Abstract
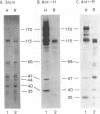
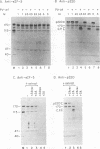
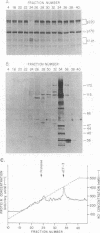
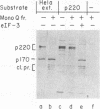
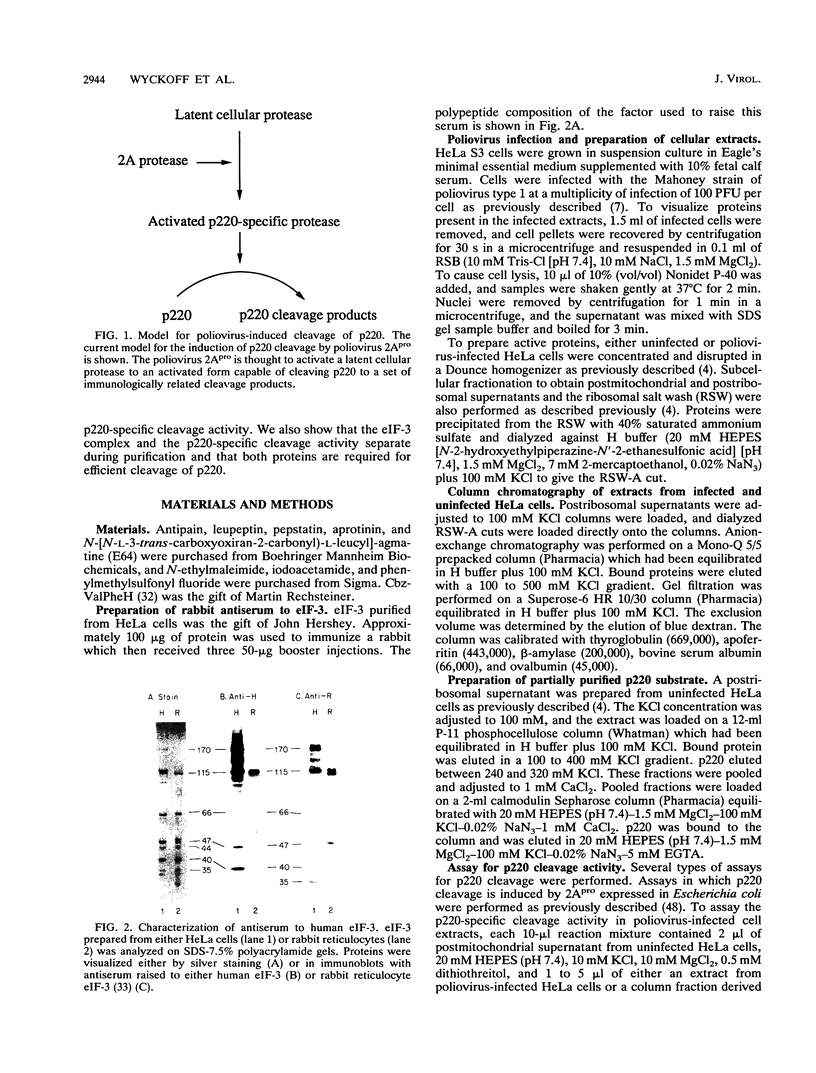
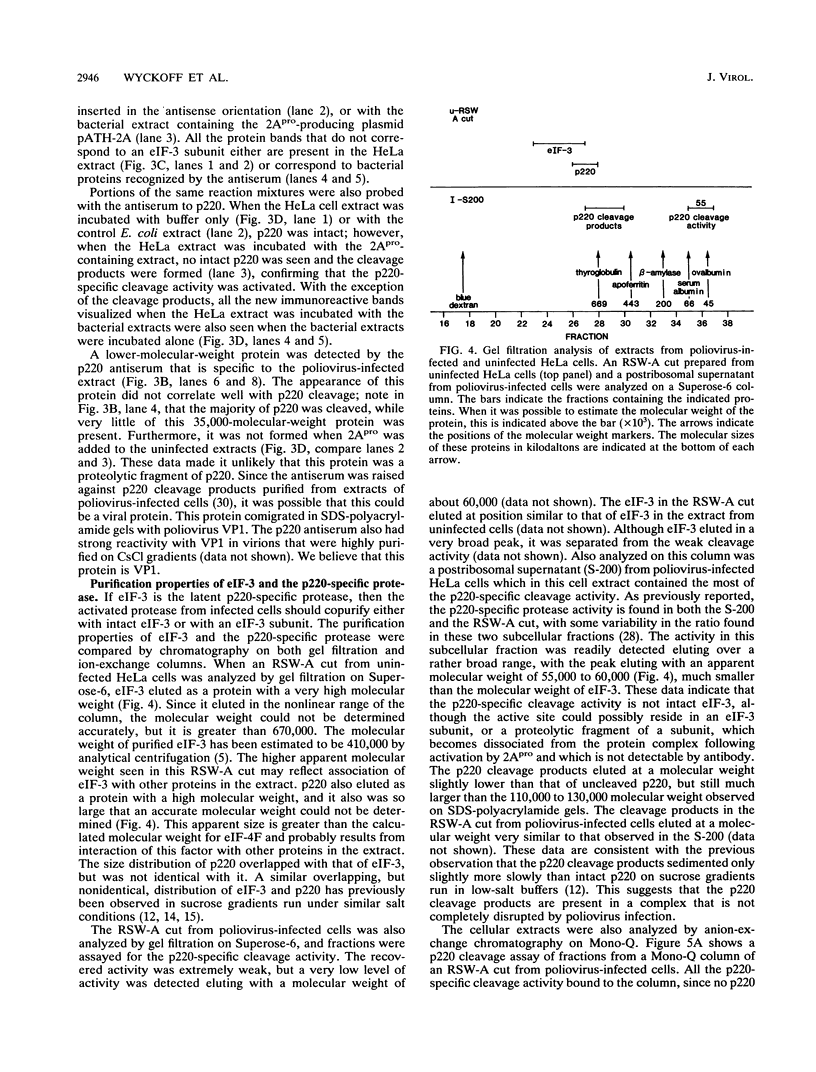
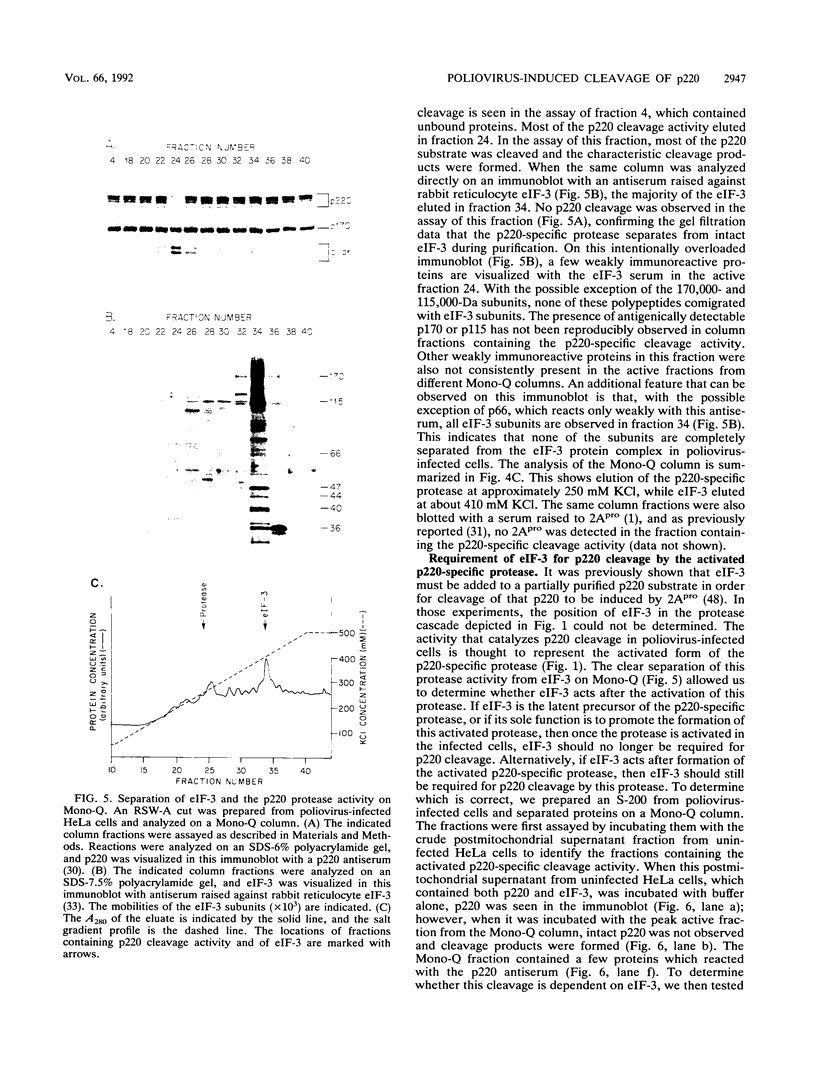
The cleavage of the p220 subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F (eIF-4F) that is induced by the poliovirus protease 2A has been shown previously to require another translation initiation factor, eIF-3. The role of eIF-3 in this cleavage reaction, however, is not known. An antiserum was raised against human eIF-3 and used to analyze the eIF-3 subunit composition in poliovirus-infected and uninfected HeLa cells and after incubation of eIF-3 in vitro with viral 2A protease. No evidence for 2Apro-dependent cleavage of any eIF-3 subunit was detected. Infected cells contain an activity that catalyzes the cleavage of p220 to a specific set of cleavage products. This activity is thought to be an activated form of a latent cellular protease. The p220-specific cleavage activity was partially purified. It was resolved from eIF-3 by both gel filtration and anion-exchange chromatography. Neither intact eIF-3 nor any detectable subunits of eIF-3 were found to copurify with the p220-specific cleavage activity. The latter activity behaves as a protein of 55,000 to 60,000 molecular weight and is inhibited by alkylating agents and metals, which indicates the presence of essential thiol groups. When this activity was incubated with partially purified p220, cleavage occurred only in the presence of eIF-3. Thus, eIF-3 appears to play a role in the p220 cleavage cascade which is subsequent to the 2Apro-induced activation of the p220-specific protease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvey J. C., Wyckoff E. E., Yu S. F., Lloyd R., Ehrenfeld E. cis- and trans-cleavage activities of poliovirus 2A protease expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6077–6083. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6077-6083.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsham G. J., Brangwyn J. K. A region of the 5' noncoding region of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA directs efficient internal initiation of protein synthesis within cells: involvement with the role of L protease in translational control. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5389–5395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5389-5395.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: changes in cleavage pattern and initiation sites by ribosomal salt wash. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley B., Ehrenfeld E. Two-dimensional gel analyses of the 24-kDa cap binding protein from poliovirus-infected and uninfected HeLa cells. Virology. 1986 Jul 30;152(2):497–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Ehrenfeld E. Effect of poliovirus double-stranded RNA on viral and host-cell protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2440–2444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaney M. A., Vakharia V. N., Lloyd R. E., Ehrenfeld E., Grubman M. J. Leader protein of foot-and-mouth disease virus is required for cleavage of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4407–4409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4407-4409.