Abstract
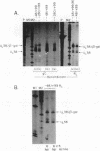
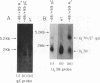
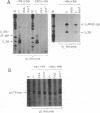
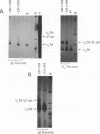
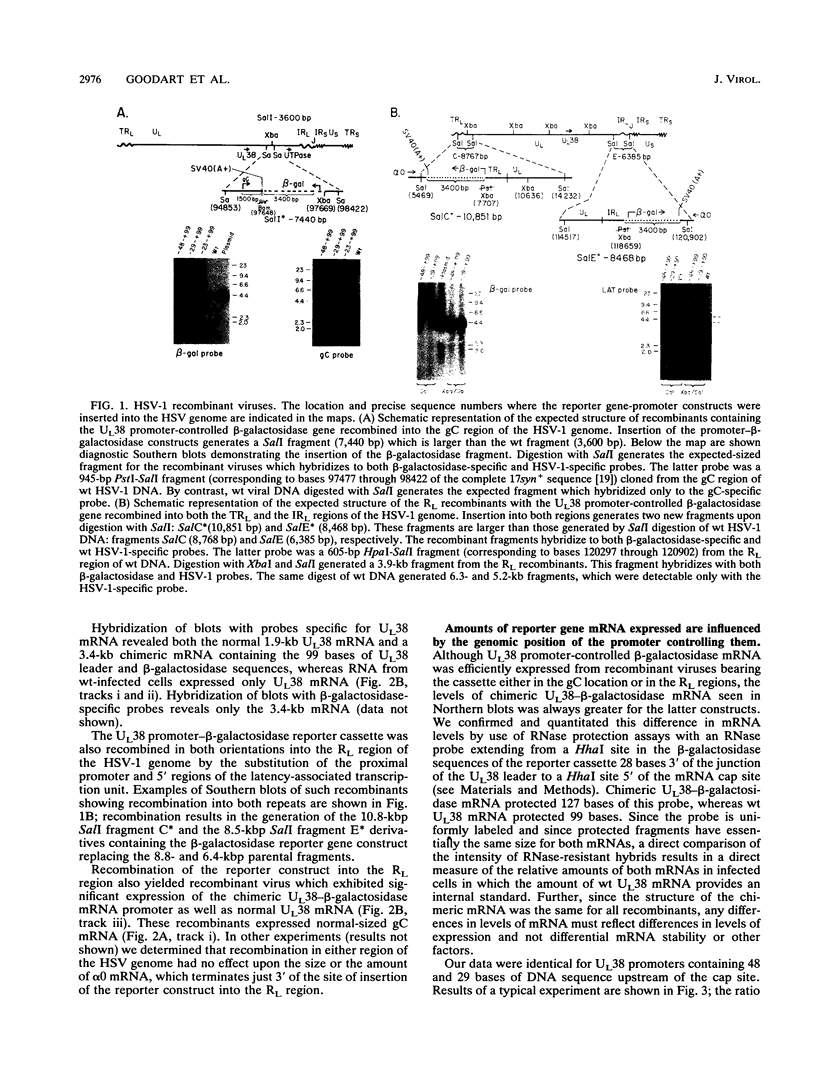
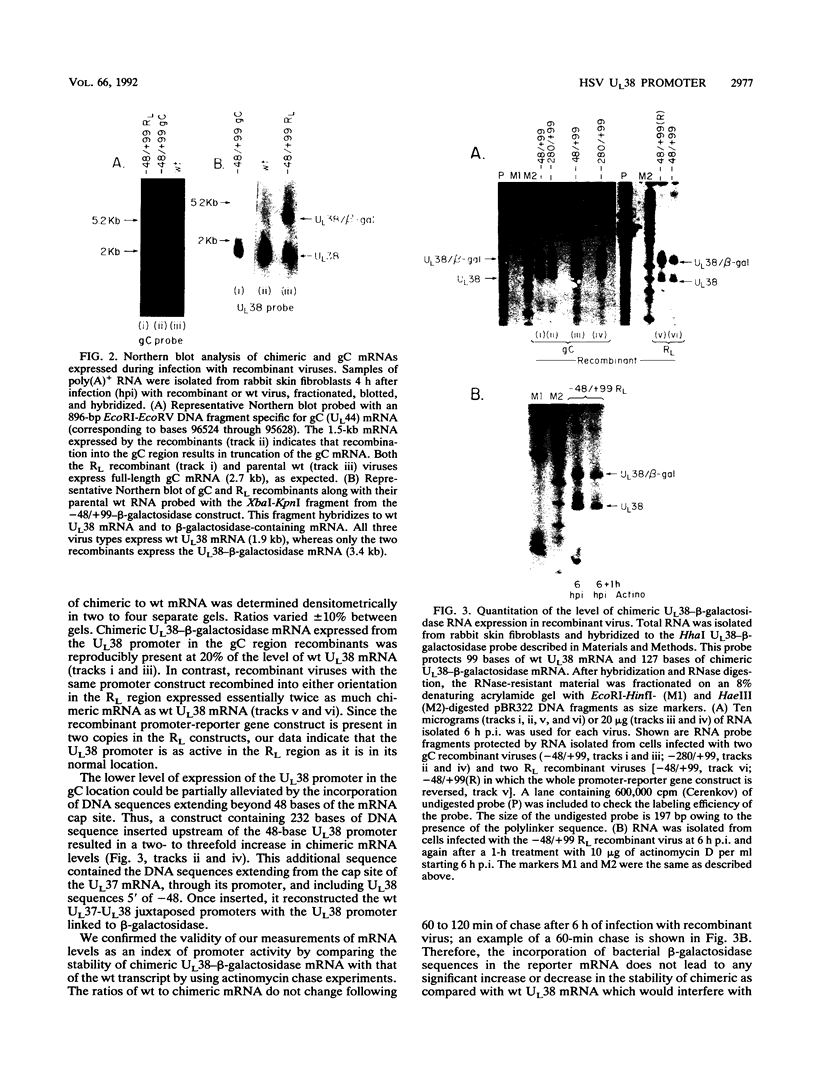
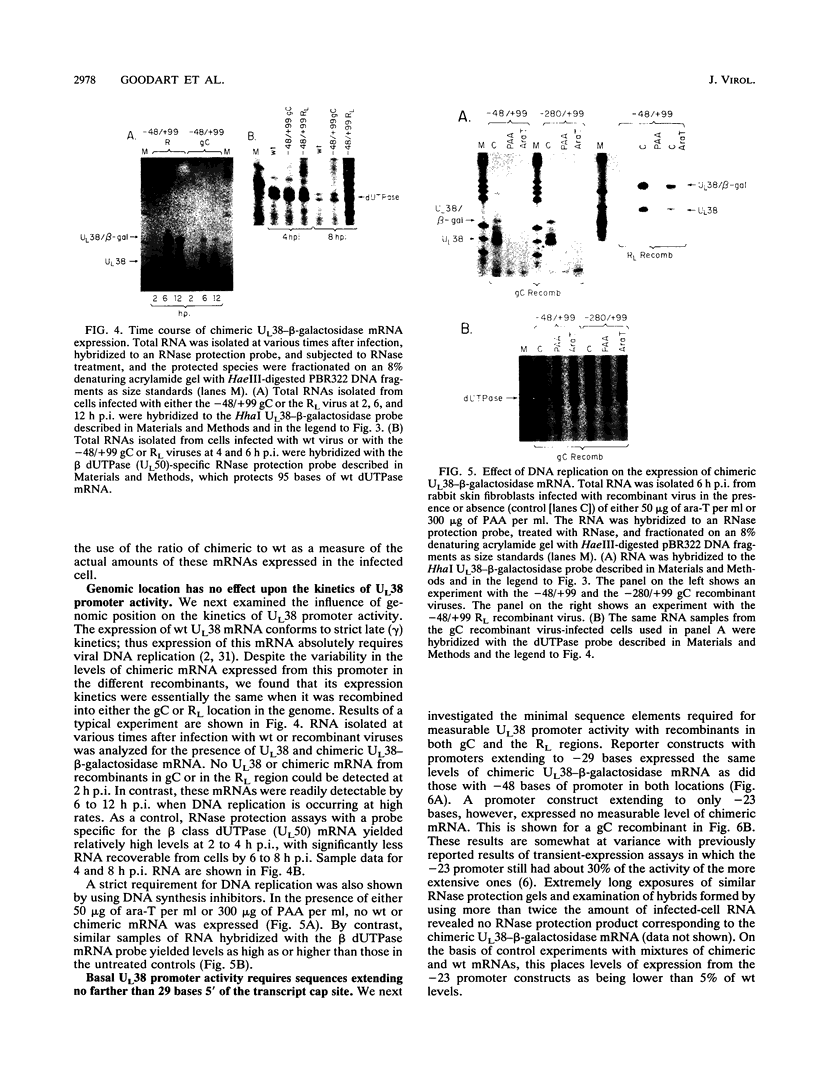
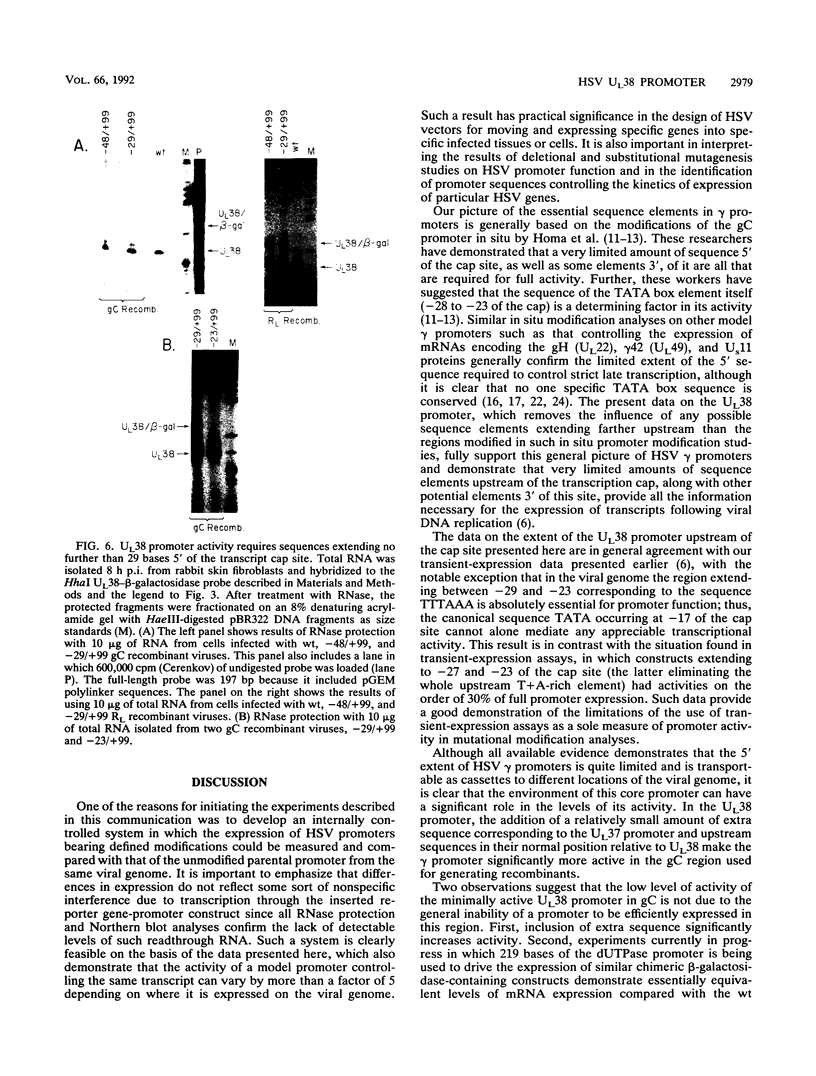
To examine the effect of genomic location on the details of expression of selected herpes simplex virus promoters, we have constructed recombination vectors for placing such promoters controlling the beta-galactosidase reporter gene into two regions of the viral genome lacking any nearby promoter or regulatory elements. The first vector generates the promoter-beta-galactosidase reporter gene inverted within the locus of the gC (UL44) translational reading frame; the second replaces the LAT promoter and the first 600 bases of the primary transcript in both copies of the RL region. These locations were chosen to obviate any possible influence of upstream but noncontiguous heterologous or homologous DNA sequence elements upon promoter activity. When the reporter gene controlled by the strict late (gamma) UL38 promoter was placed in the gC location, it was significantly less active than in its normal location; in contrast, promoter activity was comparable to wild-type values when the promoter was recombined into the RL region. The low level of activity in the gC location could be partially alleviated by the incorporation of additional DNA sequences upstream of the UL38 promoter. Despite the effect of genomic location upon the level of expression, the kinetics of expression in either location mirrors the wild-type UL38 strict late kinetics of expression. Finally, we used deletional analysis to demonstrate that no more than 29 bases of DNA sequence 5' of the mRNA cap site are required for promoter activity in either location; this result is consistent with earlier results of transient-expression assays and indicates that the UL38 promoter shares general features with other strict late (gamma) herpes simplex virus promoters.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. P., Costa R. H., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA present in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):9–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.9-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Frink R. J., Devi G. B., Gaylord B. H., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Detailed characterization of the mRNA mapping in the HindIII fragment K region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1011–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1011-1027.