Abstract
The authors provide an overview of methods for summarizing social disparities in health using the example of lung cancer. They apply four measures of relative disparity and three measures of absolute disparity to trends in US lung cancer incidence by area-socioeconomic position and race-ethnicity from 1992 to 2004. Among females, measures of absolute and relative disparity suggested that area-socioeconomic and race-ethnic disparities increased over these 12 years but differed widely with respect to the magnitude of the change. Among males, the authors found substantial disagreement among summary measures of relative disparity with respect to the magnitude and the direction of change in disparities. Among area-socioeconomic groups, the index of disparity increased by 47% and the relative concentration index decreased by 116%, while for race-ethnicity the index of disparity increased by 36% and the Theil index increased by 13%. The choice of a summary measure of disparity may affect the interpretation of changes in health disparities. Important issues to consider are the reference point from which differences are measured, whether to measure disparity on the absolute or relative scale, and whether to weight disparity measures by population size. A suite of indicators is needed to provide a clear picture of health disparity change.
Keywords: epidemiologic methods, ethnic groups, health status disparities, lung neoplasms, socioeconomic factors
One of the overarching US public health goals is the elimination of health disparities according to race or ethnicity, education or income, disability, geographic location, and sexual orientation (1). The measurement of progress toward this goal has consequences for prioritizing efforts aimed at reducing such disparities. However, there is currently no consensus on the most appropriate methods for monitoring changes in health disparities. A number of potential summary measures of health disparity have been proposed (2–7), but there have been few systematic empirical comparisons of trends in health disparities using different summary measures. In addition, most of the previous work has focused on measuring socioeconomic disparities (8, 9), whereas little empirical work has evaluated disparity measures for nominal categories, such as race, ethnicity, or geography.
Questions about health disparity trends are usually framed in a general form, such as the following: Has disparity increased or decreased? However, this general question obscures the fact that “disparity” is a complex concept (10, 11), and estimating its magnitude may depend heavily on such questions as whether to measure absolute or relative disparity, whether to account for the size (population share) of the groups being compared, and from what reference point differences are measured (4). For example, the question of whether global economic inequality has increased or decreased depends on whether countries are weighted equally or individuals are weighted equally (12, 13). This issue has not been adequately studied with regard to monitoring health disparities and has implications for policy development to reduce disparities. If there is substantial inconsistency among disparity measures, then a deeper understanding of the methodological differences among measures is needed, and a suite of indicators may be warranted.
In this paper, we describe and empirically compare selected summary measures of health disparity. As an example, we analyzed trends in social disparities for lung cancer, which remains the leading cause of US overall cancer death and is among the top three sites of incidence in each race-ethnic group (14). A number of empirical studies have also documented social disparities in lung cancer incidence (15, 16), treatment (17, 18), survival (19), and mortality (20–22).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Measures of health disparity
Our choice of measures of health disparity was guided by a previous literature review (4) that found at least three important issues to consider in choosing a summary measure of disparity. The first is whether disparity is measured on the absolute scale (i.e., differences in rates) or relative scale (i.e., ratios of rates). The second is whether all individuals in the population are weighted equally (i.e., population-weighted measures of disparity) or weighted inversely to the population size of their social group (i.e., unweighted measures of disparity). The third issue is the choice of the reference point from which differences among subgroups are measured (e.g., population average, the best observed rate, a target rate). Here, we briefly review several potential summary measures of health disparity that differ across these dimensions (summarized in Appendix table 1), separated by whether they measure disparity on the relative or absolute scale.
Measures of relative disparity
Rate ratio
The rate ratio (RR) is probably the most frequently used measure of health disparity and is calculated as RR = y1/y2, where y1 is the health status of the least healthy group and y2 is the health status of the most healthy. Although in the context of social group comparisons the rate ratio is typically based on comparing, for example, the least socially advantaged group (e.g., the lowest socioeconomic group) with the most advantaged group, as a summary measure of health disparity as one would a measure of range. That is, at each time point it measures the ratio of the rates of the best and worst group (i.e., the relative range), regardless of their social group status. Thus, the specific groups with the best and worst rates may change over time. If there is no disparity, the rate ratio takes on a value of 1.
Index of disparity
The index of disparity (IDisp) summarizes the average difference between several group rates and a reference rate and expresses the summed differences as a proportion of the reference rate (i.e., a ratio). This measure was introduced by Pearcy and Keppel (3) and is calculated as , where yj indicates the measure of health status in the jth group, and yref is the health status indicator in the reference population. Although in principle any reference group may be chosen, typically the best group rate is used as the comparison, because that represents the rate desirable for all groups to achieve (2). We use the best group rate as the reference point and note that the group with the best rate may change over time. If an external rate is used as the reference population (e.g., the total population rate, a target rate), the differences are divided by the total number of groups compared (J) rather than by J − 1. If there is no disparity, the index of disparity takes on a value of 0.
