Abstract
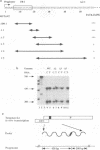
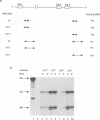
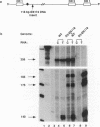
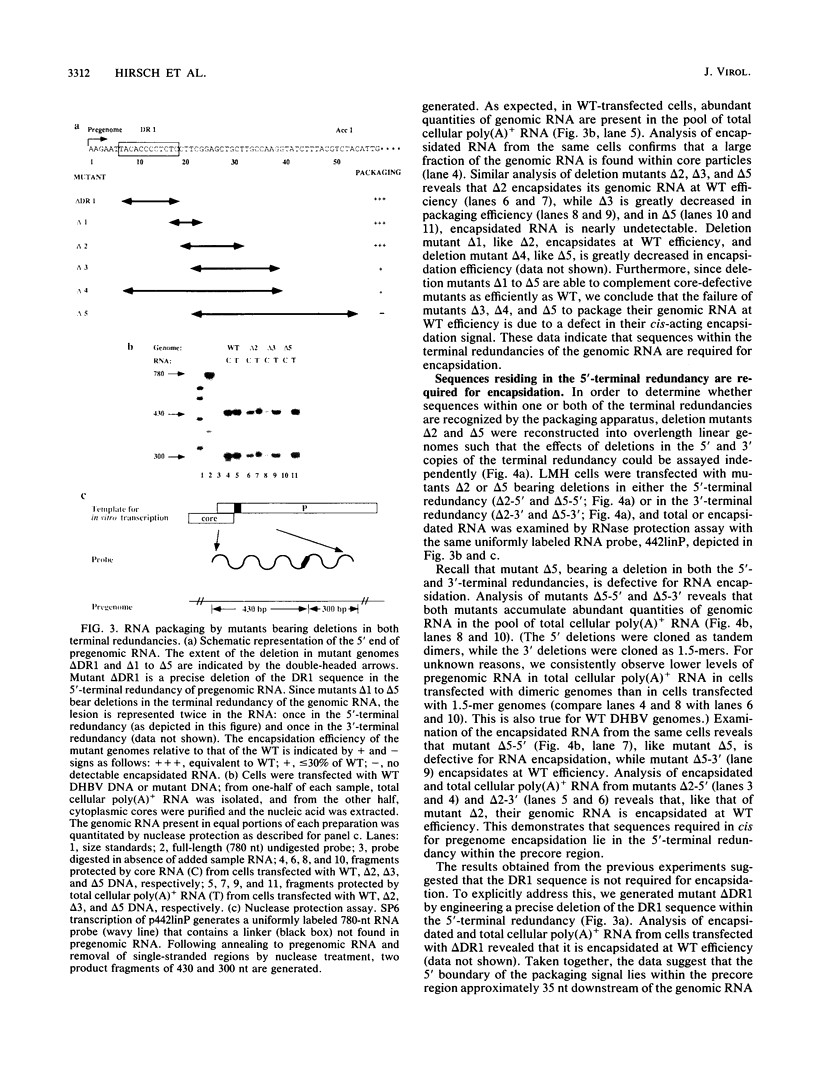
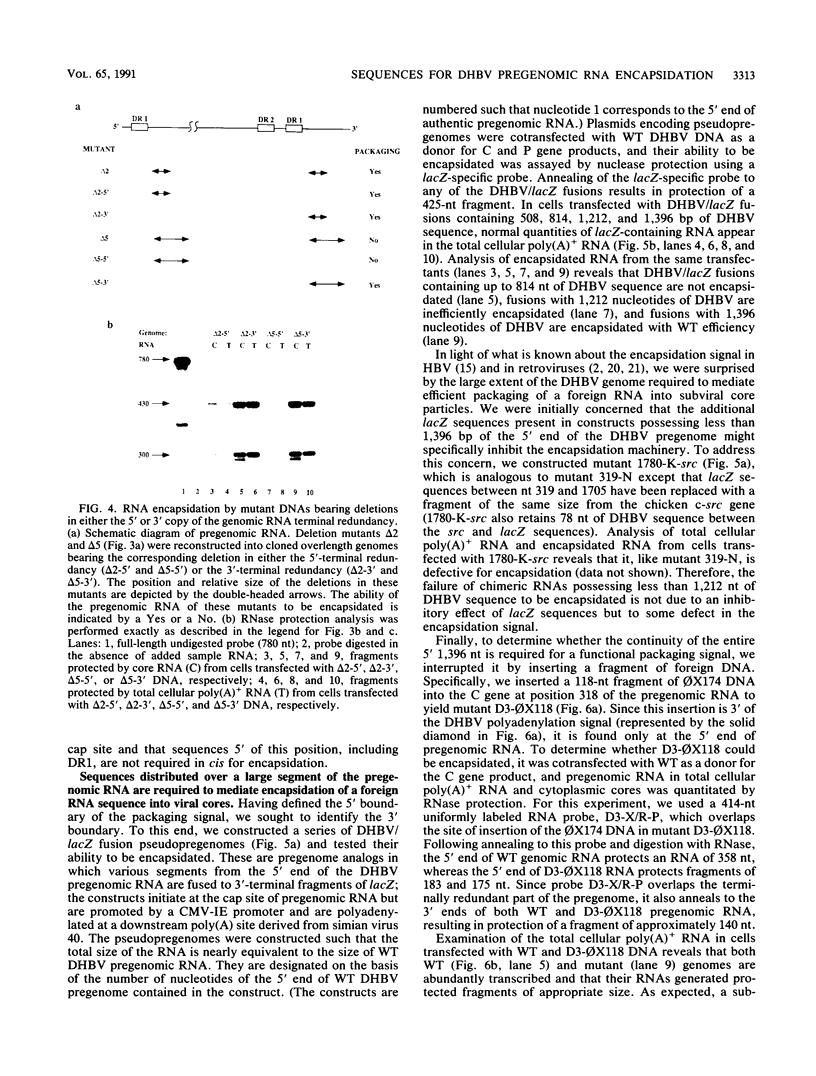
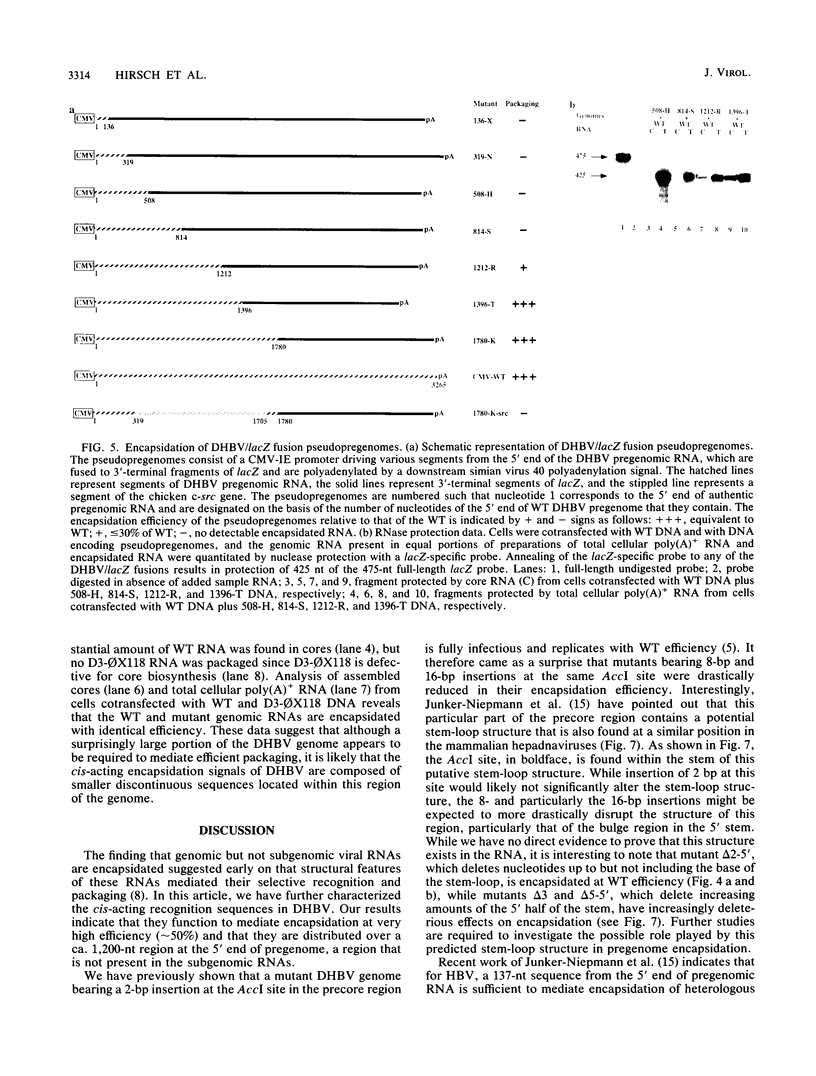
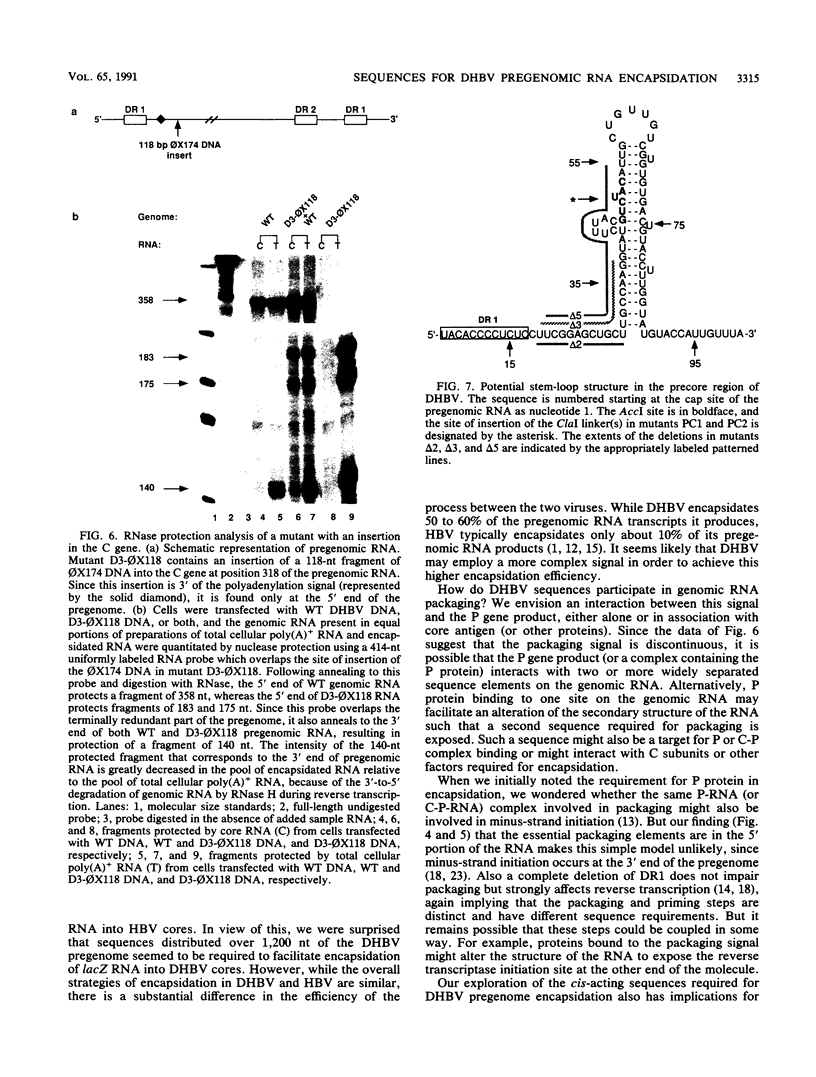
Hepadnavirus reverse transcription requires that pregenomic RNA first be selectively packaged into a cytoplasmic core particle. This process presumably requires the presence of specific recognition sequences on the pregenomic RNA. To define the cis-acting sequences required for pregenome encapsidation in the duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV), we assayed the packaging efficiency of a series of pregenomic RNA deletion mutants and hybrid DHBV/lacZ fusion transcripts. The 5' boundary of the packaging signal lies within the precore region, starting approximately 35 nucleotides from the cap site of pregenomic RNA; thus, the DR1 sequence required for proper viral DNA synthesis is not included in this signal. To define the 3' boundary of the encapsidation signal, fusion transcripts bearing foreign (lacZ) sequences fused to DHBV at different sites 3' to the pregenomic RNA start site were examined. A surprisingly large region of the DHBV genome proved to be required for packaging of such chimeras, which are efficiently encapsidated only when they contain the first 1,200 to 1,400 nucleotides of DHBV pregenomic RNA. However, mutant genomes bearing insertions within this region are packaged efficiently, making it likely that the actual recognition elements for encapsidation are smaller discontinuous sequences located within this region.