Avian Dis. 1990 Jan-Mar;34(1):146–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi H., Ono E., Gupta K. C. Initiation of translation at CUG, GUG, and ACG codons in mammalian cells. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Cowie A., Carr A., Glaichenhaus N., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The roles of individual polyoma virus early proteins in oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):713–718. doi: 10.1038/300713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie B. W., Niagro F. D., Lukert P. D., Steffens W. L., 3rd, Latimer K. S. Characterization of a new virus from cockatoos with psittacine beak and feather disease. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger J. K., Cloud S. S. The effects of age, route of exposure, and coinfection with infectious bursal disease virus on the pathogenicity and transmissibility of chicken anemia agent (CAA). Avian Dis. 1989 Oct-Dec;33(4):753–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger J. K., Cloud S. S. The isolation and characterization of chicken anemia agent (CAA) from broilers in the United States. Avian Dis. 1989 Oct-Dec;33(4):707–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischer I., Gelderblom H., Vettermann W., Koch M. A. A very small porcine virus with circular single-stranded DNA. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):64–66. doi: 10.1038/295064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischer I., Mields W., Wolff D., Vagt M., Griem W. Studies on epidemiology and pathogenicity of porcine circovirus. Arch Virol. 1986;91(3-4):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01314286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd D., Creelan J. L., Mackie D. P., Rixon F., McNulty M. S. Purification and biochemical characterization of chicken anaemia agent. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):819–823. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa N. Propagation and infectivity titration of the Gifu-1 strain of chicken anemia agent in a cell line (MDCC-MSB1) derived from Marek's disease lymphoma. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1983 Spring;23(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bülow V., Fuchs B., Bertram M. Untersuchungen über den Erreger der infektiösen Anämie bei Hühnerküken (CAA) in vitro: Vermehrung, Titration, Serumneutralisationstest und indirekter Immunfluoreszenztest. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1985 Oct;32(9):679–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bülow V., Fuchs B., Vielitz E., Landgraf H. Frühsterblichkeitssyndrom bei Küken nach Doppelinfektion mit dem Virus der Marekschen Krankheit (MDV) und einem Anämie-Erreger (CAA). Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1983 Dec;30(10):742–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bülow V., Rudolph R., Fuchs B. Folgen der Doppelinfektion von Küken mit Adenovirus oder Reovirus und dem Erreger der aviären infektiösen Anämie (CAA). Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1986 Dec;33(10):717–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]