Abstract
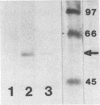
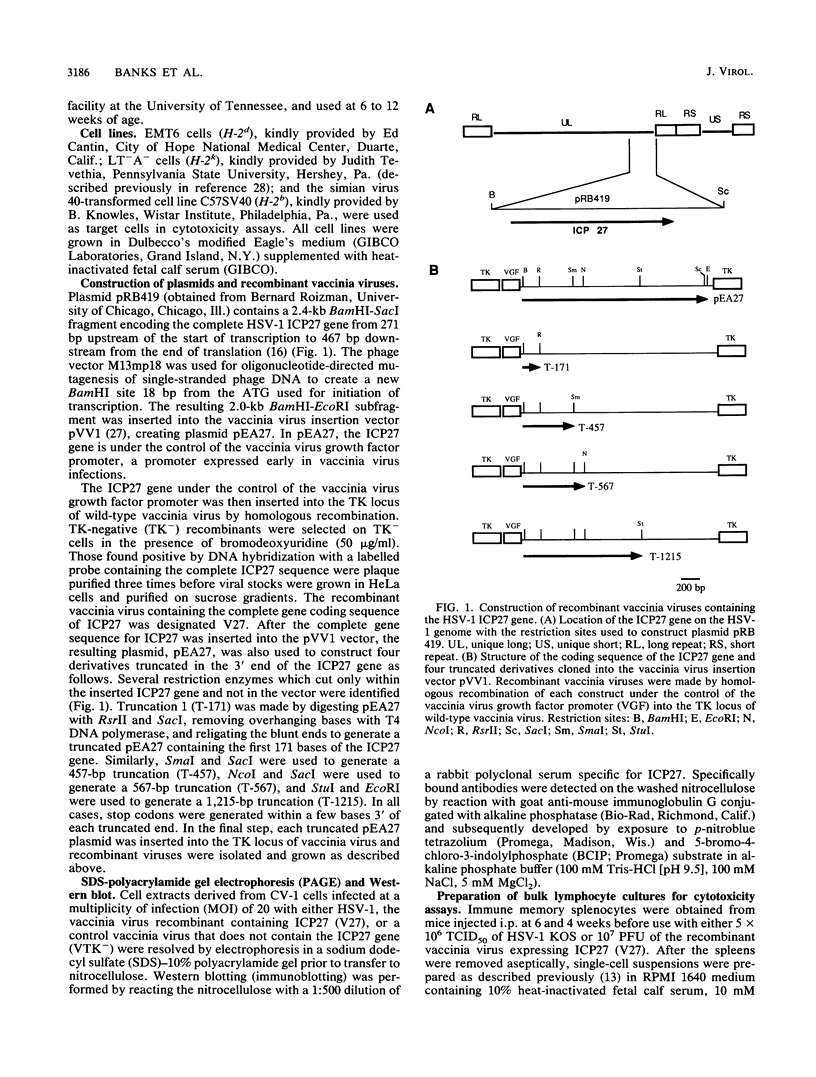
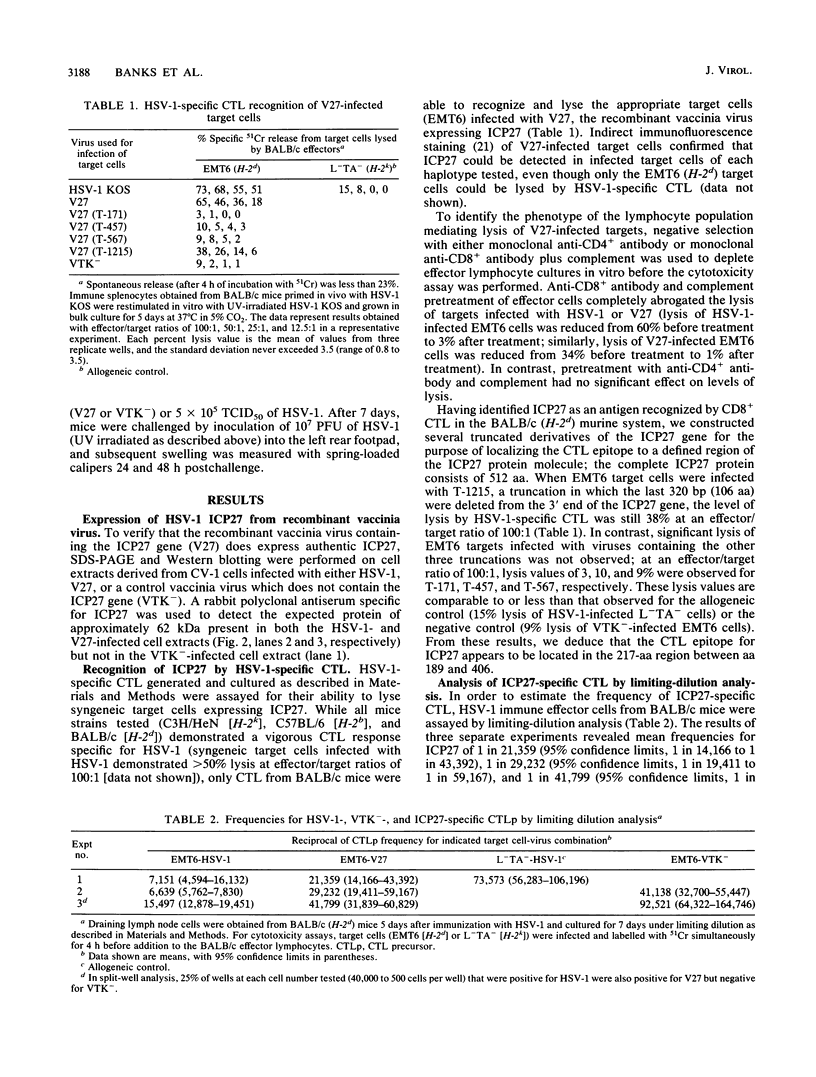
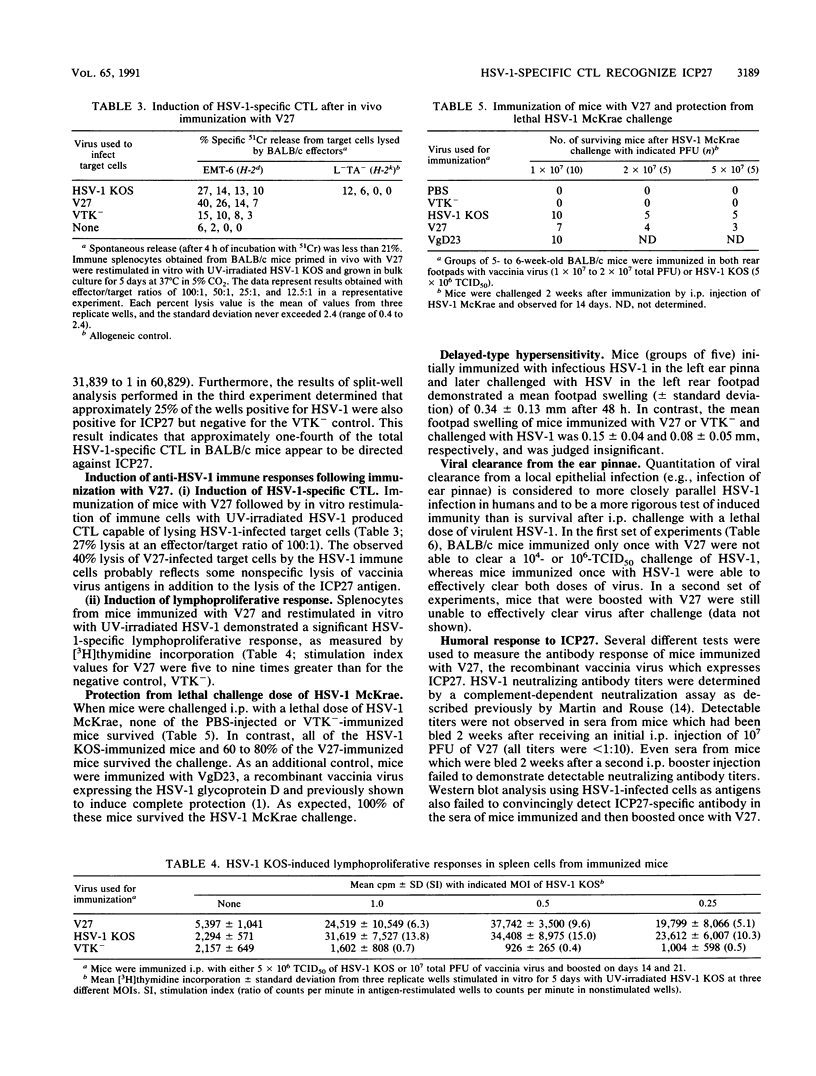
The identity of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) antigens that serve as targets for cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and their ability to induce protective immunity remain uncertain. In this article, we report the identification of the immediate-early protein ICP27 as a CTL antigen in H-2d mice but not in H-2k or H-2b mice. Calculation of the frequencies of H-2d-restricted virus-specific CTL demonstrated that approximately one-fourth of the total HSV-1-specific response was directed against ICP27. To define the location of this CTL epitope, four truncated derivatives of the ICP27 gene which place the epitope in a 217-amino-acid region (amino acids 189 to 406) near the central portion of the protein were constructed. Mice immunized with ICP27 were able both to induce HSV-1-specific CTL and to survive a lethal intraperitoneal challenge with virulent HSV-1. However, neither appreciable antibody nor delayed-type hypersensitivity responses were induced in immunized mice, and they were also unable to clear a local epithelial virus challenge. It appears that ICP27, although capable of inducing several aspects of the immune response, is by itself unable to provide complete immunity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen E. M., Weir J. P., Martin S., Mercadal C., Rouse B. T. Role of coexpression of IL-2 and herpes simplex virus proteins in recombinant vaccinia virus vectors on levels of induced immunity. Viral Immunol. 1990 Fall;3(3):207–215. doi: 10.1089/vim.1990.3.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklaws B. A., Nash A. A., Darby G. Specificity of the immune response of mice to herpes simplex virus glycoproteins B and D constitutively expressed on L cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):1103–1114. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Hickling J. K., Graham S., Sinclair J., Cranage M. P., Smith G. L., Sissons J. G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic T cells. Relative frequency of stage-specific CTL recognizing the 72-kD immediate early protein and glycoprotein B expressed by recombinant vaccinia viruses. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):919–931. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows S. R., Misko I. S., Sculley T. B., Schmidt C., Moss D. J. An Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T-cell epitope present on A- and B-type transformants. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3974–3976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3974-3976.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows S. R., Sculley T. B., Misko I. S., Schmidt C., Moss D. J. An Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T cell epitope in EBV nuclear antigen 3 (EBNA 3). J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):345–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer K. J., Mackett M., Wohlenberg C., Notkins A. L., Moss B. Vaccinia virus recombinant expressing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D prevents latent herpes in mice. