Abstract
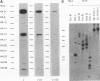
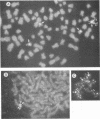
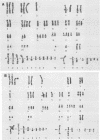
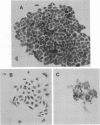
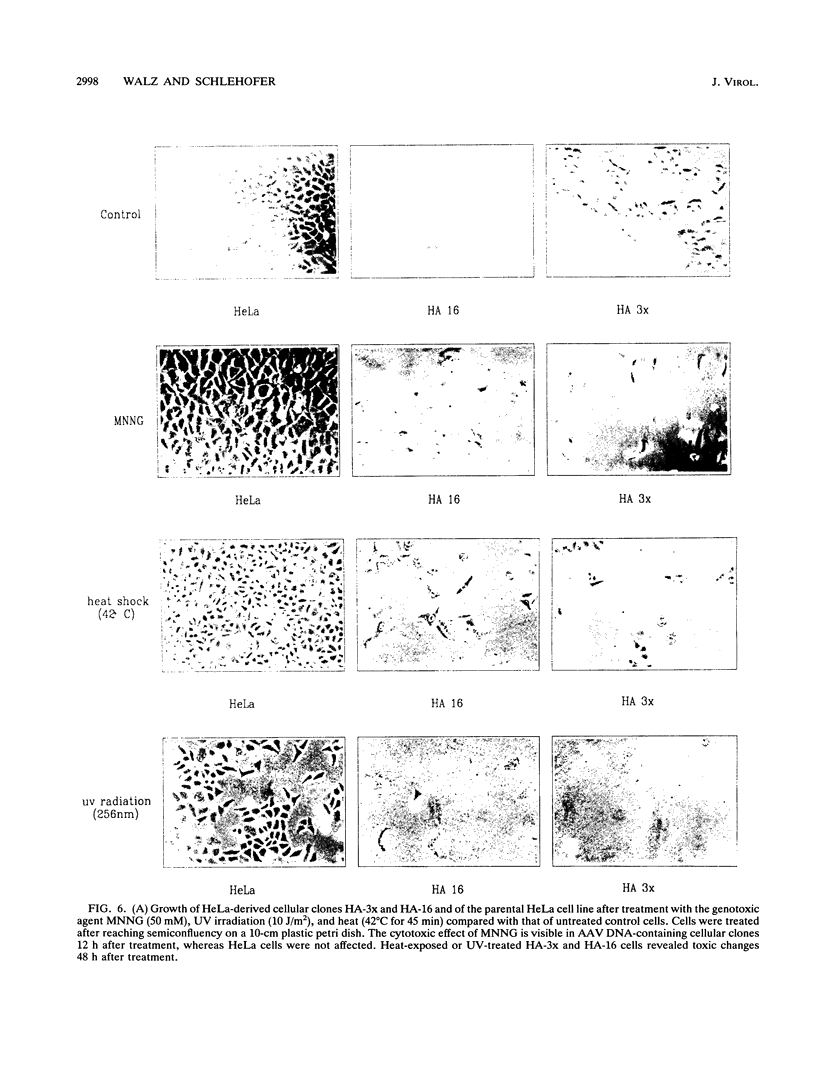
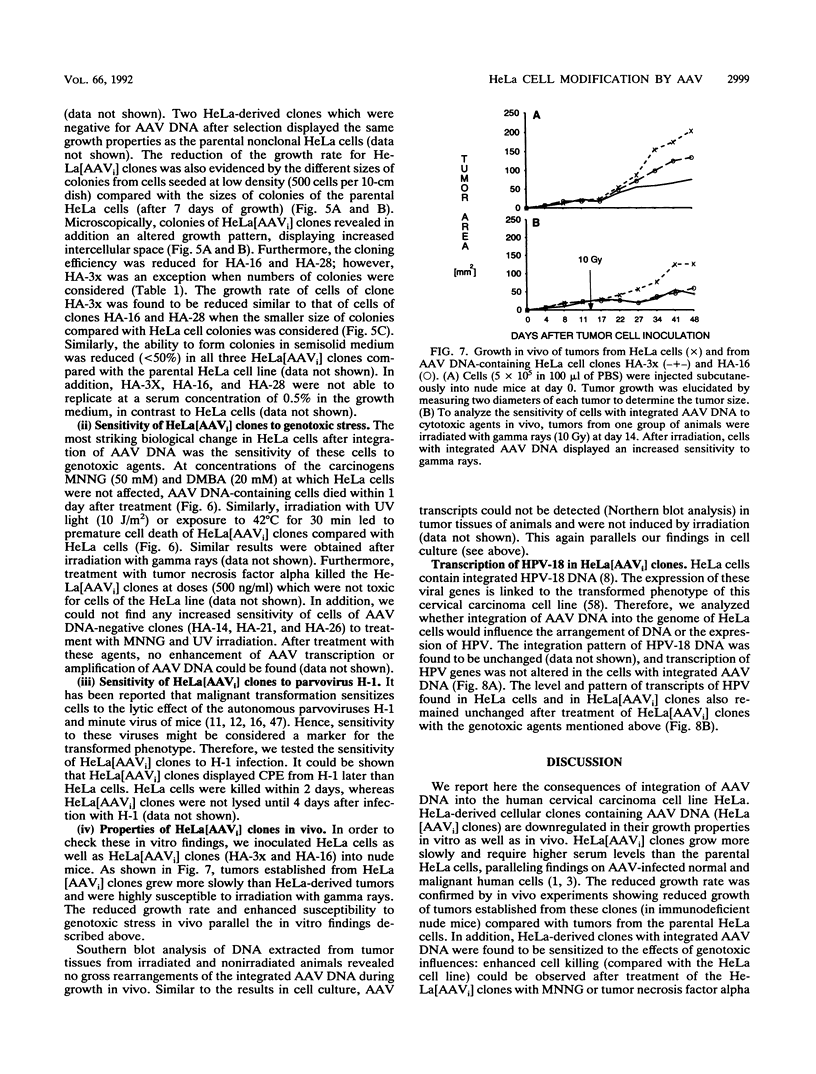
Parvoviruses are known to interfere with cellular transformation and carcinogenesis. Since infecting adeno-associated virus (AAV) frequently integrates its DNA into the cellular genome, we analyzed whether this integration influences the transformed phenotype of the human tumor cell line HeLa. Analysis of three independent HeLa cell clones with integrated AAV DNA (HA-3x, HA-16, and HA-28) revealed the following phenotypic changes of these cells: (i) reduced growth rate, (ii) increased serum requirement, (iii) reduced capacity for colony formation in soft agar, (iv) reduced cloning efficiency on plastic, (v) elevated sensitivity to genotoxic agents (N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene, human tumor necrosis factor alpha, UV irradiation [256 nm], and heat [42 degrees C]), and (vi) reduced sensitivity to the cytolytic effect of parvovirus H-1. Reduced growth rate and enhanced sensitivity to gamma irradiation were also observed in vivo when tumors from AAV DNA-containing HeLa cells were transplanted into nude mice. This alteration of the biological properties of HeLa cells was independent of the number of AAV genomes integrated, the physical structure of integrated AAV DNA, and the transcription of AAV genes. Integration of AAV DNA was found to occur preferentially on the long arm of chromosome 17 in the three HeLa cell clones analyzed. These findings demonstrate that genomic integration of AAV DNA can alter the biological properties of human tumor cells.
