Abstract
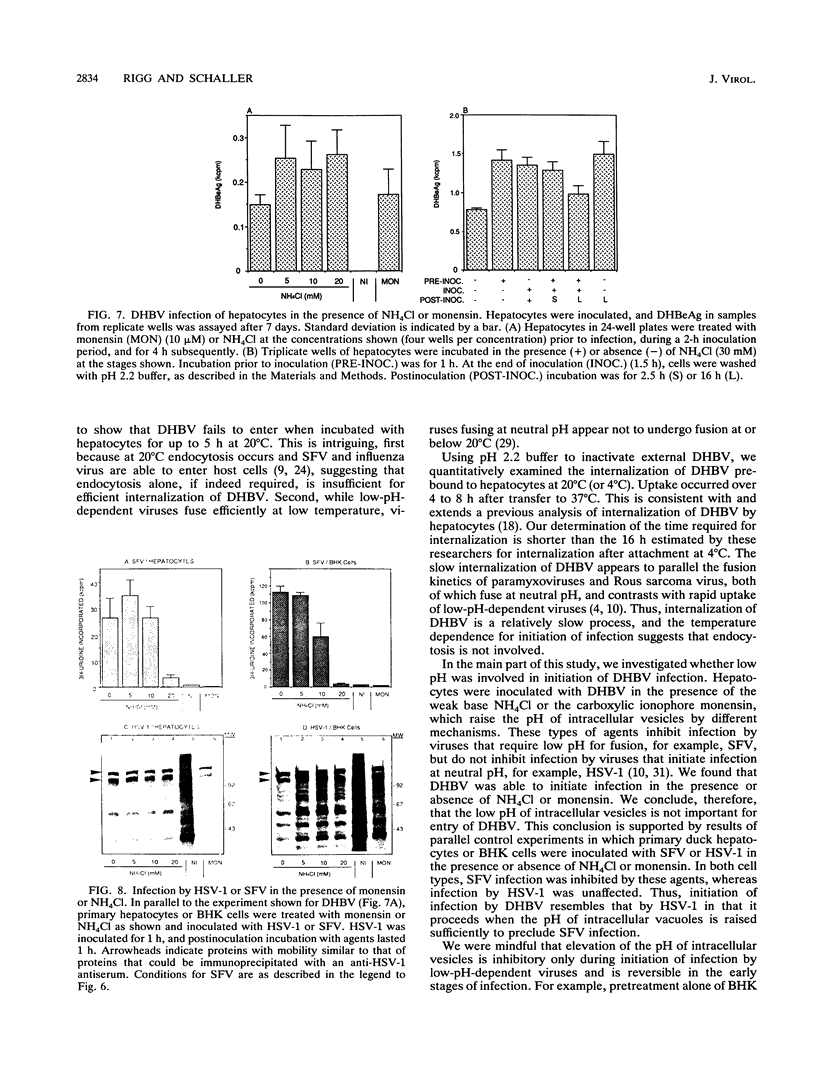
The pH dependency for initiation of infection by the hepadnavirus duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) was investigated in primary duck hepatocytes. First, an infection assay was developed using a radioimmunoblot to measure DHBV e antigen secreted into tissue culture fluid from infected hepatocytes. The quantity of this viral marker was proportional to the duration of inoculation and the amount of DHBV used as inoculum. The role of pH in initiation of DHBV infection was investigated by using this assay, but no dependence on low pH was found. DHBV was able to infect hepatocytes in the presence of NH4Cl and monensin, agents that raise the pH in intracellular vesicles and prevent penetration of viruses dependent on low pH in endosomes. In control experiments, infection by Semliki Forest virus, which is low pH dependent, was inhibited, whereas herpes simplex virus type 1 infection, which is pH independent, occurred. Attempts to trigger DHBV-cell fusion by exposure of DHBV prebound to hepatocytes to mildly acidic pH were unsuccessful. In these experiments, it was also observed that internalization of DHBV occurred only between pH 6.8 and 8.0. Additionally, in the absence of cells, infectivity of DHBV was stable at pH 4.6 to 4.8, which is lower than the pH encountered in endosomes (pH 5 to 6.6). Thus, no evidence for a role for mildly acidic pH in the initiation of DHBV infection was found. Therefore, we propose that the infection route followed by DHBV resembles that of the group of enveloped viruses, including herpesviruses, that fuse with their host cells at neutral pH.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gallagher T. M., Escarmis C., Buchmeier M. J. Alteration of the pH dependence of coronavirus-induced cell fusion: effect of mutations in the spike glycoprotein. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1916–1928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1916-1928.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galle P. R., Schlicht H. J., Kuhn C., Schaller H. Replication of duck hepatitis B virus in primary duck hepatocytes and its dependence on the state of differentiation of the host cell. Hepatology. 1989 Oct;10(4):459–465. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D. Assembly of hepadnaviral virions and subviral particles. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;168:61–83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76015-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. M., Mason D., White J. M. Fusion of Rous sarcoma virus with host cells does not require exposure to low pH. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5106–5113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5106-5113.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Marsh M., White J. Inhibition of Semliki forest virus penetration by lysosomotropic weak bases. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jan;58(Pt 1):47–61. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama A. H., Uchida T. Inhibition of multiplication of herpes simplex virus type 1 by ammonium chloride and chloroquine. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):332–335. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L. Development of antiviral therapy for chronic infection with hepatitis B virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;168:167–183. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76015-0_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Bolzau E., Helenius A. Penetration of Semliki Forest virus from acidic prelysosomal vacuoles. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Helenius A. Transport of incoming influenza virus nucleocapsids into the nucleus. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):232–244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.232-244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. O., Marsh M., Weiss R. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of CD4-bearing cells occurs by a pH-independent mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):513–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. O., Sommerfelt M. A., Marsh M., Weiss R. A. The pH independence of mammalian retrovirus infection. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):767–773. