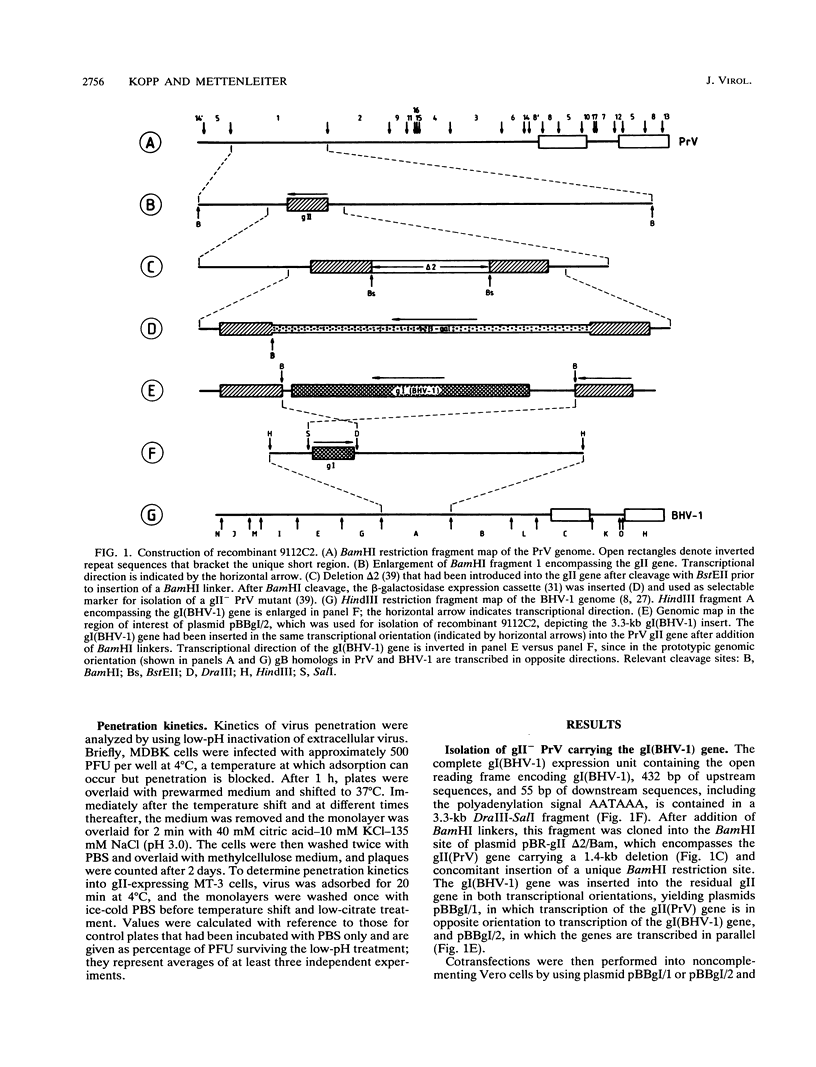
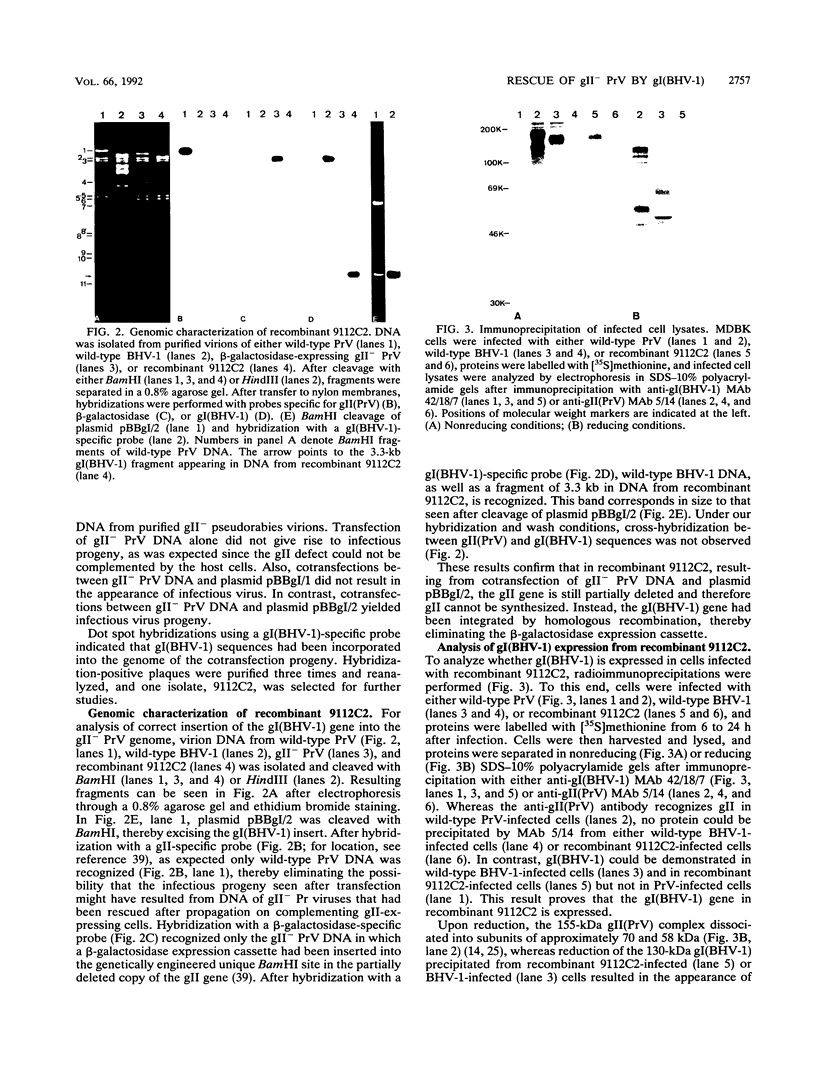
Abstract
Glycoproteins homologous to glycoprotein B (gB) of herpes simplex virus constitute the most highly conserved group of herpesvirus glycoproteins. This strong conservation of amino acid sequences might be indicative of a common functional role. Indeed, gB homologs have been implicated in the processes of viral entry and virus-mediated cell-cell fusion. Recently, we showed that pseudorabies virus (PrV) lacking the essential gB-homologous glycoprotein gII could be propagated on a cell line expressing the gB homolog of bovine herpesvirus 1, gI(BHV-1), leading to a phenotypic complementation of the gII defect (I. Rauh, F. Weiland, F. Fehler, G. Keil, and T.C. Mettenleiter, J. Virol. 65:621-631, 1991). However, this pseudotypic virus could still replicate only on complementing cell lines, thereby limiting experimental approaches to analyze the effects of the gB exchange in detail. We describe here the construction and isolation of a PrV recombinant, 9112C2, that lacks gII(PrV) but instead stably carries and expresses the gene encoding gI(BHV-1). The recombinant is able to replicate on noncomplementing cells with growth kinetics and final titers similar to those of its gII-positive wild-type PrV parent. Neutralization tests and immunoprecipitation analyses demonstrated incorporation of gI(BHV-1) into 9112C2 virions with concomitant absence of gII(PrV). Analysis of in vitro host ranges of wild-type PrV, BHV-1, and recombinant 9112C2 showed that in cells of pig, rabbit, canine, monkey, or human origin, the plating efficiency of 9112C2 was similar to that of its PrV parent. Exchange of gII(PrV) for gI(BHV-1) in recombinant 9112C2 or by phenotypic complementation of gII- PrV propagated on gI(BHV-1)-expressing cell lines resulted in penetration kinetics intermediate between those of wild-type PrV and BHV-1. In conclusion, we report the first isolation of a viral recombinant in which a lethal glycoprotein mutation has been rescued by a homologous glycoprotein of a different herpesvirus. Our data show that in gII- PrV, gI(BHV-1) in vitro fully complements the lethal defect associated with lack of gII(PrV). These results conclusively demonstrate that gI(BHV-1) in a PrV background can execute all essential functions normally provided by gII(PrV). They also indicate that the origin of gB-homologous glycoproteins influences the penetration kinetics of herpesviruses.