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Etchison D., Hershey J. W. Protein synthesis eukaryotic initiation factors 4A and 4B are not altered by poliovirus infection of HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7236–7239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Hümbelin M., Darveau A., Lee K. A., Milburn S., Hershey J. W., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Involvement of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A in the cap recognition process. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Etchison J. R. Monoclonal antibody-aided characterization of cellular p220 in uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells: subcellular distribution and identification of conformers. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2702–2710. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2702-2710.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Hansen J., Ehrenfeld E., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Milburn S., Hershey J. W. Demonstration in vitro that eucaryotic initiation factor 3 is active but that a cap-binding protein complex is inactive in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):832–837. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.832-837.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Smith K. Variations in cap-binding complexes from uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7492–7500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Leis J. P., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. Characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A, a protein involved in ATP-dependent binding of globin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5246–5252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Etchison D., Hershey J. W., Ehrenfeld E. Association of cap-binding protein with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 in initiation factor preparations from uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):200–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.200-207.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Ehrenfeld E., Brown-Luedi M. L., Hershey J. W. Alterations in initiation factor activity from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10973–10978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Ehrenfeld E. Control of protein synthesis in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. I. mRNA discrimination by crude initiation factors. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):510–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.510-521.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Fäcke M., Kräusslich H. G., Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Characterization of poliovirus 2A proteinase by mutational analysis: residues required for autocatalytic activity are essential for induction of cleavage of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4226–4231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4226-4231.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann Y., Goldstein E., Penman S. Poliovirus-induced inhibition of polypeptide initiation in vitro on native polyribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1834–1838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Rosenwirth B. Purification and partial characterization of poliovirus protease 2A by means of a functional assay. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1243–1250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1243-1250.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. G., Lee K. A., Maimone M. M., Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Dissociation of double-stranded polynucleotide helical structures by eukaryotic initiation factors, as revealed by a novel assay. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4729–4734. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Edery I., Hanecak R., Wimmer E., Sonenberg N. Poliovirus protease 3C (P3-7c) does not cleave P220 of the eucaryotic mRNA cap-binding protein complex. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):489–493. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.489-493.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Edery I., Sonenberg N. Isolation and structural characterization of cap-binding proteins from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):515–524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.515-524.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Etchison D., Ehrenfeld E. Poliovirus protease does not mediate cleavage of the 220,000-Da component of the cap binding protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2723–2727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Grubman M. J., Ehrenfeld E. Relationship of p220 cleavage during picornavirus infection to 2A proteinase sequencing. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4216–4223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4216-4223.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Jense H. G., Ehrenfeld E. Restriction of translation of capped mRNA in vitro as a model for poliovirus-induced inhibition of host cell protein synthesis: relationship to p220 cleavage. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2480–2488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2480-2488.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E., Ehrenfeld E. Cleavage of the cap binding protein complex polypeptide p220 is not effected by the second poliovirus protease 2A. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi S., Angelastro M. R., Wiseman J. S., Bey P. Inhibition of the proteolysis of rat erythrocyte membrane proteins by a synthetic inhibitor of calpain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1117–1123. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80989-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer L. J., Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W. Immunochemical characterization of mammalian protein synthesis initiation factors. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4206–4212. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn S. C., Duncan R. F., Hershey J. W. Immunoblot analysis of the structure of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF3 from HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Jan;276(1):6–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90002-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomenclature of initiation, elongation and termination factors for translation in eukaryotes. Recommendations 1988. Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry (NC-IUB). Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):1–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. E., Racaniello V. R. Inhibition of translation in cells infected with a poliovirus 2Apro mutant correlates with phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eucaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5069–5075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5069-5075.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Kramer J. C., Cladaras M. H., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. ATP-dependent unwinding of messenger RNA structure by eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7651–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Edery I., Meerovitch K., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. Bidirectional RNA helicase activity of eucaryotic translation initiation factors 4A and 4F. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1134–1144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Sommergruber W., Auer H., Volkmann P., Zorn M., Liebig H. D., Fessl F., Blaas D., Kuechler E. Substrate requirements of a human rhinoviral 2A proteinase. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):46–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90468-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Guertin D., Lee K. A. Capped mRNAs with reduced secondary structure can function in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1633–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Morgan M. A., Merrick W. C., Shatkin A. J. A polypeptide in eukaryotic initiation factors that crosslinks specifically to the 5'-terminal cap in mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. Human immunodeficiency virus tat-activated expression of poliovirus protein 2A inhibits mRNA translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2143–2146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J. Two forms of purified m7G-cap binding protein with different effects on capped mRNA translation in extracts of uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7691–7694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Sonenberg N., Shatkin A. J., Rose J. K., Leong K., Bergmann J. E., Gordon J., Baltimore D. Purification of a factor that restores translation of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA in extracts from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. K., Villalobo A., Roufogalis B. D. Calmodulin-binding proteins as calpain substrates. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 15;262(3):693–706. doi: 10.1042/bj2620693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E. E., Croall D. E., Ehrenfeld E. The p220 component of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F is a substrate for multiple calcium-dependent enzymes. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 30;29(43):10055–10061. doi: 10.1021/bi00495a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E. E., Hershey J. W., Ehrenfeld E. Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 is required for poliovirus 2A protease-induced cleavage of the p220 component of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9529–9533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. F., Lloyd R. E. Identification of essential amino acid residues in the functional activity of poliovirus 2A protease. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):615–625. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]