Abstract
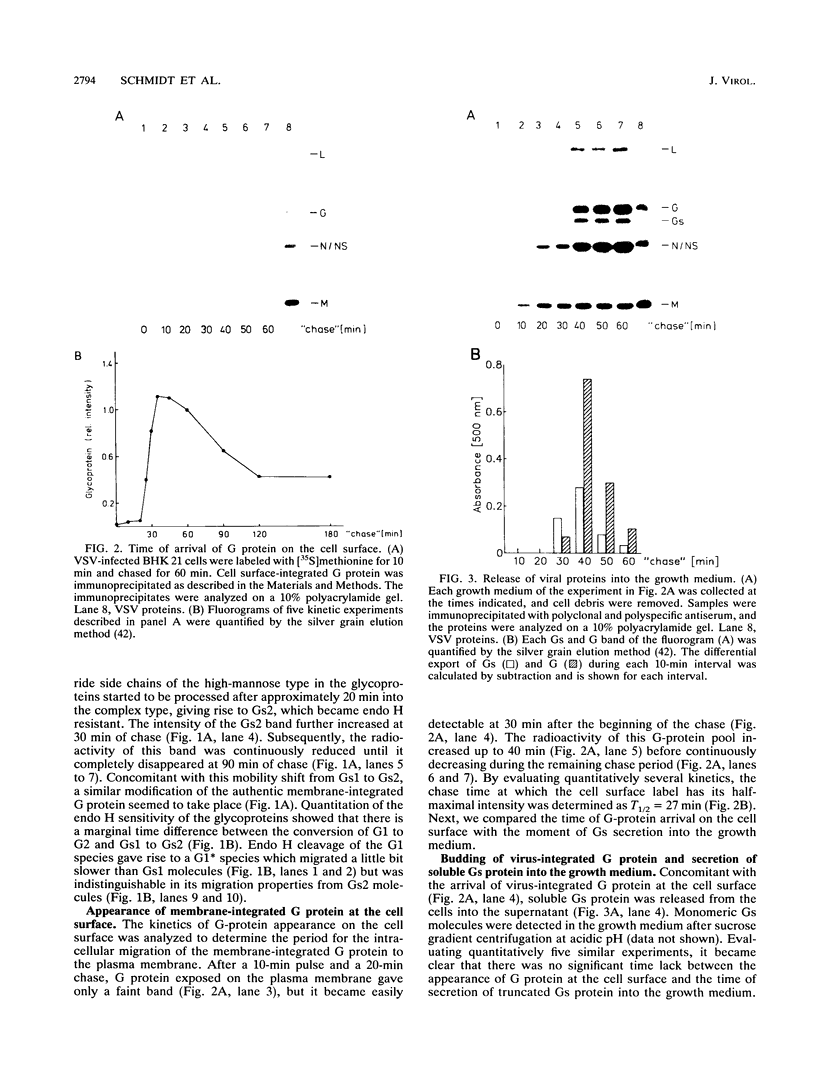
BHK cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus serotype Indiana generate intracellularly two different types of glycoproteins: the authentic membrane-integrated G protein of virions and a smaller soluble Gs protein lacking the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains which is secreted into the growth medium. A Gs1 protein species which is formed during or shortly after translation in the endoplasmic reticulum lumen is modified in the same way as the G1 protein by endoglycosidase H-sensitive oligosaccharides of the high-mannose type. Both G1 and Gs1 are almost simultaneously transported, trimmed, and processed into G2 and Gs2 species which possess carbohydrate side chains of the complex type, making both glycoproteins resistant to endoglycosidase H cleavage. Secretion of Gs2 protein into the growth medium and arrival of G2 protein on the cell surface occur concomitantly. Membrane-integrated G protein and the soluble Gs protein molecules oligomerize intracellularly into heterotrimers which can be immunoprecipitated after chemical cross-linking. Gs protein seems to contain sufficient structural information for the formation of heterotrimers which are efficiently transported to the cell surface. Heterotrimer formation between G and Gs proteins explains the rapid secretion of Gs molecules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheiter H., Dubois-Dalcq M., Lazzarini R. A. Direct visualization of protein transport and processing in the living cell by microinjection of specific antibodies. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., Kuehl W. M. Formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds on nascent immunoglobulin polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5690–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann J. E., Singer S. J. Immunoelectron microscopic studies of the intracellular transport of the membrane glycoprotein (G) of vesicular stomatitis virus in infected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1777–1787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Doherty R., O'Rourke E. J., Ariel N., Huang A. S. Effects of transport inhibitors on the generation and transport of a soluble viral glycoprotein. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):482–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Huang A. S. Further characterization of the vesicular stomatitis virus temperature-sensitive O45 mutant: intracellular conversion of the glycoprotein to a soluble form. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):210–215. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.210-215.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crise B., Ruusala A., Zagouras P., Shaw A., Rose J. K. Oligomerization of glycolipid-anchored and soluble forms of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5328–5333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5328-5333.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Keller D. S., Helenius A., Balch W. E. Role for adenosine triphosphate in regulating the assembly and transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein trimers. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):1957–1969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Ruusala A., Machamer C., Helenius J., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Differential effects of mutations in three domains on folding, quaternary structure, and intracellular transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):89–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries E., Gustafsson L., Peterson P. A. Four secretory proteins synthesized by hepatocytes are transported from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi complex at different rates. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):147–152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallione C. J., Rose J. K. A single amino acid substitution in a hydrophobic domain causes temperature-sensitive cell-surface transport of a mutant viral glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):374–382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.374-382.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garreis-Wabnitz C., Kruppa J. Intracellular appearance of a glycoprotein in VSV-infected BHK cells lacking the membrane-anchoring oligopeptide of the viral G-protein. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1469–1476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01998.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeve L., Garreis-Wabnitz C., Zauke M., Breindl M., Kruppa J. The soluble glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is formed during or shortly after the translation process. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):968–975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.968-975.