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair E. D., Blair C. C., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus virion stimulatory protein mRNA leader contains sequence elements which increase both virus-induced transcription and mRNA stability. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2499–2508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2499-2508.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson A. T., Sederati F., Devi-Rao G., Flanagan W. M., Farrell M. J., Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Feldman L. T. Identification of the latency-associated transcript promoter by expression of rabbit beta-globin mRNA in mouse sensory nerve ganglia latently infected with a recombinant herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3844–3851. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3844-3851.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper K. G., Devi-Rao G., Costa R. H., Blair E. D., Thompson R. L., Wagner E. K. Characterization of the genes encoding herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 alkaline exonucleases and overlapping proteins. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1023–1036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1023-1036.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Rice M., Hecht L. B., Silverstein S., Wagner E. K. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter controlling the expression of UL38, a true late gene involved in capsid assembly. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):769–786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.769-786.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Wagner E. K. A bi-functional reporter plasmid for the simultaneous transient expression assay of two herpes simplex virus promoters. Virus Genes. 1987 Nov;1(1):61–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00125686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Shipman C., Jr, Wagner E. K. Viral DNA synthesis is required for the efficient expression of specific herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA species. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):10–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. A specific 15-bp TATA box promoter element is required for expression of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):40–53. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Otal T. M., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Transcriptional control signals of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) gene lie within bases -34 to +124 relative to the 5' terminus of the mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3652–3666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbalzano A. N., Shepard A. A., DeLuca N. A. Functional relevance of specific interactions between herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4 and sequences from the promoter-regulatory domain of the viral thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2620–2631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2620-2631.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Everett R. D. The control of herpes simplex virus type-1 late gene transcription: a 'TATA-box'/cap site region is sufficient for fully efficient regulated activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8247–8264. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., MacLean C., Marsden H. S., Dalziel R. G., Everett R. D. The product of gene US11 of herpes simplex virus type 1 is expressed as a true late gene. J Gen Virol. 1986 May;67(Pt 5):871–883. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-5-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J. The genomes of the human herpesviruses: contents, relationships, and evolution. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:235–265. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.001315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roemer K., Johnson P. A., Friedmann T. Activity of the simian virus 40 early promoter-enhancer in herpes simplex virus type 1 vectors is dependent on its position, the infected cell type, and the presence of Vmw175. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6900–6912. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6900-6912.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Regulation of the herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) glycoprotein C gene: sequences between base pairs -34 to +29 control transient expression and responsiveness to transactivation by the products of the immediate early (alpha) 4 and 0 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3097–3111. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Johnson D. C., Pizer L. I., Everett R. D. The ICP4 binding sites in the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D (gD) promoter are not essential for efficient gD transcription during virus infection. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):623–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.623-631.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffy K. R., Weir J. P. Upstream promoter elements of the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein H gene. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):972–975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.972-975.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder D. G., Everett R. D., Wilcox K. W., Beard P., Pizer L. I. ICP4-binding sites in the promoter and coding regions of the herpes simplex virus gD gene contribute to activation of in vitro transcription by ICP4. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2510–2520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2510-2520.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G., Feldman L. T., Dobson A. T., Zhang Y. F., Flanagan W. M., Stevens J. G. Physical characterization of the herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript in neurons. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1194–1202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1194-1202.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Flanagan W. M., Devi-Rao G., Zhang Y. F., Hill J. M., Anderson K. P., Stevens J. G. The herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript is spliced during the latent phase of infection. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4577–4585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4577-4585.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls establish the cascade of herpes simplex virus protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):819–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. F., Devi-Rao G. B., Rice M., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Wagner E. K. The effect of elevated levels of herpes simplex virus alpha-gene products on the expression of model early and late genes in vivo. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. F., Wagner E. K. The kinetics of expression of individual herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts. Virus Genes. 1987 Nov;1(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00125685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]