Abstract
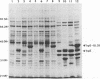
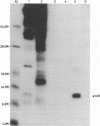
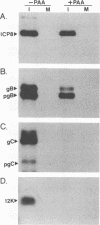
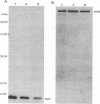
The UL35 open reading frame (ORF) of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) has been predicted from DNA sequence analysis to encode a small polypeptide with a molecular weight of 12,095. We have investigated the protein product of the UL35 ORF by using a trpE-UL35 gene fusion to produce a corresponding fusion protein in Escherichia coli. The TrpE-UL35 chimeric protein was subsequently isolated and used as a source of immunogen for the production of rabbit polyclonal antiserum directed against the UL35 gene product. The TrpE-UL35 antiserum was found to recognize a 12-kDa protein which was specifically present in HSV-1-infected cells. By utilizing the TrpE-UL35 antiserum, the kinetics of synthesis of the UL35 gene product was examined, and these studies indicate that UL35 is expressed as a gamma 2 (true late) gene. The 12-kDa protein recognized by the TrpE-UL35 antiserum was associated with purified HSV-1 virions and type A and B capsids, suggesting that the UL35 ORF may encode the 12-kDa capsid protein variably designated p12, NC7, or VP26. To confirm this assignment, immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting studies were performed to demonstrate that the TrpE-UL35 antiserum reacts with the same polypeptide as an antiserum directed against the purified p12 capsid protein (anti-NC7) (G.H. Cohen, M. Ponce de Leon, H. Diggelmann, W.C. Lawrence, S.K. Vernon, and R.J. Eisenberg, J. Virol. 34:521-531, 1980). Furthermore, the anti-NC7 serum was also found to react with the TrpE-UL35 chimeric protein isolated from E. coli, providing additional evidence that the UL35 gene encodes p12. On the basis of these studies, we conclude that UL35 represents a true late gene which encodes the 12-kDa capsid protein of HSV-1.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker T. S., Newcomb W. W., Booy F. P., Brown J. C., Steven A. C. Three-dimensional structures of maturable and abortive capsids of equine herpesvirus 1 from cryoelectron microscopy. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):563–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.563-573.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss G. J., Marsden H. S., Hay J. Herpes simplex virus proteins: DNA-binding proteins in infected cells and in the virus structure. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):124–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Hunter T. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus src gene products synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):551–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.551-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair E. D., Honess R. W. DNA-binding proteins specified by herpesvirus saimiri. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2697–2715. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone D. R., Courtney R. J. A temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1 defective in the synthesis of the major capsid polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):17–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booy F. P., Newcomb W. W., Trus B. L., Brown J. C., Baker T. S., Steven A. C. Liquid-crystalline, phage-like packing of encapsidated DNA in herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90324-r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. K., Batterson W., Roizman B. Identification and genetic mapping of a herpes simplex virus capsid protein that binds DNA. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):645–648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.645-648.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassai E. N., Sarmiento M., Spear P. G. Comparison of the virion proteins specified by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1327–1331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1327-1331.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Long D., Eisenberg R. J. Synthesis and processing of glycoproteins gD and gC of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):429–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.429-439.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Ponce de Leon M., Diggelmann H., Lawrence W. C., Vernon S. K., Eisenberg R. J. Structural analysis of the capsid polypeptides of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):521–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.521-531.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Courtney R. J. Virus-specific glycoproteins associated with the nuclear fraction of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):594–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.594-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Cohen G., Eisenberg R., Long D., Wagner E. Direct demonstration that the abundant 6-kilobase herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA mapping between 0.23 and 0.27 map units encodes the major capsid protein VP5. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.287-292.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Preparation and characterization of specific antisera to individual glycoprotein antigens comprising the major glycoprotein region of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):902–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.902-917.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flannery V. L., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. Expression of an early, nonstructural antigen of herpes simplex virus in cell transformed in vitro by herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.284-291.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 8. Characterization and composition of multiple capsid forms of subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1044–1052. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1044-1052.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Knipe D. M. Transcriptional control of herpesvirus gene expression: gene functions required for positive and negative regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich L. D., Rixon F. J., Parris D. S. Kinetics of expression of the gene encoding the 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):137–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.137-147.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. A specific 15-bp TATA box promoter element is required for expression of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):40–53. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Otal T. M., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Transcriptional control signals of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) gene lie within bases -34 to +124 relative to the 5' terminus of the mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3652–3666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K. W., Kaerner H. C. Virus-specific basic phosphoproteins associated with herpes simplex virus type a (HSV-1) particles and the chromatin of HSV-1-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1980 Feb;46(2):405–414. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Irmiere A., Gibson W. Primate cytomegalovirus assembly: evidence that DNA packaging occurs subsequent to B capsid assembly. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C. Structure of the herpes simplex virus capsid: effects of extraction with guanidine hydrochloride and partial reconstitution of extracted capsids. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):613–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.613-620.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C. Use of Ar+ plasma etching to localize structural proteins in the capsid of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4697–4702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4697-4702.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Courtney R. J. Polypeptide synthesized in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected HEp-2 cells. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Watson D. H. Some structural antigens of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):167–178. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Coates J. A., Rixon F. J. Identification and characterization of a herpes simplex virus gene product required for encapsidation of virus DNA. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1056–1064. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1056-1064.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., Davison M. D., Davison A. J. Identification of the genes encoding two capsid proteins of herpes simplex virus type 1 by direct amino acid sequencing. J Gen Virol. 1990 May;71(Pt 5):1211–1214. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-5-1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrag J. D., Prasad B. V., Rixon F. J., Chiu W. Three-dimensional structure of the HSV1 nucleocapsid. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90587-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton L. S., Pensiero M. N., Jenkins F. J. Identification and characterization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 protein encoded by the UL37 open reading frame. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6101–6109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6101-6109.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman G., Bachenheimer S. L. Characterization of intranuclear capsids made by ts morphogenic mutants of HSV-1. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90288-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. L., Sandri-Goldin R. M. Evidence that transcriptional control is the major mechanism of regulation for the glycoprotein D gene in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1474–1477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1474-1477.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildy P. Herpesvirus. Intervirology. 1986;25(3):117–140. doi: 10.1159/000149666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yei S. P., Chowdhury S. I., Bhat B. M., Conley A. J., Wold W. S., Batterson W. Identification and characterization of the herpes simplex virus type 2 gene encoding the essential capsid protein ICP32/VP19c. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1124–1134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1124-1134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]