Relative concentration index
The relative concentration index (RCI) measures the extent to which health or illness is concentrated among particular social groups. This index may be used only with ordinal social groups (i.e., those that have an inherent ranking), such as income or education. The general formula for the relative concentration index for grouped data is given by Kakwani et al. (23) as , where μ is the population average rate of health, pj is the group’s population share, yj is the group’s mean health, and Xj is the relative rank of the jth socioeconomic group, which is defined as Xj = pγ − 0.5 pj, where pγ is the cumulative share of the population up to and including group j, and pj is the share of the population in group j. Xj indicates the cumulative share of the population up to the midpoint of each group interval. One advantage of the relative concentration index is that it “reflects the socioeconomic dimension to inequalities in health” (8, p. 548). That is, when the outcome is positive (i.e., a measure of “health”), a downward health gradient (where health worsens with increasing social group rank) results in a positive relative concentration index, whereas an upward health gradient results in a negative relative concentration index. The opposite is true when the outcome is negative (i.e., a measure of “illness”). Thus, in our study, a negative relative concentration index indicates that lung cancer incidence is higher among the more disadvantaged groups. When there is no disparity, the relative concentration index is 0. It is worth noting that the relative concentration index has a specific mathematical relation with the more well-known relative index of inequality (8) and will produce similar results (4). To avoid redundancy, we do not include the relative index of inequality.
Theil index and mean log deviation
The Theil index (TI) and mean log deviation (MLD) are measures of general disproportionality developed by the economist Henri Theil (24). They summarize the disproportionality between shares of health and shares of population (expressed as a ratio on the natural logarithm scale). For grouped data, they may be written (12) as , where pj is the proportion of the population in group j, and rj is the ratio of the prevalence or rate of health in group j relative to the total rate, that is, rj = yj/μ, where yj is the rate of health in group j, and μ is the total population rate. Both measures are population weighted, are more sensitive to health differences further from the average rate (because they use the logarithm of the shares of health), and may be used for both ordinal and nominal social groups. In general, the Theil index will be somewhat more influenced by groups with high incidence ratios, whereas the mean log deviation will be somewhat more influenced by groups with large population shares (12). Both measures take on a value of 0 if there is no disparity.
Measures of absolute disparity
Rate difference
The rate difference (RD) is the absolute disparity between two health status indicators, that is, the simple arithmetic difference. It is calculated as RD = y1 − y2, where y1 and y2 are indicators of health status in the least healthy and most healthy groups, respectively. As for the rate ratio, the rate difference is often used to compare the health of less advantaged social groups with that of more advantaged groups. However, we use rate difference as a summary measure of the absolute gap between the best rate and the worst rate for a given outcome (i.e., the absolute range across all race-ethnic or socioeconomic groups), regardless of which two social groups are being compared. In this case, the rate difference will be 0 if there is no disparity.
Between-group variance
The variance summarizes all squared deviations from a population average. In the case of grouped data, this is the between-group variance (BGV), and it is calculated by squaring the differences in group rates from the population average and weighting by population size: , where pj is group j’s population size, yj is group j’s average health status, and μ is the average health status of the population. If there is no disparity, the between-group variance is 0. One way to interpret the between-group variance is as the variance that would exist in the population if each individual had the mean health of his or her social group (i.e., if there were no within-social group variation) (10). The between-group variance may be a useful indicator of absolute disparity for nominal social groups, because it weights by population group size and is sensitive to the magnitude of larger deviations from the population average because it uses a squared deviation (25).
Absolute concentration index
The absolute concentration index (ACI) measures the extent to which health or illness is concentrated among particular social groups on the absolute scale. It may only be used with ordinal social groups. It is a measure of the covariance between social rank and health, and it is derived by plotting the cumulative share of the population, ranked by social status, against the cumulative amount of ill health (i.e., the cumulative contribution of each subgroup to the mean level of health in the population). The absolute version of the concentration index is calculated by multiplying the relative concentration index by the mean of the health variable: ACI = μRCI, where RCI is the relative concentration index defined above, and μ is the mean level of health in the population. Thus, if there is no disparity (i.e., if RCI = 0), the ACI is 0.
Outcome data
To compare selected summary measures of disparity, we analyzed trends in the incidence of lung cancer from 1992 to 2004 using data from the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database (26). Because SEER data do not contain individual-level measures of socioeconomic position, we linked each case’s county of residence and the 1990 US Census to assign each case a measure of socioeconomic position based on the proportion of the county population living below the poverty line (<10, 10–14, 15–20, >20 percent), as has been done previously (27). Our measure of area-socioeconomic position therefore masks within-area individual variation in individual socioeconomic position. We obtained incidence estimates for five race-ethnic groups: non-Hispanic Whites, non-Hispanic Blacks, American Indian/Alaska Natives, Asian/Pacific Islanders, and Hispanics. Consistent with SEER guidelines for reporting race-ethnicity (28), data for Hispanics are not exclusive of Asian/Pacific Islander and American Indian/Alaska Native groups and exclude cases diagnosed in the Alaska Natives and Kentucky registries, and data for American Indian/Alaska Natives include only cases diagnosed in a contract health service delivery area. In comparing groups by race-ethnicity, it is important to note that, in order to obtain more precise incidence rates, we will inevitably mask potentially important differences between subpopulations commonly grouped together (e.g., between various American Indian tribes and between Asian and Hispanic subpopulations) (14). Because very few cases of lung cancer are diagnosed among younger individuals, we restricted our analysis to those aged 45 years or more.