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartenschlager R., Junker-Niepmann M., Schaller H. The P gene product of hepatitis B virus is required as a structural component for genomic RNA encapsidation. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5324-5332.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Palmer T. D., Gelinas R. E., Miller A. D. Evidence that the packaging signal of Moloney murine leukemia virus extends into the gag region. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1639–1646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1639-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum F., Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid assembly: primary structure requirements in the core protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3319–3330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3319-3330.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher M., Reiser W., Will H., Schaller H. Transcripts and the putative RNA pregenome of duck hepatitis B virus: implications for reverse transcription. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Enders G., Sprengel R., Peters N., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Expression of the precore region of an avian hepatitis B virus is not required for viral replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3322–3325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3322-3325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condreay L. D., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Mason W. S., Wu T. T. Efficient duck hepatitis B virus production by an avian liver tumor cell line. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3249–3258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3249-3258.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. H., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. 5'-terminal sequences influence the segregation of ground squirrel hepatitis virus RNAs into polyribosomes and viral core particles. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):35–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.35-41.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. H., Ganem D., Varmus H. Mapping the major transcripts of ground squirrel hepatitis virus: the presumptive template for reverse transcriptase is terminally redundant. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):297–308. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. C., Lavine J. E., Chang L. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as wel as for reverse transcription. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):552–555. doi: 10.1038/344552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R., Colgrove R., Ganem D. Replication of duck hepatitis B virus in two differentiated human hepatoma cell lines after transfection with cloned viral DNA. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Furtak K., Pugh J., Summers J. Synthesis of hepadnavirus particles that contain replication-defective duck hepatitis B virus genomes in cultured HuH7 cells. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):642–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.642-650.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker-Niepmann M., Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. A short cis-acting sequence is required for hepatitis B virus pregenome encapsidation and sufficient for packaging of foreign RNA. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3389–3396. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavine J., Hirsch R., Ganem D. A system for studying the selective encapsidation of hepadnavirus RNA. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4257–4263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4257-4263.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandart E., Kay A., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):782–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.782-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Baltimore D. Varying the position of a retrovirus packaging sequence results in the encapsidation of both unspliced and spliced RNAs. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):401–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.401-407.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning W. C., Mocarski E. S. Insertional mutagenesis of the murine cytomegalovirus genome: one prominent alpha gene (ie2) is dispensable for growth. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Maragos J. Identification and characterization of the woodchuck hepatitis virus origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.16-23.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kuhn C., Will H., Schaller H. Comparative sequence analysis of duck and human hepatitis B virus genomes. J Med Virol. 1985 Apr;15(4):323–333. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]