Full text
PDF

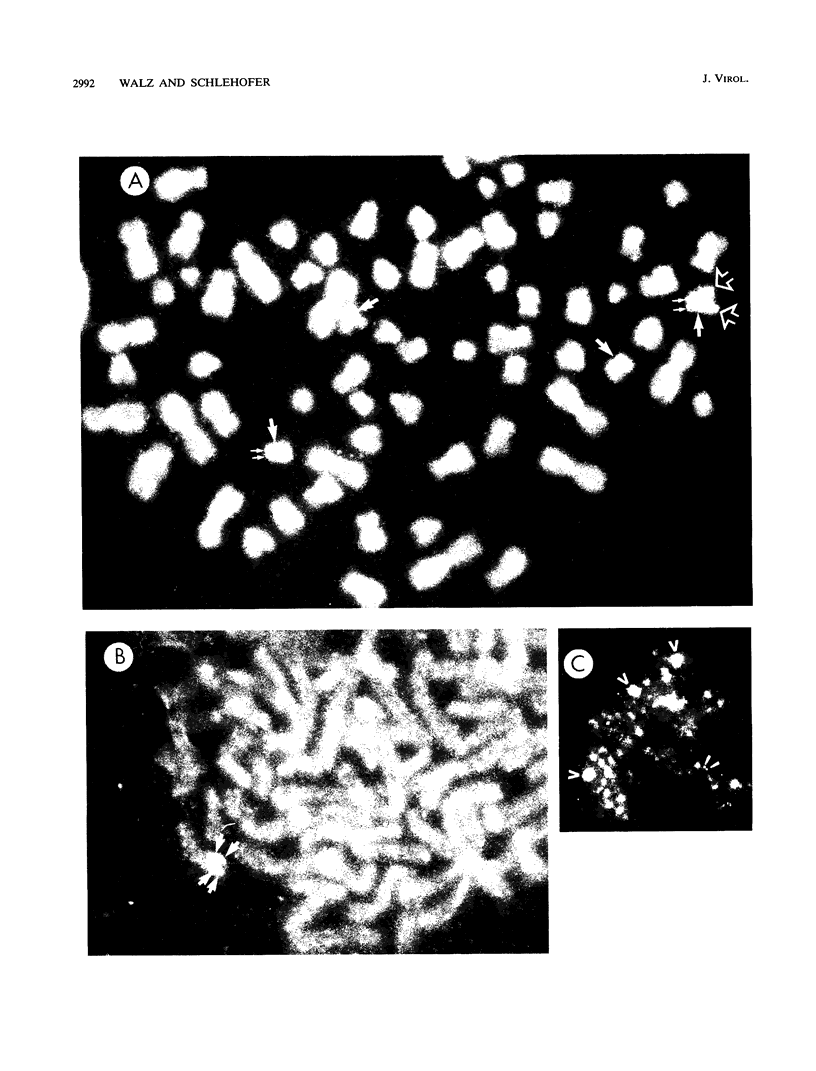


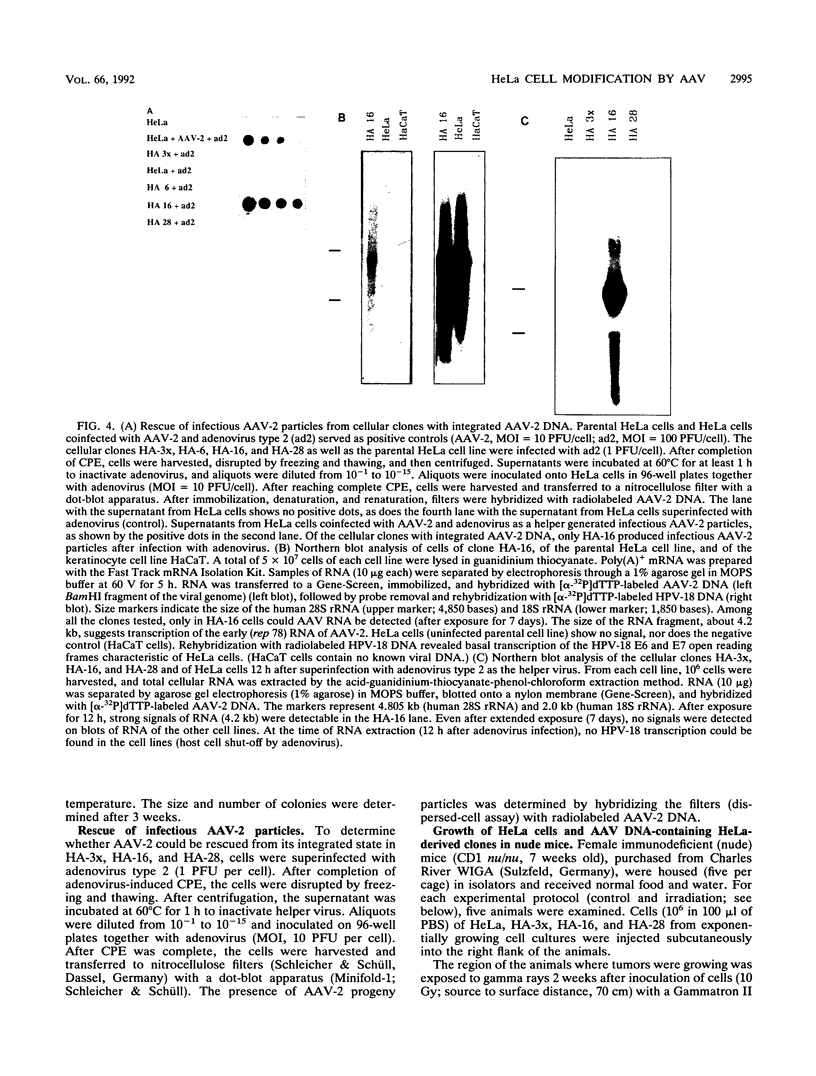
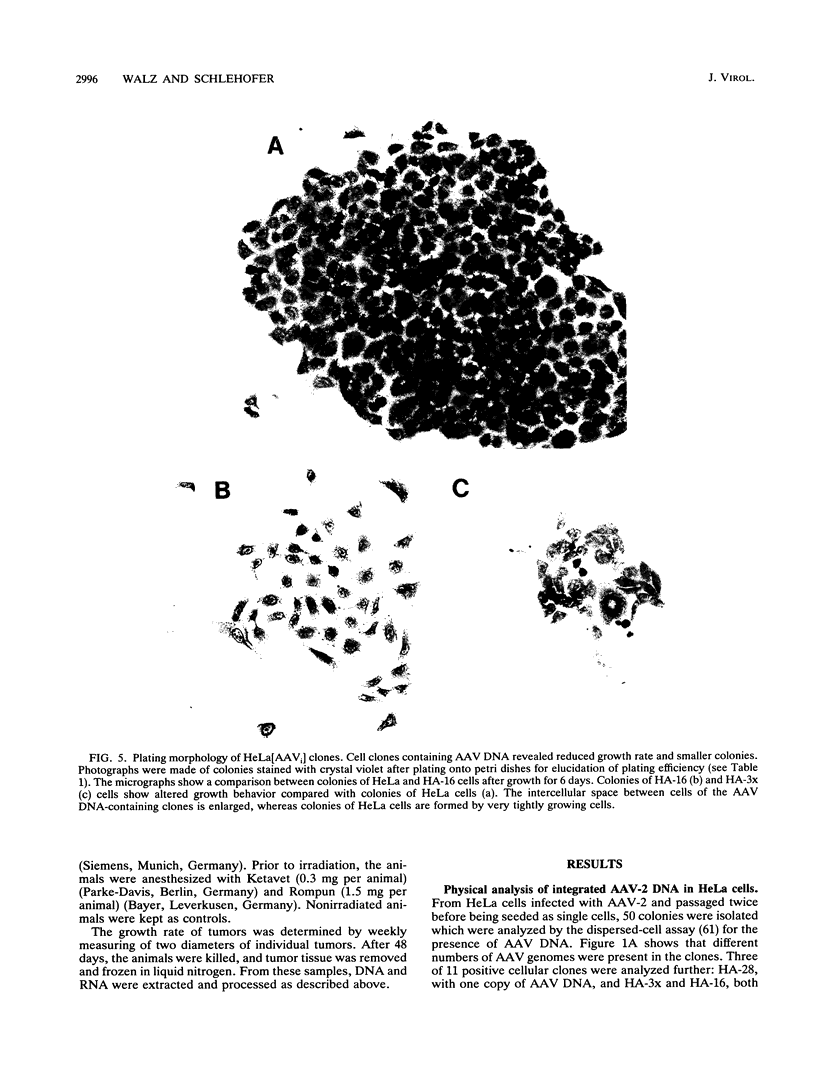




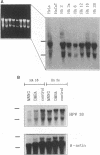
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bantel-Schaal U. Adeno-associated parvoviruses inhibit growth of cells derived from malignant human tumors. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jan 15;45(1):190–194. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantel-Schaal U. Infection with adeno-associated parvovirus leads to increased sensitivity of mammalian cells to stress. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):260–268. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90669-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantel-Schaal U., Stöhr M. Influence of adeno-associated virus on adherence and growth properties of normal cells. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):773–779. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.773-779.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benchimol S., Lamb P., Crawford L. V., Sheer D., Shows T. B., Bruns G. A., Peacock J. Transformation associated p53 protein is encoded by a gene on human chromosome 17. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Sep;11(5):505–510. doi: 10.1007/BF01534845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Bohenzky R. A. Adeno-associated viruses: an update. Adv Virus Res. 1987;32:243–306. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Hauswirth W. W. Adeno-associated viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1979;25:407–449. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklow N. R., Hoggan M. D., Sereno M. S., Brandt C. D., Kim H. W., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. A seroepidemiologic study of adenovirus-associated virus infection in infants and children. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Oct;94(4):359–366. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boukamp P., Petrussevska R. T., Breitkreutz D., Hornung J., Markham A., Fusenig N. E. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):761–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casto B. C., Goodheart C. R. Inhibition of adenovirus transformation in vitro by AAV-1. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 May;140(1):72–78. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. Q., Tuynder M. C., Cornelis J. J., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Rommelaere J. Sensitization of human keratinocytes to killing by parvovirus H-1 takes place during their malignant transformation but does not require them to be tumorigenic. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Jan;10(1):163–167. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. Q., de Foresta F., Hertoghs J., Avalosse B. L., Cornelis J. J., Rommelaere J. Selective killing of simian virus 40-transformed human fibroblasts by parvovirus H-1. Cancer Res. 1986 Jul;46(7):3574–3579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K., Hoggan M. D., Hauswirth W. W., Berns K. I. Integration of the adeno-associated virus genome into cellular DNA in latently infected human Detroit 6 cells. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):739–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.739-748.