Abstract
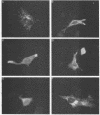
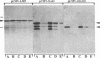
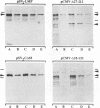
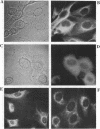
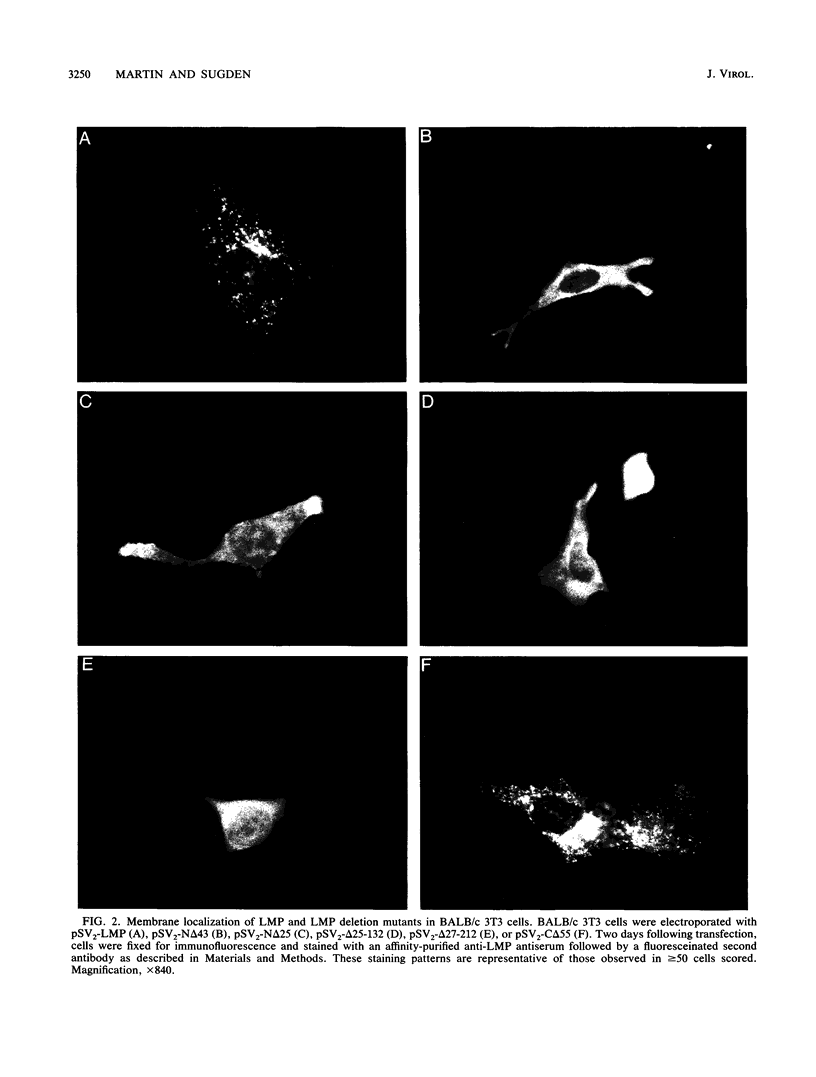
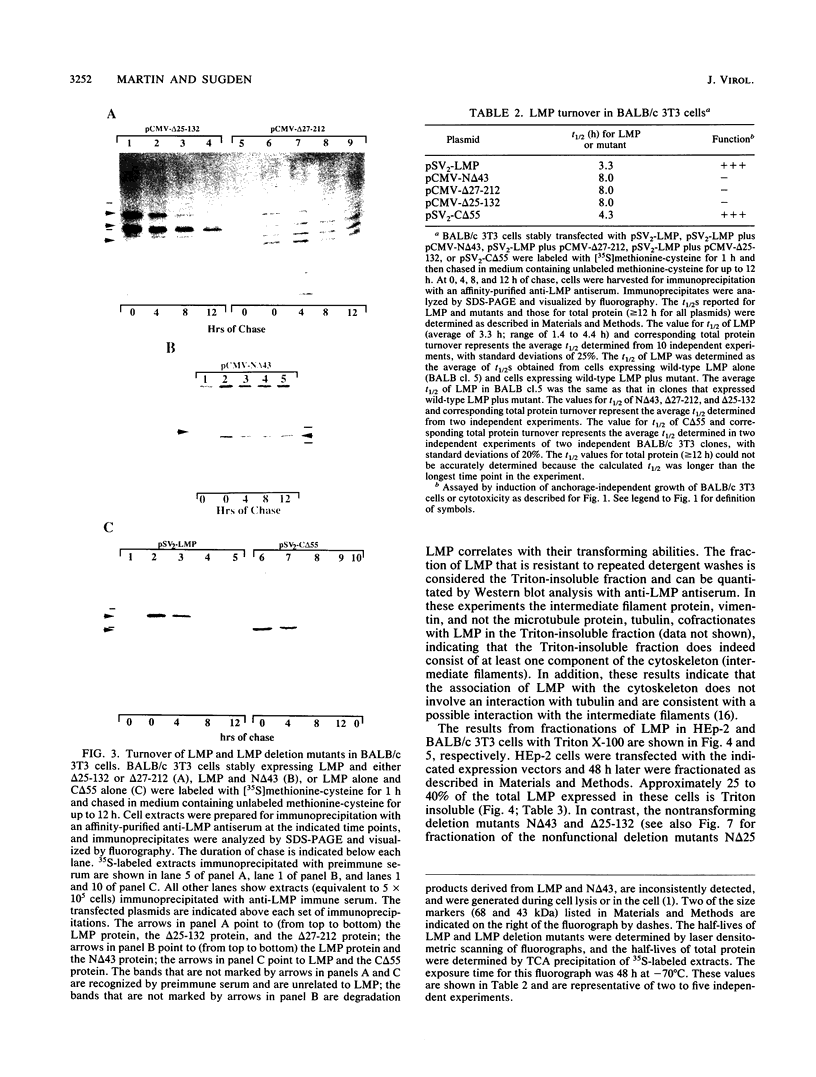
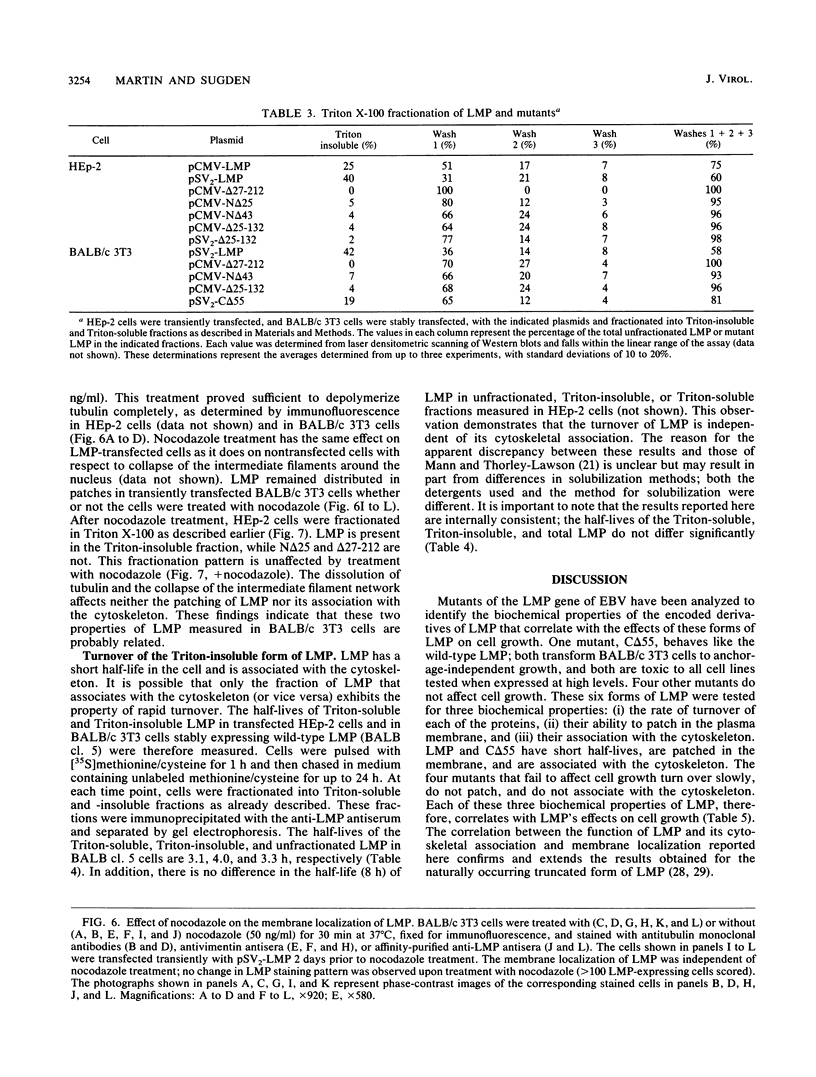
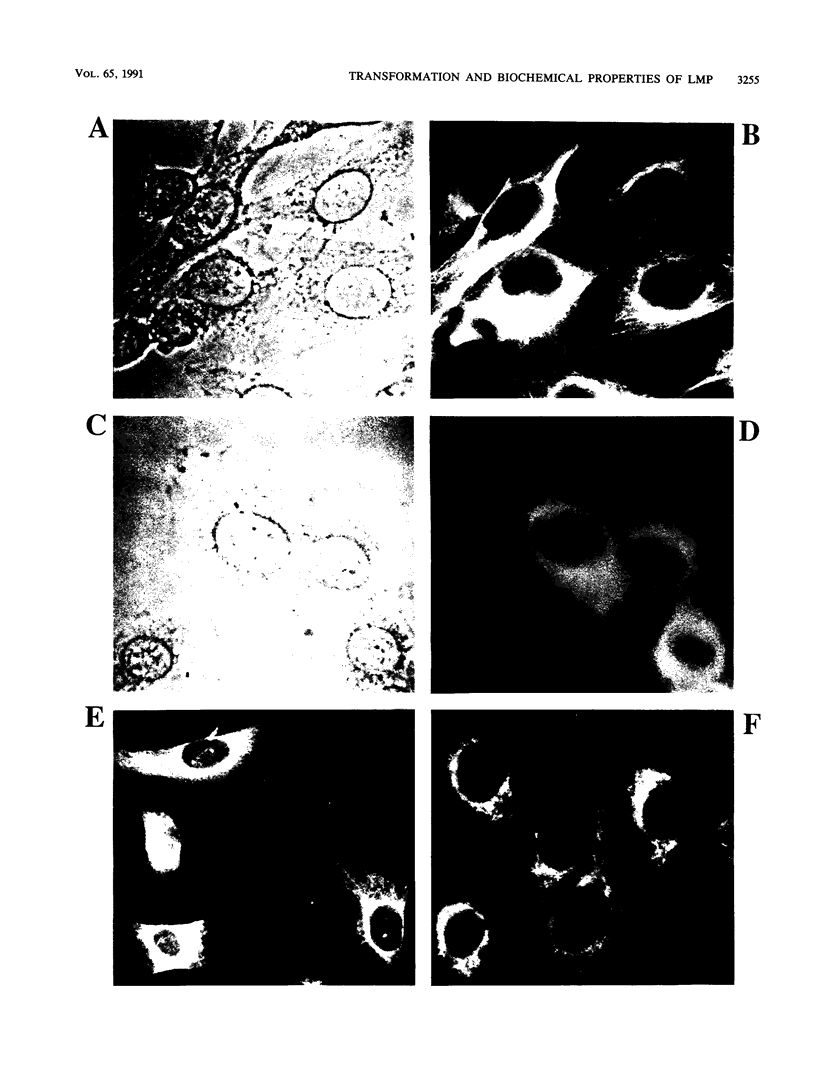
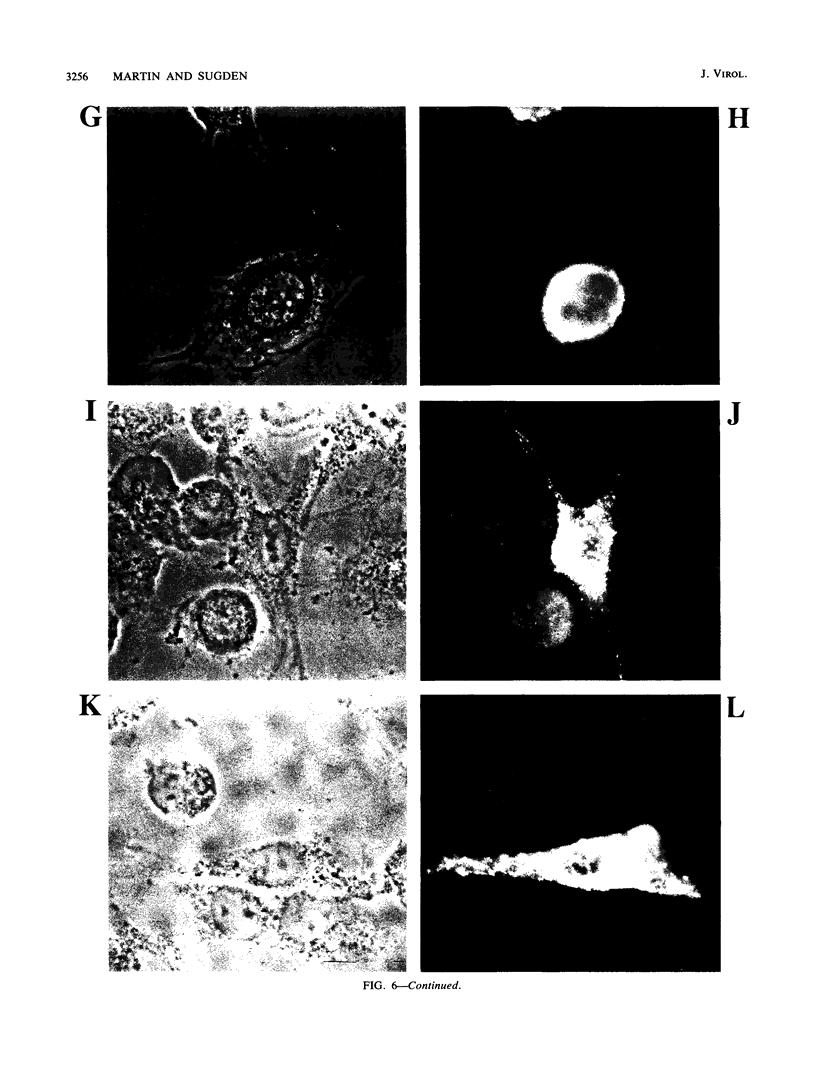
The latent membrane protein (LMP) of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) has a short half-life (V. R. Baichwal and B. Sugden, J. Virol, 61:866-875, 1987; K.P. Mann and D. Thorley-Lawson, J. Virol, 61:2100-2108, 1987), is localized in patches in the membrane (D. Liebowitz, D. Wang, and E, Kieff, J. Virol, 58:233-237, 1986), and associates with the cytoskeleton in EBV-immortalized B lymphocytes (D. Liebowitz, R. Kopan, E. Fuchs, J. Sample, and E. Kieff, Mol. Cell. Biol. 7:2299-2308, 1987; K. P. Mann and D. Thorley-Lawson, J. Virol. 61:2100-2108, 1987). Deletion mutants of LMP that are either positive or negative in the induction both of anchorage-independent growth of BALB/c 3T3 cells (V. R. Baichwal and B. Sugden, Oncogene 4:67-74, 1989) and of cytotoxicity in a variety of cells (W. Hammerschmidt, B. Sugden, and V. R. Baichwal, J. Virol. 63:2469-2475, 1989) have been studied to identify the biochemical properties of this protein that correlate with its effects on cell growth. Mutant LMP proteins that are metabolically stable, do not associate with the cytoskeleton, and exhibit a diffuse plasma membrane localization also do not induce anchorage-independent growth in rodent cells or cytotoxicity in B lymphoblastoid cells. In contrast, a mutant of LMP that is functionally identical to the wild-type protein has a half-life, membrane localization, and cytoskeletal association similar or identical to those of LMP. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that LMP's rapid turnover, association with the cytoskeleton, and patching in the membrane are required for it to affect cell growth.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. Posttranslational processing of an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded membrane protein expressed in cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):866–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.866-875.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. The multiple membrane-spanning segments of the BNLF-1 oncogene from Epstein-Barr virus are required for transformation. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. Transformation of Balb 3T3 cells by the BNLF-1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Oncogene. 1988 May;2(5):461–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankier A. T., Deininger P. L., Satchwell S. C., Baer R., Farrell P. J., Barrell B. G. DNA sequence analysis of the EcoRI Dhet fragment of B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus containing the terminal repeat sequences. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Nov;1(4):425–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson C. W., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein inhibits human epithelial cell differentiation. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):777–780. doi: 10.1038/344777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald S., van Santen V., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequence of an mRNA transcribed in latent growth-transforming virus infection indicates that it may encode a membrane protein. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.411-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Rymo L., Rhim J. S., Klein G. Morphological transformation of human keratinocytes expressing the LMP gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):447–449. doi: 10.1038/345447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuens G., de Brabander M., Nuydens R., De Mey J. The interaction between microtubules and intermediate filaments in cultured cells treated with taxol and nocodazole. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1983 Jan;7(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(83)90103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. Association of p60src with Triton X-100-resistant cellular structure correlates with morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B., Baichwal V. R. The transforming domain alone of the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus is toxic to cells when expressed at high levels. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2469–2475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2469-2475.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavathas P., Bach F. H., DeMars R. Gamma ray-induced loss of expression of HLA and glyoxalase I alleles in lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4251–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein: induction of B-cell activation antigens and membrane patch formation does not require vimentin. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4051–4054. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4051-4054.