Statistical analysis
To account for differences in the age distribution among area-socioeconomic and race-ethnic subgroups, we used nine age-specific rates (5-year age groups from 45–49 years to 85 years or more) and age-adjusted rates to the 2000 US standard population. For measures of disparity that rely on the use of the population average rate as the reference group (relative concentration index, absolute concentration index, Theil index, mean log deviation, between-group variance), we estimated the age-adjusted population average rate by calculating a weighted average of the subgroup-specific age-adjusted rates, with the overall proportion of each subgroup in the population as weights. This estimate will differ slightly from the age-adjusted rate for the total population. For example, in 1992 the overall age-adjusted incidence rate (i.e., ignoring race-ethnicity) was 261.5 per 100,000, and the population-weighted average of the race-ethnic-specific, age-adjusted rates was 260.1. For each gender group and year, these estimates were within 1 percent of the age-adjusted rate in the total population.
To generate estimates of precision, we used a resampling or “bootstrap” technique described previously (2, 5). Briefly, for each year, gender, and race-ethnic or socioeconomic subgroup, we used the observed age-adjusted rate and its standard error to reestimate each group’s rate 1,000 times, assuming a random normal distribution. We then calculated each measure of disparity 1,000 times and used the resulting distribution to estimate the standard error (SE) of each index. We estimated the change in each index from the beginning to the end of the period of observation and calculated a 95 percent confidence interval for this change by use of the formula to estimate the standard error of the change (2). Thus, changes in disparity for which the 95 percent confidence interval includes 0 would not be considered statistically significant with conventional criteria. However, because the indices are measured on different scales, we compared the overall change in disparity by calculating the percent change in each index from 1992 to 2004 (for the rate ratio, we calculated the percent change in the excess rate ratio). In order to graphically compare trends in each index, we plotted the percent change in each index since 1992 for each data year.
RESULTS
Incidence trends
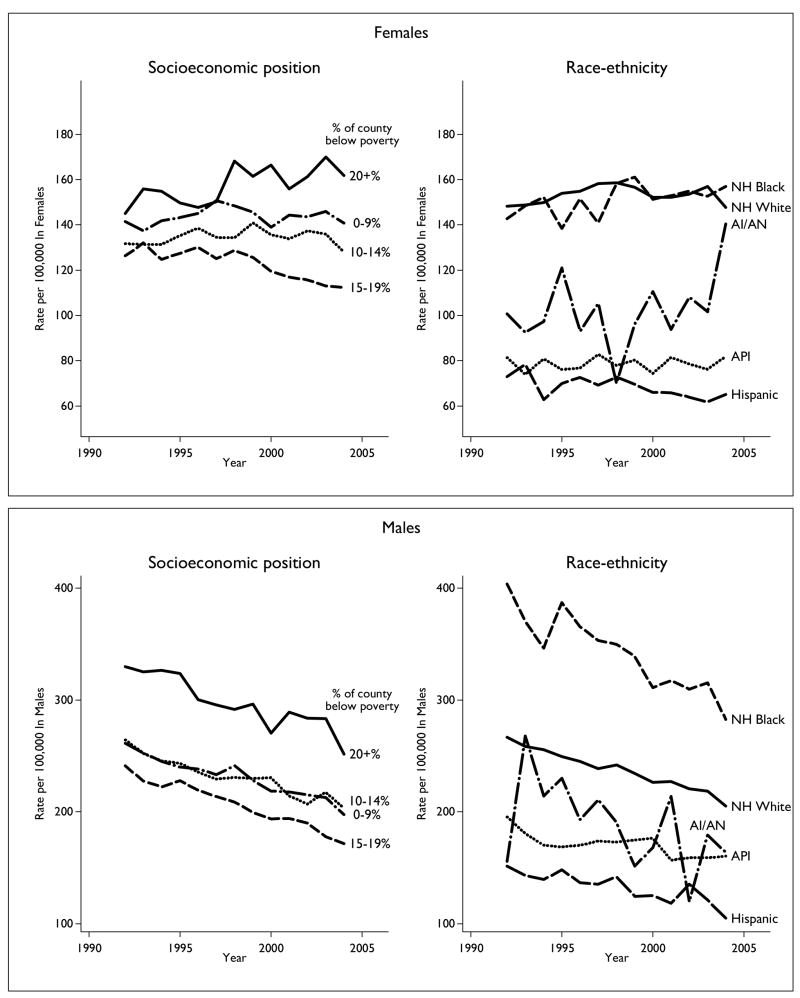
Table 1 presents age-adjusted incidence rates and population distribution for the first and last years of observation by gender, area-socioeconomic position, and race-ethnicity, as well as the percent change from 1992 to 2004. To give an overall picture of changes in the incidence of lung cancer, figure 1 shows the trends in the age-adjusted incidence of lung cancer, by gender, for social groups characterized by area-socioeconomic position (left panel) and race-ethnicity (right panel). Among males, incidence generally declined for all area-socioeconomic and race-ethnic groups, but among females the picture was more mixed, with rates decreasing among some groups (e.g., Hispanics, those living in counties with 15–19 percent of the population in poverty) and increasing among others (e.g., non-Hispanic Blacks, those living in counties with >20 percent poverty). For both females and males, there is considerably more variation in incidence by race-ethnicity than by area-socioeconomic position.
TABLE 1.
