Abstract
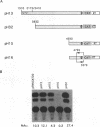
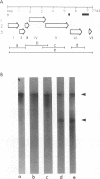
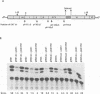
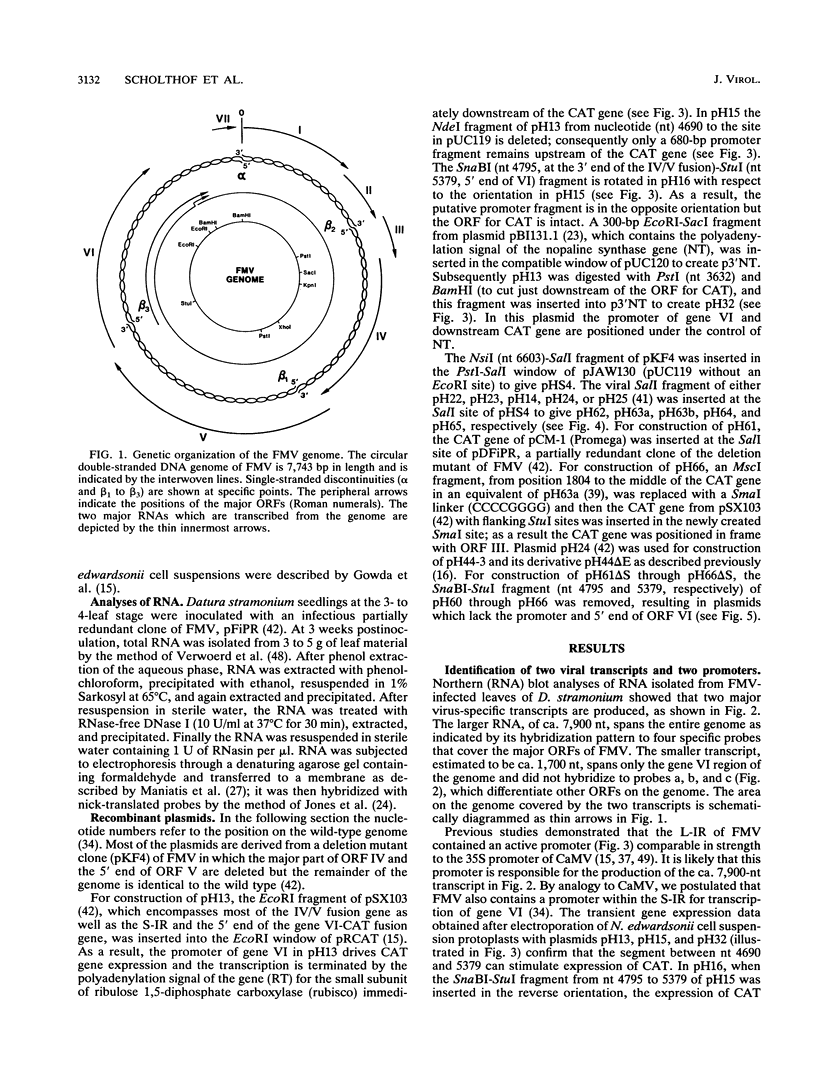
Gene expression of figwort mosaic virus (FMV), a caulimovirus, was investigated by electroporation of Nicotiana edwardsonii cell suspension protoplasts with cloned viral constructs in which a reporter gene was inserted at various positions on the genome. The results showed that the genome of FMV contains two promoters; one is used for the production of a full-length RNA and another initiates synthesis of a separate monocistronic RNA for gene VI. Evidence is provided that the full-length transcript, the probable template for reverse transcription, can serve as a polycistronic mRNA for translation of genes I through V and perhaps also gene VI. Expression of all the genes on the polycistronic mRNA is trans activated by the gene VI protein. Reporter gene expression appears most efficient when its start codon is in close proximity to the stop codon of the preceding gene, as for the native genes of caulimoviruses. We propose that the gene VI product enables expression of the polycistronic mRNA by promoting reinitiation of ribosomes to give translational coupling of individual genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughman G., Howell S. H. Cauliflower mosaic virus 35 S RNA leader region inhibits translation of downstream genes. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneville J. M., Sanfaçon H., Fütterer J., Hohn T. Posttranscriptional trans-activation in cauliflower mosaic virus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1135–1143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90769-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Pryciak P., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Biosynthesis of the reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B viruses involves de novo translational initiation not ribosomal frameshifting. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):364–368. doi: 10.1038/337364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N., Lomonossoff G. P., Hull R. Characterisation of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA sequences which encode major polyadenylated transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6735–6747. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L. K., Hohn T. Initiation of translation of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome from a polycistronic mRNA: evidence from deletion mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2731–2736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fütterer J., Gordon K., Pfeiffer P., Sanfaçon H., Pisan B., Bonneville J. M., Hohn T. Differential inhibition of downstream gene expression by the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA leader. Virus Genes. 1989 Sep;3(1):45–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00301986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fütterer J., Gordon K., Sanfaçon H., Bonneville J. M., Hohn T. Positive and negative control of translation by the leader sequence of cauliflower mosaic virus pregenomic 35S RNA. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1697–1707. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fütterer J., Hohn T. Translation of a polycistronic mRNA in the presence of the cauliflower mosaic virus transactivator protein. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3887–3896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. C., Howarth A. J., Hahn P., Brown-Luedi M., Shepherd R. J., Messing J. The complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of cauliflower mosaic virus by M13mp7 shotgun sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2871–2888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowda S., Scholthof H. B., Wu F. C., Shepherd R. J. Requirement of gene VII in cis for the expression of downstream genes on the major transcript of figwort mosaic virus. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):867–871. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90561-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowda S., Wu F. C., Scholthof H. B., Shepherd R. J. Gene VI of figwort mosaic virus (caulimovirus group) functions in posttranscriptional expression of genes on the full-length RNA transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9203–9207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Dudley R. K., Jonard G., Balàzs E., Richards K. E. Transcription of Cauliflower mosaic virus DNA: detection of promoter sequences, and characterization of transcripts. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):763–773. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa A., Verver J., Shimada A., Saito M., Goldbach R., Van Kammen A., Miki K., Kameya-Iwaki M., Hibi T. The complete sequence of soybean chlorotic mottle virus DNA and the identification of a novel promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9993–10013. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Takatsuji H., Ubasawa A., Ikeda J. E. Site-specific deletion in cauliflower mosaic virus DNA: possible involvement of RNA splicing and reverse transcription. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1673–1680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Sadler J., Longstaff M. The sequence of carnation etched ring virus DNA: comparison with cauliflower mosaic virus and retroviruses. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3083–3090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. W., Jackson A. O., Morris T. J. Defective-interfering RNAs and elevated temperatures inhibit replication of tomato bushy stunt virus in inoculated protoplasts. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):539–545. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90024-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D. X., Cavanagh D., Green P., Inglis S. C. A polycistronic mRNA specified by the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):531–544. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90423-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Taylor J. M., Hull R. Retroid virus genome replication. Adv Virus Res. 1987;32:35–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60474-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medberry S. L., Lockhart B. E., Olszewski N. E. Properties of Commelina yellow mottle virus's complete DNA sequence, genomic discontinuities and transcript suggest that it is a pararetrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5505–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Subramani S., Berg P. Effect of upstream reading frames on translation efficiency in simian virus 40 recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2704–2711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penswick J., Hübler R., Hohn T. A viable mutation in cauliflower mosaic virus, a retroviruslike plant virus, separates its capsid protein and polymerase genes. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1460–1463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1460-1463.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant A. L., Covey S. N., Grierson D. Detection of a subgenomic mRNA for gene V, the putative reverse transcriptase gene of cauliflower mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8305–8321. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richins R. D., Scholthof H. B., Shepherd R. J. Sequence of figwort mosaic virus DNA (caulimovirus group). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8451–8466. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A. Regulation of HIV gene expression by RNA-protein interactions. Trends Genet. 1991 Jan;7(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90015-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Polycistronic animal virus mRNAs. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1989;37:127–153. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6603(08)60697-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger M., Daubert S., Goodman R. M. Characteristics of a strong promoter from figwort mosaic virus: comparison with the analogous 35S promoter from cauliflower mosaic virus and the regulated mannopine synthase promoter. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Mar;14(3):433–443. doi: 10.1007/BF00028779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholelz J. E., Shepherd R. J. Host range control of cauliflower mosaic virus. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):30–37. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholthof H. B., Wu F. C., Richins R. D., Shepherd R. J. A naturally occurring deletion mutant of figwort mosaic virus (caulimovirus) is generated by RNA splicing. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):290–298. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90845-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultze M., Hohn T., Jiricny J. The reverse transcriptase gene of cauliflower mosaic virus is translated separately from the capsid gene. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1177–1185. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Marciniak R. A. HIV TAR: an RNA enhancer? Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd N. A., Jass J. R. Neuromuscular and vascular hamartoma of the small intestine: is it Crohn's disease? Gut. 1987 Dec;28(12):1663–1668. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.12.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Reverse transcription in the eukaryotic genome: retroviruses, pararetroviruses, retrotransposons, and retrotranscripts. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):455–468. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwoerd T. C., Dekker B. M., Hoekema A. A small-scale procedure for the rapid isolation of plant RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2362–2362. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]