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Kopan R., Fuchs E., Sample J., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein associates with vimentin in lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2299–2308. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Wang D., Kieff E. Orientation and patching of the latent infection membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.233-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Kasamatsu H. On the electrotransfer of polypeptides from gels to nitrocellulose membranes. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;128(2):302–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90379-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludérus M. E., van Driel R. Interaction between the chemotactic cAMP receptor and a detergent-insoluble membrane residue of Dictyostelium discoideum. Modulation by guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8326–8331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. P., Staunton D., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein found in plasma membranes of transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):710–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.710-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. P., Thorley-Lawson D. Posttranslational processing of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded p63/LMP protein. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2100–2108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2100-2108.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura R., Raymond M. J., Ji I., Rebois R. V., Ji T. H. Photoaffinity labeling of the gonadotropin receptor with native, asialo, and deglycosylated choriogonadotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6327–6331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Roehr T. J. Activation of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus by cis-acting elements in the promoter-regulatory sequence and by virus-specific trans-acting components. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):431–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.431-441.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Metzenberg S. Characterization of an antigen whose cell surface expression is induced by infection with Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):800–807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.800-807.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. The truncated form of the Epstein-Barr virus latent-infection membrane protein expressed in virus replication does not transform rodent fibroblasts. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2337-2346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Larson R., Springer T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4173–4184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4173-4184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegant F. A., Blok F. J., Defize L. H., Linnemans W. A., Verkley A. J., Boonstra J. Epidermal growth factor receptors associated to cytoskeletal elements of epidermoid carcinoma (A431) cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):87–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Defize L. H., de Kroon J., van Damme H., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Ligand-induced association of epidermal growth factor receptor to the cytoskeleton of A431 cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Apr;39(4):455–465. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]