Full text
PDF


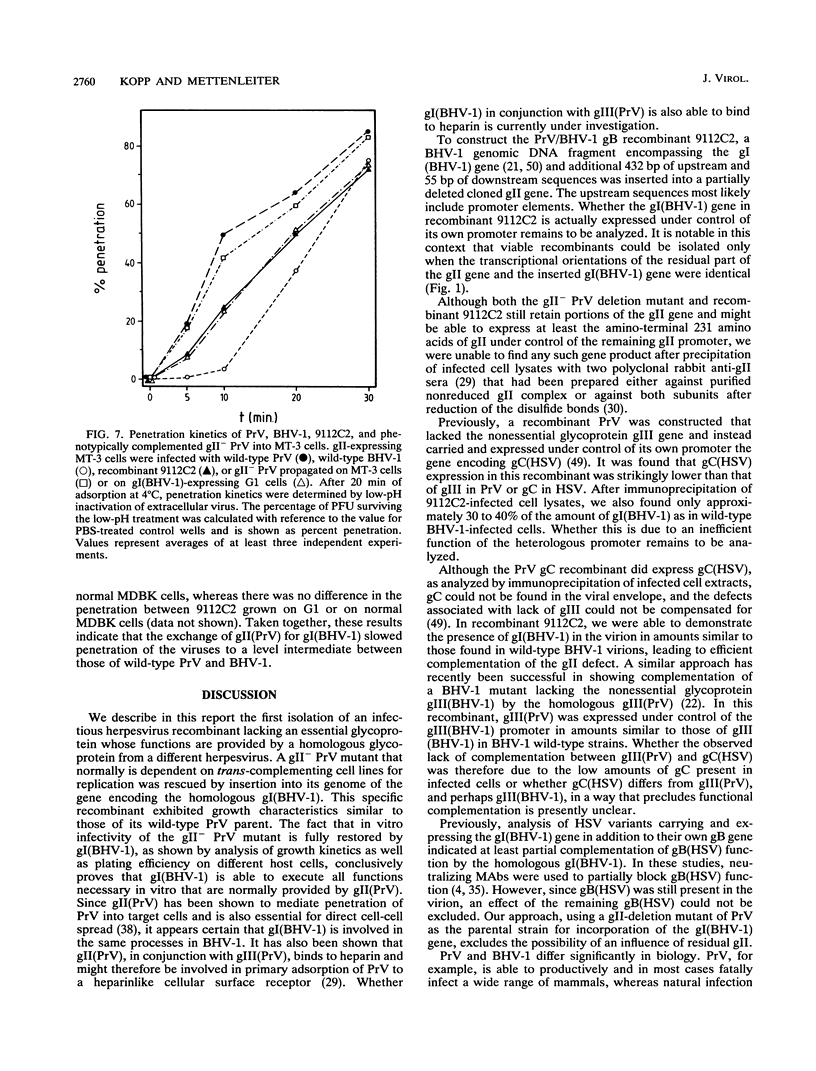


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., Demarchi J. M., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of defective interfering viral particles present in a population of pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blewett E. L., Misra V. Cleavage of the bovine herpesvirus glycoprotein B is not essential for its function. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2083–2090. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush C. E., Pritchett R. F. A comparison of the genomes of bovine herpesvirus type 1 and pseudorabies virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Aug;66(Pt 8):1811–1817. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-8-1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. H., Gu B., Person S. Role of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1 in viral entry and cell fusion. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2596–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2596-2604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N., Bzik D. J., Bond V. C., Person S., Snipes W. Nucleotide sequences of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) affecting virus entry, cell fusion, and production of glycoprotein gb (VP7). Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):411–423. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels M., Giuliani C., Wild P., Beck T. M., Loepfe E., Wyler R. The genome of bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) strains exhibiting a neuropathogenic potential compared to known BHV-1 strains by restriction site mapping and cross-hybridization. Virus Res. 1986 Oct;6(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehler F., Herrmann J. M., Saalmüller A., Mettenleiter T. C., Keil G. M. Glycoprotein IV of bovine herpesvirus 1-expressing cell line complements and rescues a conditionally lethal viral mutant. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):831–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.831-839.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick D. R., Zamb T. J., Babiuk L. A. Expression of bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein gI in transfected bovine cells induces spontaneous cell fusion. J Gen Virol. 1990 May;71(Pt 5):1215–1219. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-5-1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Santos R. E., Spear P. G. Neutralizing antibodies specific for glycoprotein H of herpes simplex virus permit viral attachment to cells but prevent penetration. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3435–3443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3435-3443.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herold B. C., WuDunn D., Soltys N., Spear P. G. Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus type 1 plays a principal role in the adsorption of virus to cells and in infectivity. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1090–1098. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1090-1098.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highlander S. L., Sutherland S. L., Gage P. J., Johnson D. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies specific for herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D inhibit virus penetration. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3356–3364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3356-3364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN A. S., VATTER A. E. A comparison of herpes simplex and pseudorabies viruses. Virology. 1959 Apr;7(4):394–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klupp B. G., Mettenleiter T. C. Sequence and expression of the glycoprotein gH gene of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):732–741. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90614-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence W. C., D'urso R. C., Kundel C. A., Whitbeck J. C., Bello L. J. Map location of the gene for a 130,000-dalton glycoprotein of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):405–414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.405-414.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X. P., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Pseudorabies virus gIII and bovine herpesvirus 1 gIII share complementary functions. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5553–5557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5553-5557.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligas M. W., Johnson D. C. A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1486-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukàcs N., Thiel H. J., Mettenleiter T. C., Rziha H. J. Demonstration of three major species of pseudorabies virus glycoproteins and identification of a disulfide-linked glycoprotein complex. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):166–173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.166-173.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manservigi R., Spear P. G., Buchan A. Cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus is promoted and suppressed by different viral glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield J. E., Good P. J., VanOort H. J., Campbell A. R., Reed D. E. Cloning and cleavage site mapping of DNA from bovine herpesvirus 1 (Cooper strain). J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):259–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.259-264.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lukàcs N., Thiel H. J., Schreurs C., Rziha H. J. Location of the structural gene of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein complex gII. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C. Molecular biology of pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) virus. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991;14(2):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(91)90128-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Rauh I. A glycoprotein gX-beta-galactosidase fusion gene as insertional marker for rapid identification of pseudorabies virus mutants. J Virol Methods. 