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünberg J., Kruppa A., Paschen P., Kruppa J. Intracellular formation of two soluble glycoproteins in BHK cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus serotype New Jersey. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):678–686. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90081-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas I. G., Wabl M. Immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):387–389. doi: 10.1038/306387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Maturation of viral proteins in cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1149-1158.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Separate pathways of maturation of the major structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1128–1139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1128-1139.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
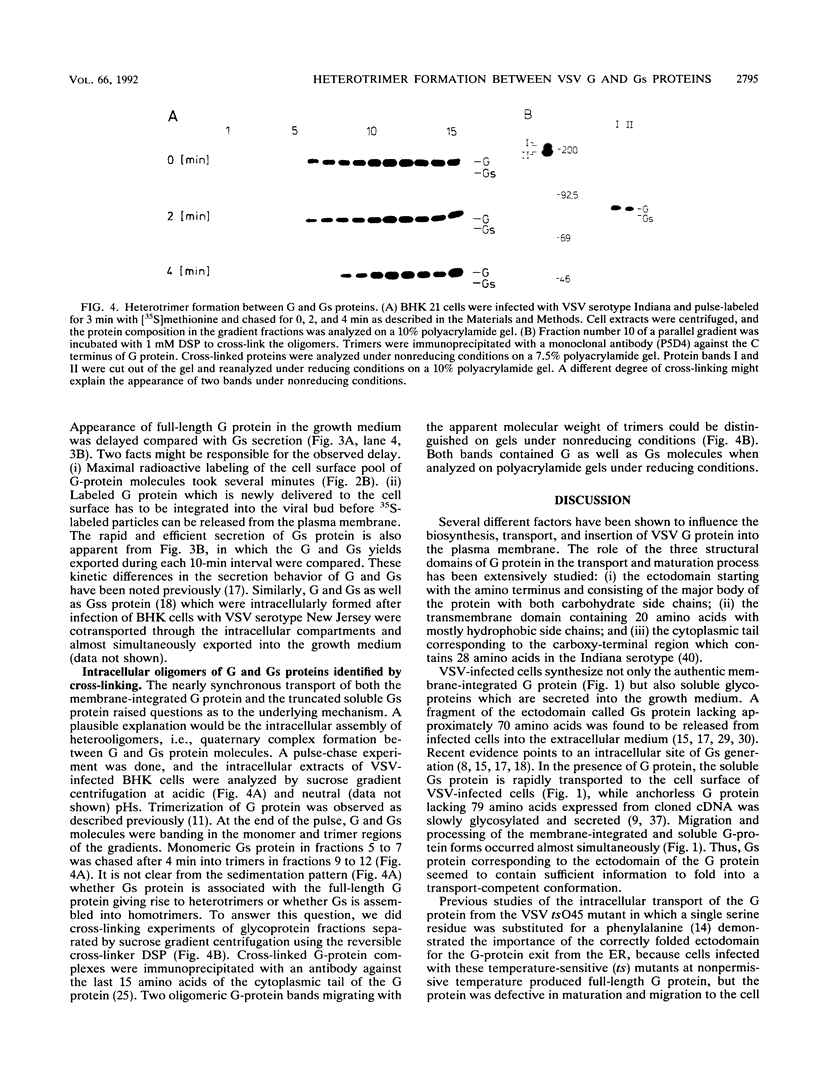
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E. Microinjected antibodies against the cytoplasmic domain of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein block its transport to the cell surface. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):931–941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruppa J. Transfer of carbohydrates on to nascent glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):295–300. doi: 10.1042/bj1810295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Huang A. S. Shedding of the glycoprotein from vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):330–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.330-339.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Huang A. S. Synthesis and distribution of vesicular stomatitis virus-specific polypeptides in the absence of progeny production. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Kong N., Snider M., Strous G. J. Hepatoma secretory proteins migrate from rough endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi at characteristic rates. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):80–83. doi: 10.1038/304080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., Varela V. A., Parce J. W. Dynamic nature of the quaternary structure of the vesicular stomatitis virus envelope glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2442–2449. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Doms R. W., Bole D. G., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Heavy chain binding protein recognizes incompletely disulfide-bonded forms of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6879–6883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D., Kluxen B., Kruppa J. Accessibility to proteases of the cytoplasmic G protein domain of vesicular stomatitis virus is increased during intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2057–2065. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsikkö K., Simons K. The budding mechanism of spikeless vesicular stomatitis virus particles. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1913–1920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Control of protein exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Altered cytoplasmic domains affect intracellular transport of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Expression from cloned cDNA of cell-surface secreted forms of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Identification of the components of the murine T cell antigen receptor complex. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suissa M. Spectrophotometric quantitation of silver grains eluted from autoradiograms. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. B., Swiedler S. J., Hart G. W. Intracellular transport of membrane glycoproteins: two closely related histocompatibility antigens differ in their rates of transit to the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):725–734. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S., Sher B., Kudryk B., Redman C. M. Intracellular assembly of human fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13407–13410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagouras P., Ruusala A., Rose J. K. Dissociation and reassociation of oligomeric viral glycoprotein subunits in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1976–1984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1976-1984.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva A. M., Balch W. E., Helenius A. Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum: folding and misfolding of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein in cells and in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):857–866. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]