Abstract
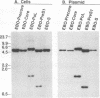
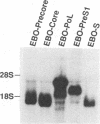
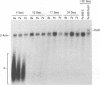
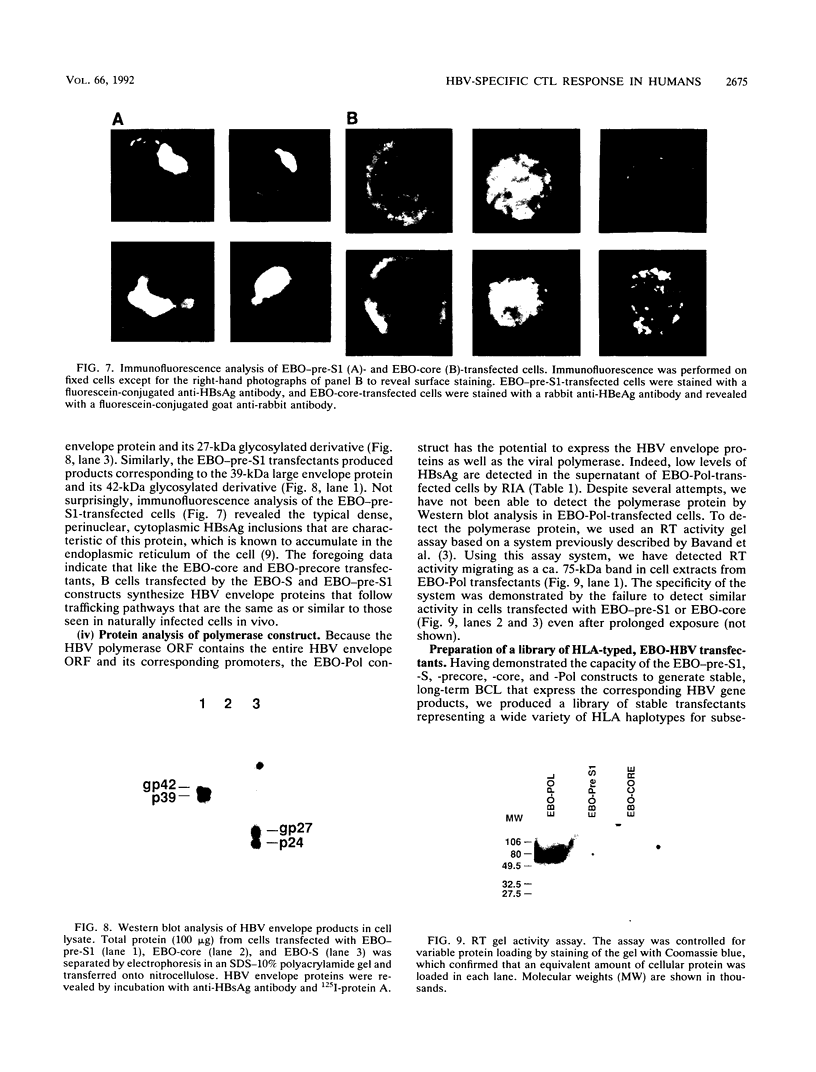
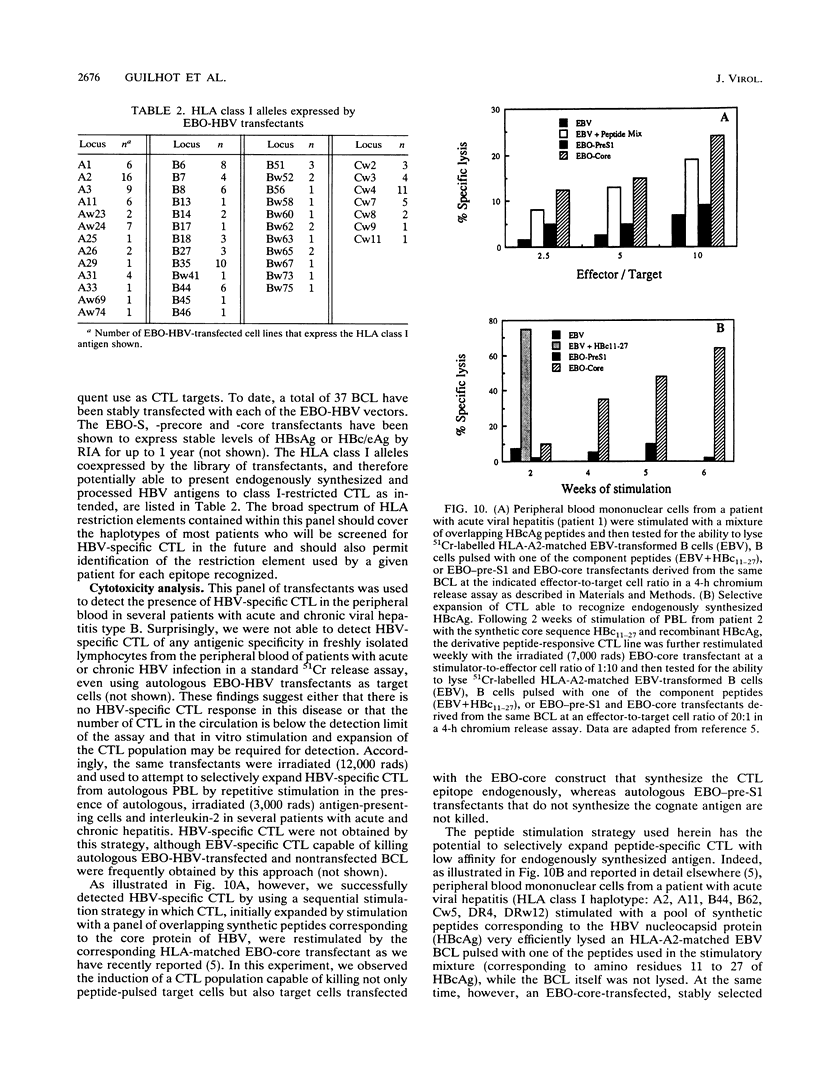
To analyze the hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific cytotoxic T-cell (CTL) response during acute and chronic viral hepatitis, target cells that express HBV-encoded antigens in the context of the appropriate HLA restriction element must be available for each subject studied. Since HBV is not infectious for human cells in vitro, such target cells must be produced by DNA-mediated gene transfer into cultured human primary cells or cell lines. For this purpose, we have developed a panel of Epstein-Barr virus-based episomal expression vectors containing each of the HBV open reading frames under the transcriptional control of the simian virus 40 early promoter. Transfection of Epstein-Barr virus-immortalized B-cell lines with this panel of recombinants consistently leads to stable expression of the HBV envelope, nucleocapsid, and polymerase proteins. The HBV X gene product is transiently expressed following transfection, but stable expression of this protein cannot be maintained on a long-term basis. To assess the suitability of this system for the identification of HBV-specific CTL in humans, a panel of EBO-HBV transfectants of defined HLA haplotype was used to monitor the HBV-specific CTL response in a patient with acute viral hepatitis type B. Transfectants that stably express the HBV nucleocapsid (core) antigen were found to serve as excellent targets for the detection of HLA class I-restricted CTL that recognize endogenously synthesized HBV core antigen in this patient; they were also successfully used to stimulate the specific expansion of these CTL in vitro.