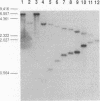
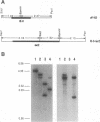
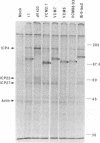
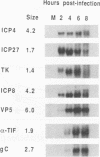
Abstract
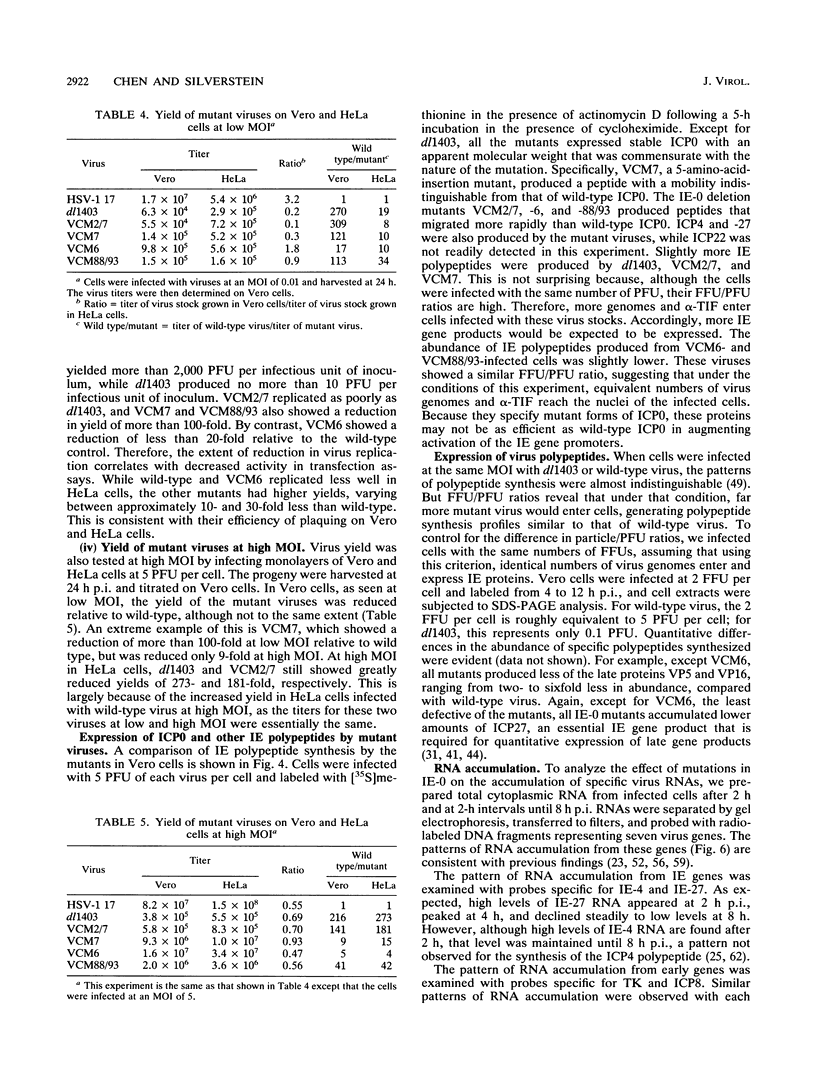
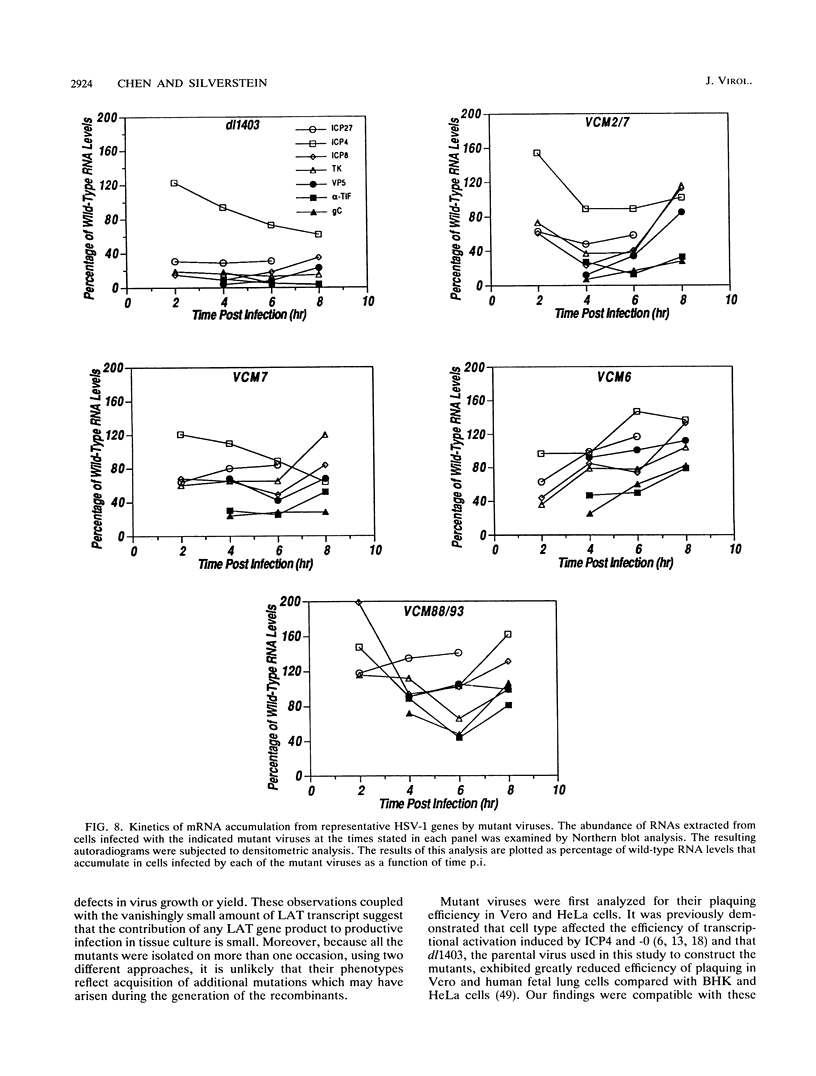
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) mutants with codon insertions and deletions in IE-0, the gene encoding ICP0, were constructed. The HSV-1 deletion mutant dl1403 (N. D. Stow and E. C. Stow, J. Gen. Virol. 67:2571-2585, 1986) and an IE-0:lacZ transplacement vector isolated in this study were used to facilitate the construction of mutant viruses. Mutant viruses, all of which produced stable ICP0, were examined for their ability to plaque and grow on both Vero and HeLa cells because previous results showed that HSV-1 immediate-early (IE) gene promoters and their products are differentially expressed in these cells (J. Chen, X. Zhu, and S. Silverstein, Virology 180:207-220, 1991; I. H. Gelman and S. Silverstein, J. Virol. 61:2286-2296, 1987). Viruses with IE-0 genes that only poorly activated reporter genes in transient expression assays plaqued less efficiently on Vero cells and consistently accumulated decreased levels of late proteins. These mutants were also examined in single-step growth curve experiments and for the dependence of virus yield on multiplicity of infection (MOI). At low MOIs, their yields were less in Vero cells than in HeLa cells; by contrast, at high MOIs, there was no apparent difference in yield in either cell type, although each virus produced considerably fewer progeny than wild-type virus. Analysis of steady-state levels of RNA from genes representing each of the three major kinetic classes demonstrated that lower levels of RNAs accumulate in these mutants. We conclude from these studies that while ICP0 is not essential for virus growth in tissue culture, defects in this gene result in impairment of virus replication and delay the expression of early and late gene transcripts.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Faber S., Wilcox K. W., Pizer L. I. Herpes simplex virus immediate early infected-cell polypeptide 4 binds to DNA and promotes transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. Z., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 plays a critical role in the de novo synthesis of infectious virus following transfection of viral DNA. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4579–4589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4579-4589.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W., Schaffer P. A. A cellular function can enhance gene expression and plating efficiency of a mutant defective in the gene for ICP0, a transactivating protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4078–4090. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4078-4090.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 regulates expression of immediate-early, early, and late genes in productively infected cells. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2904–2915. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2904-2915.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. X., Zhu X. X., Silverstein S. Mutational analysis of the sequence encoding ICP0 from herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):207–220. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements G. B., Stow N. D. A herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a deletion within immediate early gene 1 is latency-competent in mice. J Gen Virol. 1989 Sep;70(Pt 9):2501–2506. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-9-2501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed mutational analysis of Vmw110, a trans-acting transcriptional activator encoded by herpes simplex virus type 1. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2069–2076. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Analysis of the functional domains of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early polypeptide Vmw110. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90521-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Construction and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 mutants with defined lesions in immediate early gene 1. J Gen Virol. 1989 May;70(Pt 5):1185–1202. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-5-1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Promoter sequence and cell type can dramatically affect the efficiency of transcriptional activation induced by herpes simplex virus type 1 and its immediate-early gene products Vmw175 and Vmw110. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Rice M., Hecht L. B., Silverstein S., Wagner E. K. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter controlling the expression of UL38, a true late gene involved in capsid assembly. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):769–786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.769-786.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Co-ordinate regulation of herpes simplex virus gene expression is mediated by the functional interaction of two immediate early gene products. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):395–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Herpes simplex virus immediate-early promoters are responsive to virus and cell trans-acting factors. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2286–2296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2286-2296.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Identification of immediate early genes from herpes simplex virus that transactivate the virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5265–5269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Balmaceda C. G., Roeder R. G. The cell type-specific octamer transcription factor OTF-2 has two domains required for the activation of transcription. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1635–1643. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08283.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Knipe D. M. Transcriptional control of herpesvirus gene expression: gene functions required for positive and negative regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus mRNA species mapping in EcoRI fragment I. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):594–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.594-607.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris-Hamilton E., Bachenheimer S. L. Accumulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNAs of different kinetic classes in the cytoplasm of infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):144–151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.144-151.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A., Everett R. D., Zhu X. X., Silverstein S., Preston C. M. Herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein Vmw110 reactivates latent herpes simplex virus type 2 in an in vitro latency system. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3513–3515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3513-3515.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrin D. L., Schmidt G. W. Rapid, reversible staining of northern blots prior to hybridization. Biotechniques. 1988 Mar;6(3):196-7, 199-200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XI. Identification and relative molar rates of synthesis of structural and nonstructural herpes virus polypeptides in the infected cell. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1347–1365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1347-1365.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib D. A., Coen D. M., Bogard C. L., Hicks K. A., Yager D. R., Knipe D. M., Tyler K. L., Schaffer P. A. Immediate-early regulatory gene mutants define different stages in the establishment and reactivation of herpes simplex virus latency. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):759–768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.759-768.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Silver S., Hubenthal-Voss J., McKnight J. L., Roizman B. Regulation of herpes simplex virus 1 genes: alpha gene sequence requirements for transient induction of indicator genes regulated by beta or late (gamma 2) promoters. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. M., McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 deletion mutants exhibit altered patterns of transcription and are DNA deficient. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.18-27.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Rixon F. J., Everett R. D., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J. Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2365–2380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Knipe D. M. Stimulation of expression of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein by two viral functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):957–963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Knipe D. M. Gene-specific transactivation by herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3814–3823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3814-3823.