Age-adjusted (year 2000 standard) incidence of lung cancer and population distribution among those aged 45 years or more according to area-socioeconomic position and race-ethnicity, by gender, United States, 1992–2004
| 1992 | 2004 | Percent change, 1992–2004* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate | % of population | Rate | % of population | Rate | % of population | |
| Females | ||||||
| ≥20 | 126.3 | 8.8 | 112.4 | 7.7 | 11.0 | 0.1 |
| 15–19 | 131.7 | 18.3 | 127.9 | 18.6 | −2.8 | 1 |
| 10–14 | 141.4 | 45.2 | 140.8 | 46.0 | −0.5 | 1.7 |
| 0–9 | 135.6 | 45.2 | 132.0 | 46.0 | −2.7 | |
| Total | ||||||
| Males | ||||||
| ≥20 | 241.1 | 8.4 | 171.6 | 7.4 | −28.8 | −0.2 |
| 15–19 | 264.3 | 18.4 | 203.3 | 19.0 | −23.1 | 2 |
| 10–14 | 261.2 | 45.7 | 197.7 | 46.2 | −24.3 | 1.1 |
| 0–9 | 262.3 | 45.7 | 195.9 | 46.2 | −25.3 | 0.0 |
| Total | 262.3 | 100.0 | 195.9 | 100.0 | −25.3 | 0.0 |
| Race-ethnicity‡ | ||||||
| Females | ||||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 148.2 | 73.2 | 147.8 | 65.6 | −0.3 | −10.4 |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 142.8 | 8.6 | 156.9 | 9.5 | 9.9 | 10.7 |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 81.4 | 8.4 | 81.9 | 11.9 | 0.7 | 41.1 |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 100.8 | 0.5 | 140.3 | 0.7 | 39.3 | 33.2 |
| Hispanic | 72.9 | 9.3 | 65.2 | 12.3 | −10.6 | 32.9 |
| Total | 135.3 | 100.0 | 131.8 | 100.0 | −2.6 | |
| Males | ||||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 266.8 | 73.7 | 205.0 | 67.0 | −23.2 | −9.0 |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 403.5 | 7.9 | 282.6 | 8.5 | −30.0 | 7.9 |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 195.5 | 8.5 | 160.5 | 11.3 | −17.9 | 32.6 |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 155.9 | 0.6 | 163.7 | 0.7 | 5.0 | 29.7 |
| Hispanic | 151.4 | 9.4 | 104.9 | 12.5 | −30.7 | 32.9 |
| Total | 261.5 | 100.0 | 195.5 | 100.0 | −25.2 | |
Estimates for the percent change may differ slightly from that calculated directly from the table values because of rounding.
Based on the proportion of the population in poverty in 1990 in the county of residence for each incident case.
Hispanic is not mutually exclusive of Asian/Pacific Islander and American Indian/Alaska Native.
FIGURE 1.
Age-adjusted (year 2000 standard) incidence of lung cancer in those aged 45 years or more among socioeconomic (left) and race-ethnic (right) groups, by gender, United States, 1992–2004. Top panels, females; bottom panels, males. NH, non-Hispanic; AI/AN, American Indian/Alaska Native; API, Asian/Pacific Islander.
Change in area-socioeconomic disparity
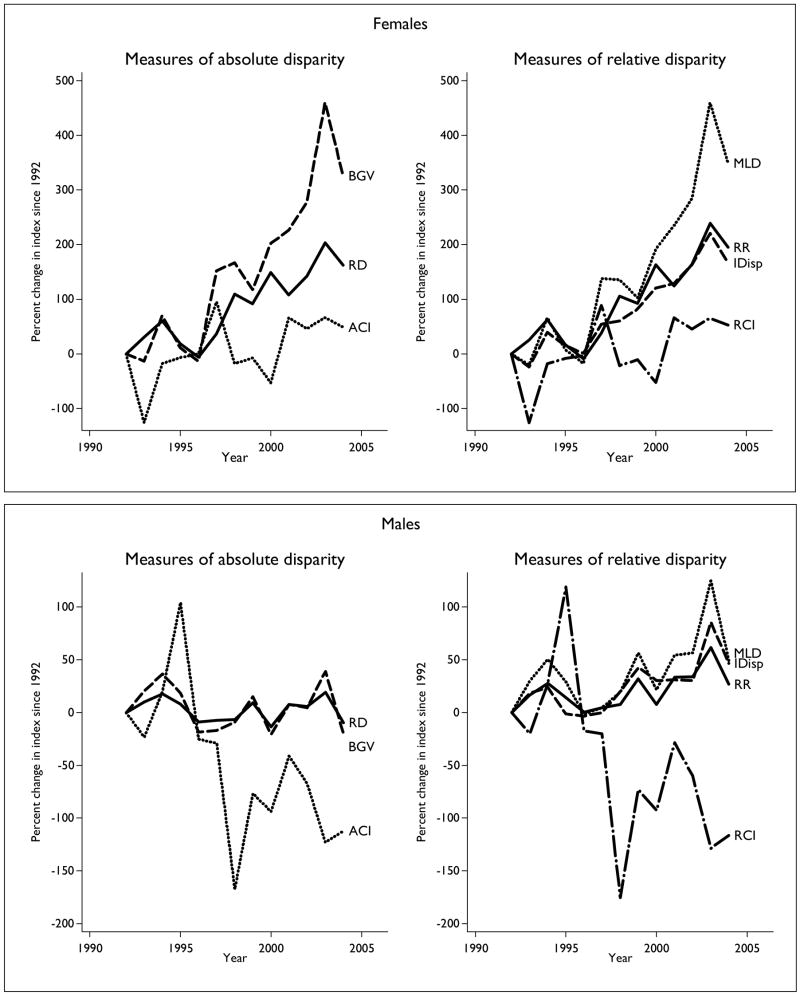
Table 2 shows the change in absolute and relative disparity among area-socioeconomic groups from 1992 to 2004, and figure 2 displays disparity trends across the entire period. Generally speaking, all of the measures of disparity suggest that area-socioeconomic disparities in lung cancer incidence are increasing among females. However, the magnitude of the increase differed widely across disparity measures, ranging from a 52.9 percent increase in the relative concentration index to a 348.7 percent increase in the mean log deviation (changes in the Theil index, not shown, were virtually identical to the mean log deviation). In addition, the two measures that are sensitive to the direction of the gradient (relative concentration index and absolute concentration index) are the only measures for which the 95 percent confidence interval includes 0. The estimated increases in disparity are smaller for these measures because, while rates among the 20 percent poverty group increased most, rates among the 15–19 percent poverty group, which is considerably larger, declined most (figure 1). Among males, the picture was less consistent, with some measures indicating that area-socioeconomic disparities have increased and some suggesting a decrease. For example, in terms of relative disparity, the index of disparity showed a statistically significant increase in area-socioeconomic disparity of 46.6 percent, while the relative concentration index decreased by 116.3 percent, suggesting that lung cancer incidence has become less concentrated among those in poor areas. In terms of absolute disparity, the rate difference and between-group variance suggest that area-socioeconomic disparity decreased by 20 percent or less, but the absolute concentration index suggests a much larger decrease of 112.1 percent.