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):737–740. doi: 10.1126/science.2986288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J., Kees U., Kümel G., Kirchner H., Krammer P. H. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) glycoprotein gC as the immunodominant antigen for HSV-1-specific memory cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):575–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke T., Graham F. L., Rosenthal K. L., Johnson D. C. Identification of an immunodominant cytotoxic T-lymphocyte recognition site in glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus by using recombinant adenovirus vectors and synthetic peptides. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1177–1186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1177-1186.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen H. S., Feng M. F., Horohov D. W., Moore R. N., Rouse B. T. Role of T-lymphocyte subsets in recovery from herpes simplex virus infection. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):56–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.56-59.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Cantin E., Rouse B. T. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Their relevance in herpesvirus infections. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;532:257–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb36344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Cantin E., Rouse B. T. Evaluation of antiviral immunity using vaccinia virus recombinants expressing cloned genes for herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jun;70(Pt 6):1359–1370. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-6-1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Courtney R. J., Fowler G., Rouse B. T. Herpes simplex virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize virus nonstructural proteins. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2265–2273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2265-2273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Moss B., Berman P. W., Laskey L. A., Rouse B. T. Mechanisms of antiviral immunity induced by a vaccinia virus recombinant expressing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D: cytotoxic T cells. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):726–734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.726-734.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Rouse B. T. The mechanisms of antiviral immunity induced by a vaccinia virus recombinant expressing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D: clearance of local infection. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3431–3437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Zhu X. X., Silverstein S. J., Courtney R. J., Yao F., Jenkins F. J., Rouse B. T. Murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for herpes simplex virus type 1 recognize the immediate early protein ICP4 but not ICP0. J Gen Virol. 1990 Oct;71(Pt 10):2391–2399. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-10-2391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Silver S., Hubenthal-Voss J., McKnight J. L., Roizman B. Regulation of herpes simplex virus 1 genes: alpha gene sequence requirements for transient induction of indicator genes regulated by beta or late (gamma 2) promoters. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin-Taylor E., Willey D. E., Cantin E. M., Eberle R., Moss B., Openshaw H. A recombinant vaccinia virus expressing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein B induces cytotoxic T lymphocytes in mice. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1731–1734. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. The repressing and enhancing functions of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP27 map to C-terminal regions and are required to modulate viral gene expression very early in infection. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3471–3485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3471-3485.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Young L. S., Calender A., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Lenoir G. M., Rickinson A. B. Different patterns of Epstein-Barr virus gene expression and of cytotoxic T-cell recognition in B-cell lines infected with transforming (B95.8) or nontransforming (P3HR1) virus strains. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):894–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.894-901.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash A. A., Jayasuriya A., Phelan J., Cobbold S. P., Waldmann H., Prospero T. Different roles for L3T4+ and Lyt 2+ T cell subsets in the control of an acute herpes simplex virus infection of the skin and nervous system. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):825–833. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Klassen T., Baringer J. R. Type-common and type-specific monoclonal antibody to herpes simplex virus type 1. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):724–732. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.724-732.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal K. L., Smiley J. R., South S., Johnson D. C. Cells expressing herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gC but not gB, gD, or gE are recognized by murine virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2438–2447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2438-2447.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Norley S., Martin S. Antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocyte induction and vaccination. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):16–33. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkmer H., Bertholet C., Jonjić S., Wittek R., Koszinowski U. H. Cytolytic T lymphocyte recognition of the murine cytomegalovirus nonstructural immediate-early protein pp89 expressed by recombinant vaccinia virus. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):668–677. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Bennett M., Allen E. M., Elkins K. L., Martin S., Rouse B. T. Recombinant vaccinia virus expressing the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C protects mice against herpes simplex virus challenge. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2587–2594. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H., Hengartner H., Nabholz M., Lernhardt W., Schreier M. H., Haas W. Fine specificity of a continuously growing killer cell clone specific for H-Y antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):592–597. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]