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. S., Boundy A., O'Hare P., Pizzorno M. C., Ciufo D. M., Hayward G. S. Direct correlation between a negative autoregulatory response element at the cap site of the herpes simplex virus type 1 IE175 (alpha 4) promoter and a specific binding site for the IE175 (ICP4) protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4307–4320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4307-4320.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J., Stow N. D., Stow E. C., Preston C. M. Herpes simplex virus genes involved in latency in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3009–3018. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Schaffer P. A. Deletion mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 exhibit impaired growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.829-839.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekulovich R. E., Leary K., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 can act as a trans-repressor or a trans-activator in combination with ICP4 and ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4510-4522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Regulation of the herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) glycoprotein C gene: sequences between base pairs -34 to +29 control transient expression and responsiveness to transactivation by the products of the immediate early (alpha) 4 and 0 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3097–3111. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Spivack J. G., O'Boyle D. R., 2nd, Lavi E., Fraser N. W. Latent herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription in human trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3493–3496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3493-3496.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Stow E. C. Isolation and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a deletion within the gene encoding the immediate early polypeptide Vmw110. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2571–2585. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L., Knipe D. M. Herpes simplex virus alpha protein ICP27 can inhibit or augment viral gene transactivation. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):496–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G., Feldman L. T., Dobson A. T., Zhang Y. F., Flanagan W. M., Stevens J. G. Physical characterization of the herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript in neurons. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1194–1202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1194-1202.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walboomers J. M., Schegget J. T. A new method for the isolation of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):256–258. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90151-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls establish the cascade of herpes simplex virus protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):819–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Analysis of the DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):670–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. F., Wagner E. K. The kinetics of expression of individual herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts. Virus Genes. 1987 Nov;1(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00125685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. X., Chen J. X., Silverstein S. Isolation and characterization of a functional cDNA encoding ICP0 from herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):957–960. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.957-960.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. X., Chen J. X., Young C. S., Silverstein S. Reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus by adenovirus recombinants encoding mutant IE-0 gene products. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4489–4498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4489-4498.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. X., Papavassiliou A. G., Stunnenburg H. G., Silverstein S. Transactivation by herpes simplex virus proteins ICP4 and ICP0 in vaccinia virus infected cells. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90822-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. X., Young C. S., Silverstein S. Adenovirus vector expressing functional herpes simplex virus ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4544–4553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4544-4553.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]