TABLE 2.
Change in relative and absolute area-socioeconomic disparity in lung cancer incidence, United States, 1992–2004
| Measures of relative disparity | Measures of absolute disparity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate ratio | Index of disparity | Relative concentration index (× 100) | Mean log deviation(× 1,000) | Rate difference | Between-group variance | Absolute concentration index | |
| Females | |||||||
| Index, 1992 | 1.2 | 10.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 19.8 | 56.0 | 2.1 |
| Index, 2004 | 1.4 | 27.7 | 2.4 | 6.3 | 49.4 | 219.2 | 3.2 |
| Change, 1992–2004 | 0.3 | 17.3 | 0.8 | 4.8 | 30.5 | 163.5 | 1.1 |
| 95% CI* for change | 0.2, 0.4 | 8.9, 25.7 | −0.8, 2.5 | 2.3, 7.3 | 15.9, 45.2 | 76.1, 250.9 | −1.1, 3.2 |
| % change, 1992–2004† | 194.9 | 166.3 | 52.9 | 348.7 | 162.4 | 325.7 | 48.8 |
| Males | |||||||
| Index, 1992 | 1.4 | 18.4 | −0.8 | 3.5 | 89.0 | 529.5 | −2.2 |
| Index, 2004 | 1.5 | 26.7 | 0.1 | 5.1 | 79.7 | 412.7 | 0.3 |
| Change, 1992–2004 | 0.1 | 8.5 | 1.0 | 1.6 | −8.6 | −102.5 | 2.5 |
| 95% CI for change | 0.0, 0.2 | 0.4, 16.6 | −0.5, 2.5 | −0.7, 4.0 | −34.4, 17.2 | −380.0, 175.0 | −0.9, 5.9 |
| % change, 1992–2004† | 26.8 | 46.6 | −116.3 | 49.4 | −9.7 | −20.2 | −112.1 |
CI, confidence interval.
Estimates for the percent change may differ slightly from that calculated directly from the table values because of rounding.
FIGURE 2.
Percent change since 1992 in the US absolute concentration index (ACI), between-group variance (BGV), and rate difference (RD) as measures of absolute area-socioeconomic disparity (left), as well as the index of disparity (IDisp), relative concentration index (RCI), rate ratio (RR), and mean log deviation (MLD) as measures of relative area-socioeconomic disparity (right) in lung cancer incidence. Top panels, females; bottom panels, males.
