Abstract
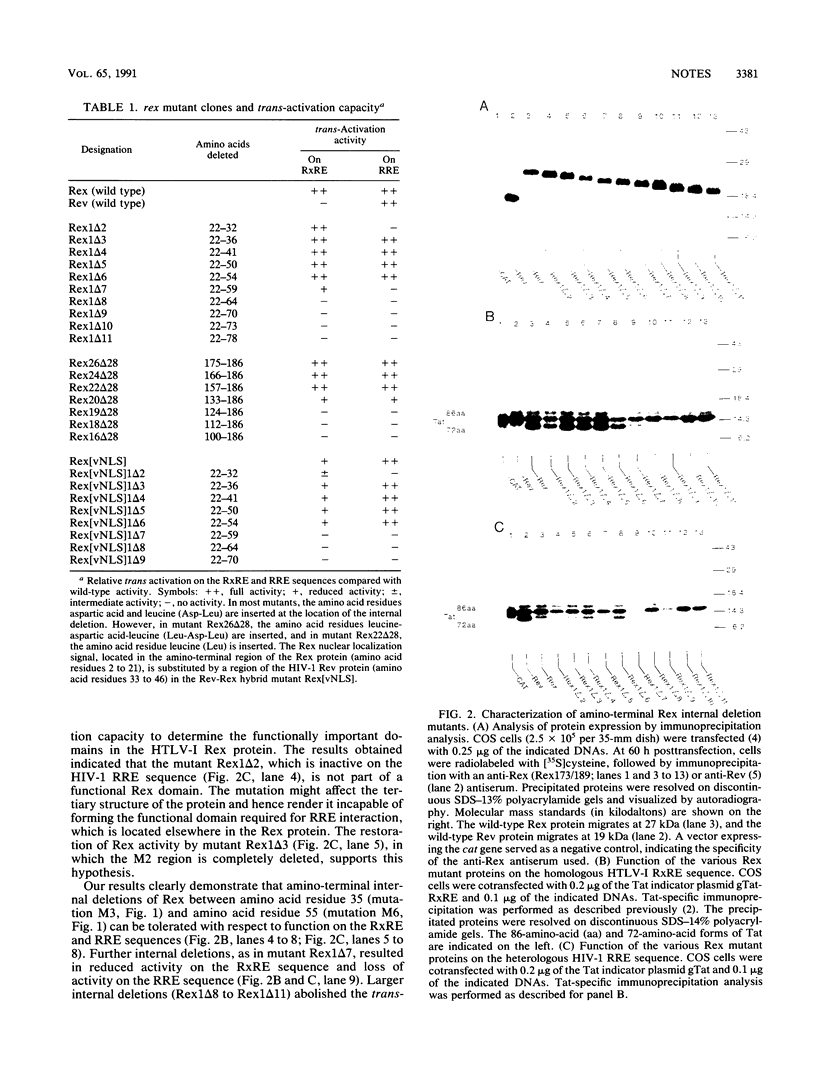
Expression of the human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) rex gene is a prerequisite for the expression of the retroviral structural proteins. We have generated internal deletion mutants of this 27-kDa nucleolar trans-acting gene product to define functional domains in the Rex protein. The phenotype of the various mutant proteins was tested on the homologous HTLV-I rex response element sequence and the heterologous human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) rev response element sequence. Our results indicate that a region between amino acid residues 55 and 132 in the 189-amino-acid Rex protein is required for Rex-mediated trans activation on both retroviral response element sequences. In addition, substitution of the Rex nuclear localization signal by a sequence of the HIV-1 rev gene product targets the Rex protein to the correct subcellular compartment required for Rex function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed Y. F., Hanly S. M., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Structure-function analyses of the HTLV-I Rex and HIV-1 Rev RNA response elements: insights into the mechanism of Rex and Rev action. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1014–1022. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein S., Pirker F. P., Hofer L., Zimmermann K., Bachmayer H., Böhnlein E., Hauber J. Transdominant repressors for human T-cell leukemia virus type I rex and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 rev function. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.81-88.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. Identification of sequences important in the nucleolar localization of human immunodeficiency virus Rev: relevance of nucleolar localization to function. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):881–885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.881-885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Hauber J., Campbell K., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. Subcellular localization of the human immunodeficiency virus trans-acting art gene product. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2498–2501. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2498-2501.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly T. J., Cook K. S., Gray G. S., Maione T. E., Rusche J. R. Specific binding of HIV-1 recombinant Rev protein to the Rev-responsive element in vitro. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):816–819. doi: 10.1038/342816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton E. T., Powell D. M., Dayton A. I. Functional analysis of CAR, the target sequence for the Rev protein of HIV-1. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1625–1629. doi: 10.1126/science.2688093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon P. J., Nelbock P., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. Function of the human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 Rev proteins is dependent on their ability to interact with a structured region present in env gene mRNA. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4428–4437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4428-4437.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Derse D., Athanassopoulos A., Campbell M., Pavlakis G. N. Cross-activation of the Rex proteins of HTLV-I and BLV and of the Rev protein of HIV-1 and nonreciprocal interactions with their RNA responsive elements. New Biol. 1989 Dec;1(3):318–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Cladaras C., Copeland T., Pavlakis G. N. rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects the stability and transport of the viral mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Felber B. K., Cladaras C., Athanassopoulos A., Tse A., Pavlakis G. N. The rev (trs/art) protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects viral mRNA and protein expression via a cis-acting sequence in the env region. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1265–1274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1265-1274.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarskjöld M. L., Heimer J., Hammarskjöld B., Sangwan I., Albert L., Rekosh D. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus env expression by the rev gene product. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1959-1966.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly S. M., Rimsky L. T., Malim M. H., Kim J. H., Hauber J., Duc Dodon M., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Comparative analysis of the HTLV-I Rex and HIV-1 Rev trans-regulatory proteins and their RNA response elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1534–1544. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 regulator of virion expression (Rev) protein binds to an RNA stem-loop structure located within the Rev response element region. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90671-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka M., Inoue J., Yoshida M., Seiki M. Post-transcriptional regulator (rex) of HTLV-1 initiates expression of viral structural proteins but suppresses expression of regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):519–523. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02840.