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R., Kibrick S., Swan I. C. Effect of adeno-associated virus on cancer expression by herpesvirus-transformed hamster cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Oct;55(4):957–959. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.4.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georg-Fries B., Biederlack S., Wolf J., zur Hausen H. Analysis of proteins, helper dependence, and seroepidemiology of a new human parvovirus. Virology. 1984 Apr 15;134(1):64–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa H., Shiroki K., Shimojo H. Establishment and characterization of KB cell lines latently infected with adeno-associated virus type 1. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):84–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbronn R., Bürkle A., Stephan S., zur Hausen H. The adeno-associated virus rep gene suppresses herpes simplex virus-induced DNA amplification. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3012–3018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3012-3018.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbronn R., Schlehofer J. R., zur Hausen H. Selective killing of carcinogen-treated SV40-transformed Chinese hamster cells by a defective parvovirus. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):439–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry C. J. Adenovirus-associated (satellite) viruses. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1973;18:273–293. doi: 10.1159/000393171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L. The adeno-associated virus Rep78 gene inhibits cellular transformation induced by bovine papillomavirus. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Carter B. J. Effect of adeno-associated virus on transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by ras gene and on tumorigenicity of an NIH 3T3 transformed cell line. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):3023–3026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschstein R. L., Smith K. O., Peters E. A. Inhibition of adenovirus 12 oncogenicity by adeno-associated virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jul;128(3):670–673. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Berns K. I. Organization of adeno-associated virus DNA in latently infected Detroit 6 cells. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):460–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Menninger J. C., Ward D. C., Berns K. I. Mapping and direct visualization of a region-specific viral DNA integration site on chromosome 19q13-qter. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):831–834. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90470-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Siniscalco M., Samulski R. J., Zhu X. D., Hunter L., Laughlin C. A., McLaughlin S., Muzyczka N., Rocchi M., Berns K. I. Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2211–2215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin C. A., Cardellichio C. B., Coon H. C. Latent infection of KB cells with adeno-associated virus type 2. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):515–524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.515-524.