Change in race-ethnic disparity
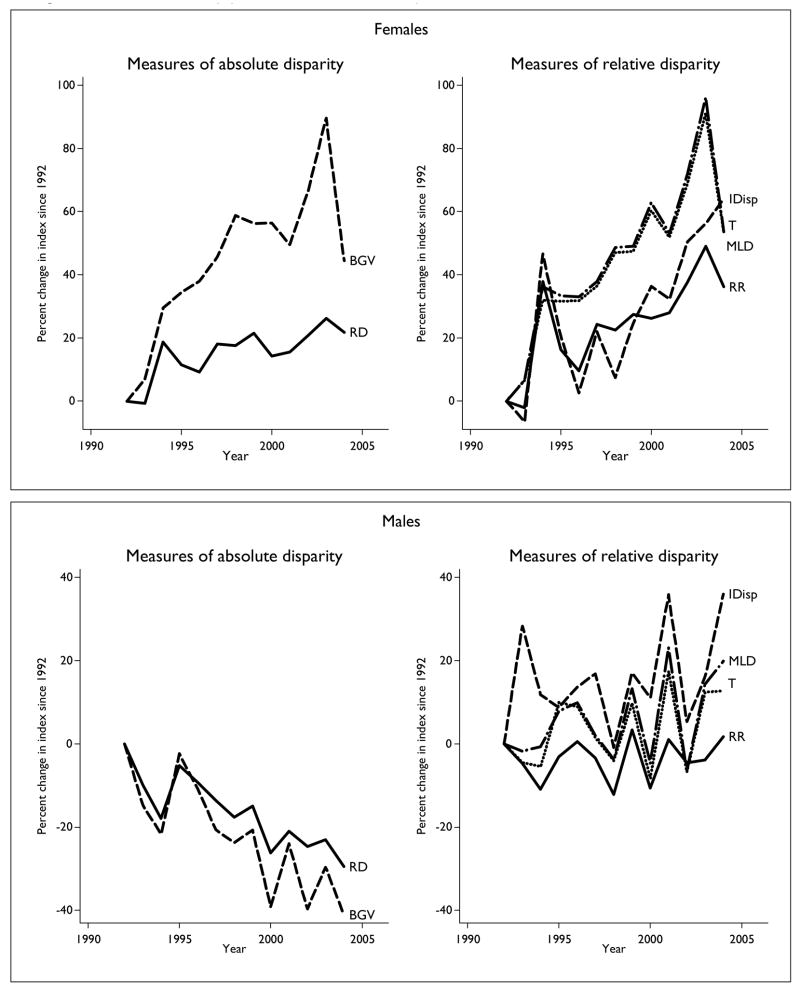
Table 3 shows the change in absolute and relative disparity among race-ethnic groups from 1992 to 2004, and figure 3 shows disparity trends. Among females, all of the measures of disparity suggest that race-ethnic disparity in lung cancer incidence has increased, but again the magnitude of change differed across measures. For example, the rate ratio increased by a nonsignificant 36.2 percent, while the Theil index and mean log deviation increased significantly by roughly 50 percent. Figure 3 also shows a lack of agreement among measures of relative disparity that differ with respect to population weighting. Among females, for example, from 1994 to 1998, the unweighted index of disparity declined while the population-weighted Theil index and mean log deviation increased, but from 2003 to 2004, the index of disparity increased and the Theil index and mean log deviation decreased sharply. Among males, the measures of relative race-ethnic disparity suggested that disparity has either increased by as little as 1.7 percent (rate ratio) or by as much as 36.0 percent (index of disparity), while the measures of absolute disparity all indicated statistically significant declines in race-ethnic disparity (table 3).
TABLE 3.
Change in relative and absolute race-ethnic disparity in lung cancer incidence, United States, 1992–2004
| Measures of relative disparity | Measures of absolute disparity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate ratio | Index of disparity | Theil index (× 1,000) | Mean log deviation (× 1,000) | Rate difference | Between-group variance | |
| Females | ||||||
| Index, 1992 | 2.1 | 66.0 | 23.7 | 27.8 | 76.9 | 749.7 |
| Index, 2004 | 2.4 | 102.4 | 36.0 | 42.2 | 93.9 | 1,073.9 |
| Change, 1992–2004 | 0.4 | 39.9 | 12.4 | 14.6 | 16.4 | 328.4 |
| 95% CI* for change | −0.2, 0.9 | −3.1, 82.8 | 5.1, 19.7 | 5.1, 24.2 | −2.1, 34.9 | 118.7, 538.1 |
| % change, 1992–2004† | 36.2 | 64.0 | 53.4 | 53.7 | 21.8 | 44.5 |
| Males | ||||||
| Index, 1992 | 2.9 | 83.5 | 23.7 | 24.7 | 260.7 | 3,192.3 |
| Index, 2004 | 2.7 | 93.6 | 26.7 | 29.4 | 177.2 | 1,876.5 |
| Change, 1992–2004 | 0.0 | 24.7 | 3.0 | 4.9 | −74.4 | −1,305.7 |
| 95% CI for change | −0.8, 0.9 | −26, 75.4 | −3.3, 9.3 | −2.4, 12.1 | −116.1, −32.7 | −1,990.5, −621 |
| % change, 1992–2004† | 1.7 | 36.0 | 12.8 | 19.9 | −29.5 | −41.1 |
CI, confidence interval.
Estimates for the percent change may differ slightly from that calculated directly from the table values because of rounding.
FIGURE 3.
Percent change since 1992 in the US between-group variance (BGV) and rate difference (RD) as measures of absolute race-ethnic disparity (left), as well as the index of disparity (IDisp), mean log deviation (MLD), Theil index (TI), and rate ratio (RR) as measures of relative race-ethnic disparity (right) in lung cancer incidence. Top panels, females; bottom panels, males.
DISCUSSION
Interpretation of trends in lung cancer disparities
On the basis of all the disparity indicators, we conclude that area-socioeconomic and race-ethnic disparities are generally increasing among females and declining for males. However, our analysis found inconsistencies among disparity measures with respect to both the magnitude and the direction of change in health disparities. In particular, among males, the index of disparity suggests that relative disparity among area-socioeconomic groups has significantly increased, but the relative concentration index suggests a significant decrease. The relative concentration index differs from the index of disparity, because it weights groups by their population size, uses the total population rate as the reference point, and is sensitive to the socioeconomic gradient. The relative concentration index thus takes account of the order of socioeconomic groups by placing additional weight on the health of the more disadvantaged (29), whereas the index of disparity does not. To see which of these differences might be responsible for the disagreement between the index of disparity and the relative concentration index, we made three separate modifications to the index of disparity by weighting it by population size, by using the population average as the reference group, and by population weighting plus using the population average as the reference group. However, even with these modifications, the index of disparity still showed 60.9, 31.0, and 7.4 percent increases in disparity, respectively (results not shown). Thus, the reason the relative concentration index demonstrated a decrease in disparity was the additional weight it places on the health of the more disadvantaged groups. The most rapid decline in incidence (a 28.8 percent decrease) among males was seen in the second-lowest area-socioeconomic group, those in counties with a poverty rate of 15–19 percent (table 1). The worst-off area-socioeconomic group (>20 percent in poverty) showed a relatively slow decline in incidence, but this group constitutes only around 8 percent of the population, so this change had less impact on the population-weighted relative concentration index.