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Nagata K., Hanaoka M., Nakai M., Matsumoto T., Kinoshita K. I., Shirakawa S., Miyoshi I. Adult T-cell leukemia: antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Seiki M., Yoshida M. The second pX product p27 chi-III of HTLV-1 is required for gag gene expression. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Yoshida M., Seiki M. Transcriptional (p40x) and post-transcriptional (p27x-III) regulators are required for the expression and replication of human T-cell leukemia virus type I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3653–3657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh M., Inoue J., Toyoshima H., Akizawa T., Higashi M., Yoshida M. HTLV-1 rex and HIV-1 rev act through similar mechanisms to relieve suppression of unspliced RNA expression. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1275–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa T., Seiki M., Iwashita S., Imagawa K., Shimizu F., Yoshida M. p27x-III and p21x-III, proteins encoded by the pX sequence of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8359–8363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota S., Siomi H., Satoh T., Endo S., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Functional similarity of HIV-I rev and HTLV-I rex proteins: identification of a new nucleolar-targeting signal in rev protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90767-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazinski D., Grzadzielska E., Das A. Sequence-specific recognition of RNA hairpins by bacteriophage antiterminators requires a conserved arginine-rich motif. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90882-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Fenrick R., Cullen B. R. Immunodeficiency virus rev trans-activator modulates the expression of the viral regulatory genes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):181–183. doi: 10.1038/335181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Tiley L. S., McCarn D. F., Rusche J. R., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires binding of the Rev trans-activator to its RNA target sequence. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90670-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosaka T., Siomi H., Adachi Y., Ishibashi M., Kubota S., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Nucleolar targeting signal of human T-cell leukemia virus type I rex-encoded protein is essential for cytoplasmic accumulation of unspliced viral mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9798–9802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Nelbock P., Cochrane A. W., Rosen C. A. Secondary structure is the major determinant for interaction of HIV rev protein with RNA. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):845–848. doi: 10.1126/science.2406903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins A., Cochrane A. W., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional characterization of the human immunodeficiency virus rev protein. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(3):256–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Mier J. W., Woods A. M., Gallo R. C. T-cell lines established from human T-lymphocytic neoplasias by direct response to T-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6815–6819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsky L., Dodon M. D., Dixon E. P., Greene W. C. Trans-dominant inactivation of HTLV-I and HIV-1 gene expression by mutation of the HTLV-I Rex transactivator. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):453–456. doi: 10.1038/341453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsky L., Hauber J., Dukovich M., Malim M. H., Langlois A., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Functional replacement of the HIV-1 rev protein by the HTLV-1 rex protein. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):738–740. doi: 10.1038/335738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Inoue J., Hidaka M., Yoshida M. Two cis-acting elements responsible for posttranscriptional trans-regulation of gene expression of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7124–7128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Shida H., Nam S. H., Nosaka T., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Sequence requirements for nucleolar localization of human T cell leukemia virus type I pX protein, which regulates viral RNA processing. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Itoh M., Inoue J., Seiki M., Takaku F., Yoshida M. Secondary structure of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 rex-responsive element is essential for rex regulation of RNA processing and transport of unspliced RNAs. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2825–2832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2825-2832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Mohammed S., Chinnadurai G. Functional domains of the HIV-1 rev gene required for trans-regulation and subcellular localization. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90228-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Miyoshi I., Hinuma Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Sequence-specific RNA binding by the HIV-1 Rev protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):714–716. doi: 10.1038/342714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]