1990 Oct;30(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90043-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Zuckermann F., Ben-Porat T. Role of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gI in virus release from infected cells. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2764–2769. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2764-2769.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Zsak L., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Kern H., Ben-Porat T. Interaction of glycoprotein gIII with a cellular heparinlike substance mediates adsorption of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.278-286.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer A. L., Petrovskis E. A., Duffus W. P., Thomsen D. R., Post L. E. Cloning and sequence of an infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus (BHV-1) gene homologous to glycoprotein H of herpes simplex virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 8;1090(2):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Blewett E. L. Construction of herpes simplex viruses that are pseudodiploid for the glycoprotein B gene: a strategy for studying the function of an essential herpesvirus gene. J Gen Virol. 1991 Feb;72(Pt 2):385–392. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-2-385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Nelson R., Smith M. Sequence of a bovine herpesvirus type-1 glycoprotein gene that is homologous to the herpes simplex gene for the glycoprotein gB. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):542–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Matsuzaki T., Sugahara Y., Okada J., Hasebe M., Iwamura Y., Ohnishi M., Kanno T., Shimizu M., Honda E. BHV-1 adsorption is mediated by the interaction of glycoprotein gIII with heparinlike moiety on the cell surface. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):666–670. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90900-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Armentrout M. A., Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Post L. E. DNA sequence of the gene for pseudorabies virus gp50, a glycoprotein without N-linked glycosylation. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):216–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.216-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauh I., Mettenleiter T. C. Pseudorabies virus glycoproteins gII and gp50 are essential for virus penetration. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5348–5356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5348-5356.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauh I., Weiland F., Fehler F., Keil G. M., Mettenleiter T. C. Pseudorabies virus mutants lacking the essential glycoprotein gII can be complemented by glycoprotein gI of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):621–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.621-631.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Dorney D. J., Wathen M. W., Whealy M. E., Gold C., Watson R. J., Holland L. E., Weed S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. The pseudorabies virus gII gene is closely related to the gB glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2691–2701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2691-2701.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreurs C., Mettenleiter T. C., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Glycoprotein gIII of pseudorabies virus is multifunctional. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2251–2257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2251-2257.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikoo S. K., Fitzpatrick D. R., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and expression of functional bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoprotein gIV in transfected bovine cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5132–5142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5132-5142.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Wathen L. M. Isolation, characterization, and physical mapping of a pseudorabies virus mutant containing antigenically altered gp50. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):57–62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.57-62.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weise K., Kaerner H. C., Glorioso J., Schröder C. H. Replacement of glycoprotein B gene sequences in herpes simplex virus type 1 strain ANG by corresponding sequences of the strain KOS causes changes of plaque morphology and neuropathogenicity. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1909–1919. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII is required for efficient virus growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2512–2515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2512-2515.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Replacement of the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII gene with its postulated homolog, the glycoprotein gC gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4055–4059. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4055-4059.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitbeck J. C., Bello L. J., Lawrence W. C. Comparison of the bovine herpesvirus 1 gI gene and the herpes simplex virus type 1 gB gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3319–3327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3319-3327.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsak L., Mettenleiter T. C., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Release of pseudorabies virus from infected cells is controlled by several viral functions and is modulated by cellular components. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5475–5477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5475-5477.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]