Our example also showed disagreement about the direction of change for race-ethnic disparities. Measures of absolute disparity declined among males, but some measures of relative disparity increased. Thus, answering the question of whether race-ethnic disparities are improving depends, in part, on whether the absolute or relative scale is used. Yet even among the measures of relative disparity there was disagreement, with the index of disparity suggesting that race-ethnic disparities increased by 36 percent among males but the measures of entropy (Theil index and mean log deviation) suggesting an increase of roughly half that size. Further, despite the similarity in both magnitude and direction of change among females, the index of disparity and measures of entropy went in opposite directions during some intervals between 1992 and 2004. The measures of entropy differ from the index of disparity because they weight by population size, use the total population rate as the reference point, and measure differences using the natural logarithm. In additional analyses, we attempted to minimize these differences by recalculating the index of disparity weighted by population size and using the population average as the reference rate. With these two modifications, the index of disparity still showed a 24.2 percent increase among males (table 3), suggesting that the use of the natural logarithm in the measures of entropy is the likely reason for the difference.
Implications for monitoring health disparities
The US public health goals for 2010 include a clear commitment to reducing health disparities. A first step in this process is to develop indicators that measure change in health disparities over time. Our results indicate that the choice of the metric for summarizing social disparities in health affects estimates of the magnitude and even the direction of change in disparity, which has clear implications for how changes in disparity may be interpreted. The fact that, depending on the summary measure of disparity chosen, the same underlying data can generate evidence consistent with both increasing disparities or decreasing disparities suggests the potential for confusion and a need for greater understanding of the issues involved in choosing a summary measure of health disparity among both researchers and policymakers. The choice of disparity measure has implications not only for monitoring progress toward the goal of eliminating social disparities in health but also for other questions, such as which health outcomes show the largest disparities and whether disparities are larger across some social group categories than others.
The differences that we observed result from different conceptions of disparity on which these measures are based, and our results suggest that attempts to evaluate trends in health disparities require judgments about which conception of disparity is important for the question at hand. In particular, choices about the appropriate reference point from which to measure disparity, whether disparity should be measured in absolute or relative terms, whether to weight social groups according to the fraction of the population they represent, and whether to place additional weight on particular subgroups of interest (e.g., the poor or the least healthy) should be explicit when assessing health disparity change. These choices may be framed as methodological decisions, but they also reflect value judgments, and this is no different for measuring health inequality than for economic inequality. As Amartya Sen has noted, “In one way or another, usable measures of inequality must combine factual features with normative ones” (10, p. 3). For example, the decision of whether or not to use a population-weighted measure of disparity is a decision about how much value to place on the health of individuals: Population-weighted measures count all individuals equally, while unweighted measures count all groups equally and weight individuals inversely with respect to the size of their social group (12). Population-weighted measures therefore capture changes in the distribution of social groups over time and would serve to complement a view that regards this as an important aspect of health disparity. Alternatively, unweighted measures would complement a view that social groups with normative importance should be weighted equally, regardless of their population size. Either one of these choices may be justifiable, but because this is likely to have consequences for one’s conclusions about the magnitude of disparity, the reasons for choosing one versus another conception of disparity should be made clear at the outset.
We used the example of socioeconomic and race-ethnic trends in lung cancer incidence to compare selected measures of disparity, but our results are likely to apply in assessments of other outcomes or for other social group comparisons. Elsewhere, we have systematically compared this same set of summary measures of disparity across 22 separate analyses of cancer incidence, mortality, and risk factors and found that, in nearly half of all cases, a substantive judgment about disparity trends required a priori decisions about whether disparities should be measured in absolute or relative terms or whether to use population-weighted versus unweighted disparity measures (30).
It is important to reiterate that the methods we evaluated here are not meant as a substitute for a careful analysis of social disparities in health among particular groups or the causes of observed health disparities. Rather, they provide a cautionary note about the importance of carefully thinking through the implications of specific measures of disparity before using them to monitor health disparity trends. Quantifying health disparity requires judgments about what aspects of the distribution of health are important. Making explicit the rationale for choosing particular summary measures of disparity will allow for a more effective understanding of the evidence base used to monitor progress toward health disparity goals and objectives.
Acknowledgments
This project was carried out under contract with the National Cancer Institute (contract 263-MQ-611198).
The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the National Cancer Institute.
Abbreviations
- SE
standard error
- SEER
Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results
APPENDIX
APPENDIX TABLE 1.