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. A., Damico C. A., Wieties K. M., Hansen T. H., Connolly J. M. Correlation between CD8 dependency and determinant density using peptide-induced, Ld-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):849–858. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki K., Miyazaki J., Hino O., Tomita N., Chisaka O., Matsubara K., Yamamura K. Expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):207–211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavand M. R., Laub O. Two proteins with reverse transcriptase activities associated with hepatitis B virus-like particles. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):626–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.626-628.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P. Hepatitis B virus. The major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1988 May 15;61(10):1942–1956. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880515)61:10<1942::aid-cncr2820611003>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertoletti A., Ferrari C., Fiaccadori F., Penna A., Margolskee R., Schlicht H. J., Fowler P., Guilhot S., Chisari F. V. HLA class I-restricted human cytotoxic T cells recognize endogenously synthesized hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10445–10449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield V., Emanuel J. R., Spickofsky N., Levenson R., Margolskee R. F. Ouabain-resistant mutants of the rat Na,K-ATPase alpha 2 isoform identified by using an episomal expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1367–1372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Curtiss L. K., Jensen F. C. Physiologic concentrations of normal human plasma lipoproteins inhibit the immortalization of peripheral B lymphocytes by the Epstein-Barr virus. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):329–336. doi: 10.1172/JCI110260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Filippi P., McLachlan A., Milich D. R., Riggs M., Lee S., Palmiter R. D., Pinkert C. A., Brinster R. L. Expression of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide inhibits hepatitis B surface antigen secretion in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):880–887. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.880-887.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
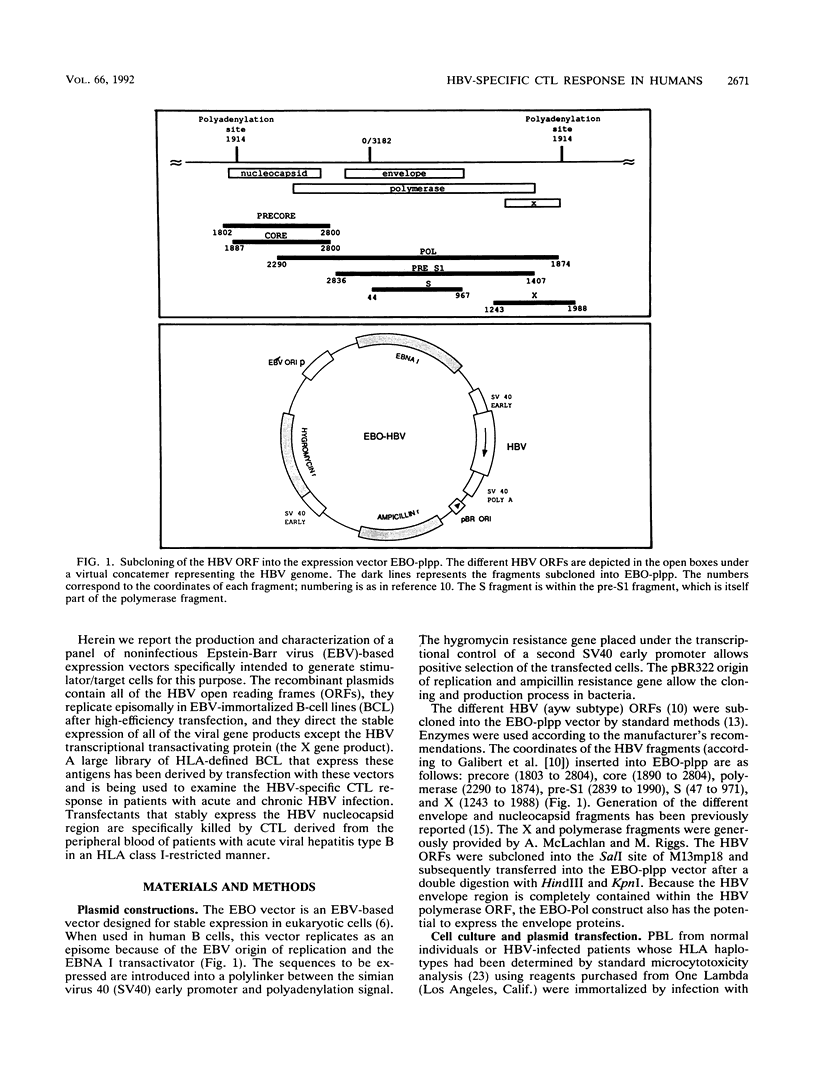
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Alexander H., Shih J. W., Purcell R. H., Dapolito G., Engle R., Green N., Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A. Chemically synthesized peptides of hepatitis B surface antigen duplicate the d/y specificities and induce subtype-specific antibodies in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2365–2369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolskee R. F., Kavathas P., Berg P. Epstein-Barr virus shuttle vector for stable episomal replication of cDNA expression libraries in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2837–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
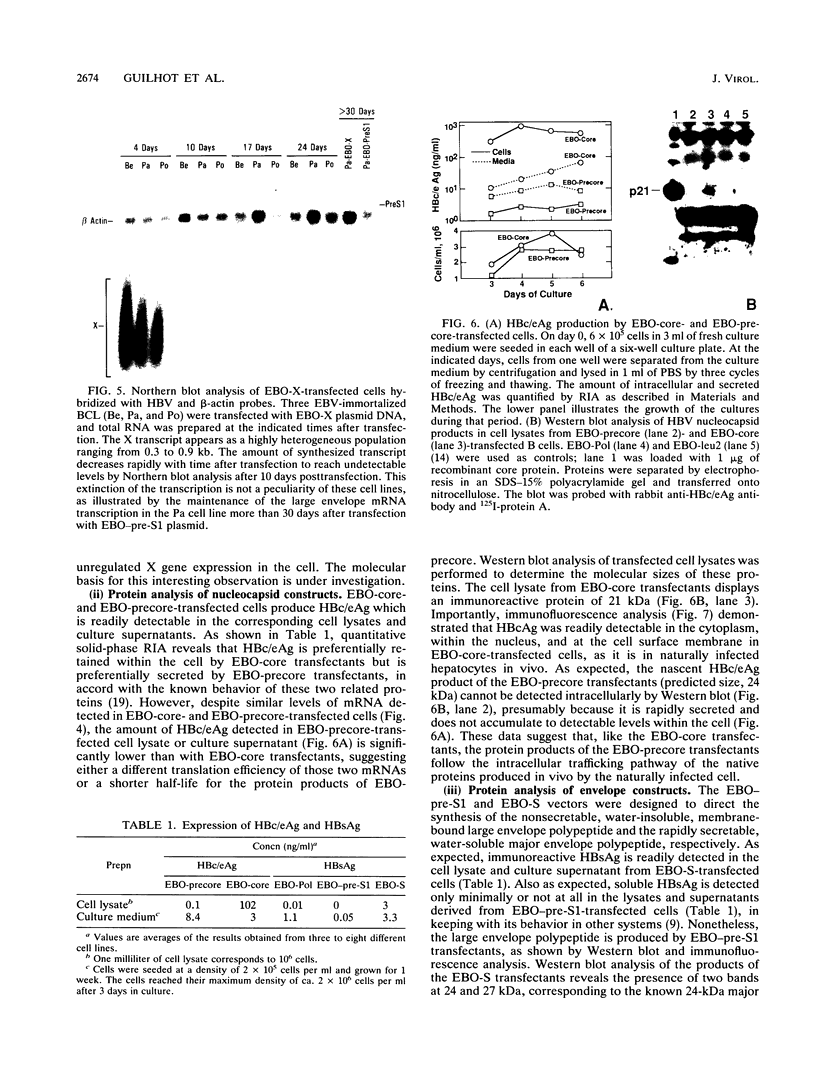
- McLachlan A., Milich D. R., Raney A. K., Riggs M. G., Hughes J. L., Sorge J., Chisari F. V. Expression of hepatitis B virus surface and core antigens: influences of pre-S and precore sequences. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):683–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.683-692.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M. U., Bortolotti F., Pontisso P., Rondanelli E. G., Williams R., Realdi G., Alberti A., Eddleston A. L. Definition of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific target antigens recognized by cytotoxic T cells in acute HBV infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 May;68(2):242–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M., Vergani G. M., Alberti A., Vergani D., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Specificity of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: evidence that T cells are directed against HBV core antigen expressed on hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2773–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama T., Guilhot S., Klopchin K., Moss B., Pinkert C. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Kanagawa O., Chisari F. V. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatocellular injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):361–364. doi: 10.1126/science.1691527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Laub O., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus gene function: the precore region targets the core antigen to cellular membranes and causes the secretion of the e antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1578–1582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penna A., Chisari F. V., Bertoletti A., Missale G., Fowler P., Giuberti T., Fiaccadori F., Ferrari C. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize an HLA-A2-restricted epitope within the hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid antigen. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1565–1570. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Schaller H. The secretory core protein of human hepatitis B virus is expressed on the cell surface. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5399–5404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5399-5404.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Mullins J. I., Essex M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Bernoco D., Park M. S., Ozturk G., Iwaki Y. Microdroplet testing for HLA-A, -B, -C, and -D antigens. The Phillip Levine Award Lecture. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;69(2):103–120. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]