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Cremer T., Borden J., Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Delineation of individual human chromosomes in metaphase and interphase cells by in situ suppression hybridization using recombinant DNA libraries. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):224–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01790090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor H. D., Drake S., Stahmann J., Mumford D. M. Antibodies to adeno-associated satellite virus and herpes simplex in sera from cancer patients and normal adults. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Sep 1;126(1):100–104. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(76)90472-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor H. D., Houlditch G. S., Mumford D. M. Influence of adeno-associated satellite virus on adenovirus-induced tumours in hamsters. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 10;241(106):44–46. doi: 10.1038/newbio241044b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Merry D., Givol D. The gene for human p53 cellular tumor antigen is located on chromosome 17 short arm (17p13). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):130–134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Mohandas T., Wolf D., Prokocimer M., Rotter V., Koeffler H. P. Human p53 gene localized to short arm of chromosome 17. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):783–784. doi: 10.1038/319783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahreini P., Srivastava A. Rescue and replication of the adeno-associated virus 2 genome in mortal and immortal human cells. Intervirology. 1989;30(2):74–85. doi: 10.1159/000150078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrove J. M., Duckworth D. H., Berns K. I. Inhibition of adenovirus-transformed cell oncogenicity by adeno-associated virus. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Cornelis J. J. Antineoplastic activity of parvoviruses. J Virol Methods. 1991 Aug;33(3):233–251. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90024-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salome N., van Hille B., Geuskens M., Rommelaere J. Partial reversion of conditional transformation correlates with a decrease in the sensitivity of rat cells to killing by the parvovirus minute virus of mice but not in their capacity for virus production: effect of a temperature-sensitive v-src oncogene. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4797–4807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4797-4807.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Helper-free stocks of recombinant adeno-associated viruses: normal integration does not require viral gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3822–3828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3822-3828.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Srivastava A., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Rescue of adeno-associated virus from recombinant plasmids: gene correction within the terminal repeats of AAV. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Zhu X., Xiao X., Brook J. D., Housman D. E., Epstein N., Hunter L. A. Targeted integration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) into human chromosome 19. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3941–3950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlehofer J. R., Ehrbar M., zur Hausen H. Vaccinia virus, herpes simplex virus, and carcinogens induce DNA amplification in a human cell line and support replication of a helpervirus dependent parvovirus. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlehofer J. R., Heilbronn R., Georg-Fries B., zur Hausen H. Inhibition of initiator-induced SV40 gene amplification in SV40-transformed Chinese hamster cells by infection with a defective parvovirus. Int J Cancer. 1983 Nov 15;32(5):591–595. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlehofer J. R., Heilbronn R. Infection with adeno-associated virus type 5 inhibits mutagenicity of herpes simplex virus type 1 or 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide. Mutat Res. 1990 Aug;244(4):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(90)90079-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt J., Schlehofer J. R., Mergener K., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Amplification of bovine papillomavirus DNA by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, ultraviolet irradiation, or infection with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprecher-Goldberger S., Thiry L., Lefébvre N., Dekegel D., de Halleux F. Complement-fixation antibodies to adenovirus-associated viruses, cytomegaloviruses and herpes simplex viruses in patients with tumors and in control individuals. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Oct;94(4):351–358. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustacelebi S., Williams J. F. Temperature-sensitive mutants of adenovirus defective in interferon induction at non-permissive temperature. Nature. 1972 Jan 7;235(5332):52–53. doi: 10.1038/235052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Callaham M. F., Huberman E. Perturbation of the cell cycle by adeno-associated virus. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Keshet I. Indiscriminate recombination in simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4861–4865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalkinoglu A. O., Schlehofer J. R., zur Hausen H. Inhibition of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced methotrexate and adriamycin resistance in CHO cells by adeno-associated virus type 2. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jun 15;45(6):1195–1203. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalkinoglu A. O., Zentgraf H., Hübscher U. Origin of adeno-associated virus DNA replication is a target of carcinogen-inducible DNA amplification. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3175–3184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3175-3184.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Maza L. M., Carter B. J. Inhibition of adenovirus oncogenicity in hamsters by adeno-associated virus DNA. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Dec;67(6):1323–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Bauknecht T., Bartsch D., zur Hausen H. Influence of chromosomal integration on glucocorticoid-regulated transcription of growth-stimulating papillomavirus genes E6 and E7 in cervical carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]