Summary table of characteristics of potential health disparity measures
| Disparity measure (abbreviation) |
Absolute or relative |
Reference group |
All social groups |
Reflect socioeconomic status gradient |
Social group weighting |
Inequality aversion parameter |
Graphical analogue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate ratio (RR) | Relative | Best | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Index of disparity (IDisp) | Relative | Best | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Relative concentration index (RCI) | Relative | Average | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Theil index (TI) | Relative | Average | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Mean log deviation (MLD) | Relative | Average | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Rate difference (RD) | Absolute | Best | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Between-group variance (BGV) | Absolute | Average | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Absolute concentration index (ACI) | Absolute | Average | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: none declared.
References
- 1.US Department of Health and Human Services. Healthy People 2010: understanding and improving health. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Keppel KG, Pearcy JN, Klein RJ. Measuring progress in Healthy People 2010. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2004. (DHHS publication no. (PHS) 2004-1237) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pearcy JN, Keppel KG. A summary measure of health disparity. Public Health Rep. 2002;117:273–80. doi: 10.1016/S0033-3549(04)50161-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Harper S, Lynch J. Methods for measuring cancer disparities: a review using data relevant to Healthy People 2010 cancer-related objectives. Washington, DC: National Cancer Institute; 2006. ( http://seer.cancer.gov/publications/disparities/) [Google Scholar]
- 5.Keppel K, Pamuk E, Lynch J, et al. Methodological issues in measuring health disparities. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2005. (Vital and health statistics, series 2: data evaluation and methods research, no. 141). ( http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/series/sr_02/sr02_141.pdf) [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Regidor E. Measures of health inequalities: part 1. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2004;58:858–61. doi: 10.1136/jech.2003.015347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Regidor E. Measures of health inequalities: part 2. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2004;58:900–3. doi: 10.1136/jech.2004.023036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wagstaff A, Paci P, van Doorslaer E. On the measurement of inequalities in health. Soc Sci Med. 1991;33:545–57. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(91)90212-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mackenbach JP, Kunst AE. Measuring the magnitude of socio-economic inequalities in health: an overview of available measures illustrated with two examples from Europe. Soc Sci Med. 1997;44:757–71. doi: 10.1016/s0277-9536(96)00073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sen AK, Foster JE. On economic inequality. Oxford, United Kingdom: Clarendon Press; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Temkin LS. Inequality. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Firebaugh G. The new geography of global income inequality. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Milanovic B. Worlds apart: measuring international and global inequality. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Howe HL, Wu X, Ries LAG, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2003, featuring cancer among U.S. Hispanic/Latino populations. Cancer. 2006;107:1711–42. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Krieger N, Quesenberry C, Peng T, et al. Social class, race/ethnicity, and incidence of breast, cervix, colon, lung, and prostate cancer among Asian, black, Hispanic, and white residents of the San Francisco Bay area, 1988–92 (United States) Cancer Causes Control. 1999;10:525–37. doi: 10.1023/a:1008950210967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Haiman CA, Stram DO, Wilkens LR, et al. Ethnic and racial differences in the smoking-related risk of lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:333–42. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa033250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bach PB, Cramer LD, Warren JL, et al. Racial differences in the treatment of early-stage lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1198–205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199910143411606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shavers VL, Brown ML. Racial and ethnic disparities in the receipt of cancer treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:334–57. doi: 10.1093/jnci/94.5.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McDavid K, Tucker TC, Sloggett A, et al. Cancer survival in Kentucky and health insurance coverage. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:2135–44. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.18.2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Singh GK, Miller BA, Hankey BF. Changing area socioeconomic patterns in U.S. cancer mortality, 1950–1998: part II—lung and colorectal cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:916–25. doi: 10.1093/jnci/94.12.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Steenland K, Henley J, Thun M. All-cause and cause-specific death rates by educational status for two million people in two American Cancer Society cohorts, 1959–1996. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;156:11–21. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwf001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Devesa SS, Grauman DJ, Blot WJ, et al. Cancer surveillance series: changing geographic patterns of lung cancer mortality in the United States, 1950 through 1994. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91:1040–50. doi: 10.1093/jnci/91.12.1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kakwani N, Wagstaff A, van Doorslaer E. Socioeconomic inequalities in health: measurement, computation, and statistical inference. J Econom. 1997;77:87–103. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Theil H. Economics and information theory. Amsterdam, Netherlands: North-Holland; 1967. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chakravarty SR. The variance as a subgroup decomposable measure of inequality. Soc Indic Res. 2001;53:79–95. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Surveillance Research Program, National Cancer Institute. SEER*stat software, version 6.2.5. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2006. ( www.Seer.Cancer.Gov/seerstat) [Google Scholar]
- 27.Singh GK, Miller BA, Hankey BF, et al. NCI Cancer Surveillance Monograph Series, no. 4. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2003. Area socioeconomic variations in U.S. cancer incidence, mortality, stage, treatment, and survival, 1975–1999. (NIH publication no. 03-5417). ( http://seer.cancer.gov/publications/ses/) [Google Scholar]
- 28.National Cancer Institute. Race recode changes. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2007. ( http://seer.cancer.gov/seerstat/variables/seer/yr1973_2004/race_ethnicity/) [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wagstaff A. Inequality aversion, health inequalities and health achievement. J Health Econ. 2002;21:627–41. doi: 10.1016/s0167-6296(02)00006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Harper S, Lynch J. Selected comparisons of measures of health disparities using databases containing data relevant to Healthy People 2010 cancer-related goals. Washington, DC: National Cancer Institute; (in press) [Google Scholar]