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offensperger W. B., Offensperger S., Walter E., Blum H. E., Gerok W. Inhibition of duck hepatitis B virus infection by lysosomotropic agents. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):415–418. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petcu D. J., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Taylor J. M., Mason W. S. Suramin inhibits in vitro infection by duck hepatitis B virus, Rous sarcoma virus, and hepatitis delta virus. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., McAtee F. J., Evans L. H. Infectious entry of murine retroviruses into mouse cells: evidence of a postadsorption step inhibited by acidic pH. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):806–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.806-812.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. Infection and uptake of duck hepatitis B virus by duck hepatocytes maintained in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):564–572. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri A., Booy F. P., Doms R. W., White J. M., Blumenthal R. Conformational changes and fusion activity of influenza virus hemagglutinin of the H2 and H3 subtypes: effects of acid pretreatment. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3824–3832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3824-3832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal K. S., Killius J., Hodnichak C. M., Venetta T. M., Gyurgyik L., Janiga K. Mild acidic pH inhibition of the major pathway of herpes simplex virus entry into HEp-2 cells. J Gen Virol. 1989 Apr;70(Pt 4):857–867. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-4-857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Galle P., Schaller H. The hepatitis-B viruses: molecular biology and recent tissue culture systems. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;7:197–212. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_7.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Salfeld J., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus pre-C region encodes a signal sequence which is essential for synthesis and secretion of processed core proteins but not for virus formation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3701-3709.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Fernholz D., Wildner G., Will H. Mechanism, kinetics, and role of duck hepatitis B virus e-antigen expression in vivo. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90591-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasakumar N., Ogra P. L., Flanagan T. D. Characteristics of fusion of respiratory syncytial virus with HEp-2 cells as measured by R18 fluorescence dequenching assay. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4063–4069. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4063-4069.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., White J. M., Helenius A. Intermediates in influenza induced membrane fusion. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4231–4241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. In vitro experimental infection of primary duck hepatocyte cultures with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.17-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Fusion of Semliki forest virus with the plasma membrane can be induced by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):264–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittels M., Spear P. G. Penetration of cells by herpes simplex virus does not require a low pH-dependent endocytic pathway. Virus Res. 1991 Mar;18(2-3):271–290. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(91)90024-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WuDunn D., Spear P. G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.52-58.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosuka O., Omata M., Ito Y. Expression of pre-S1, pre-S2, and C proteins in duck hepatitis B virus infection. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):82–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura A., Ohnishi S. Uncoating of influenza virus in endosomes. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):497–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.497-504.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]