Abstract
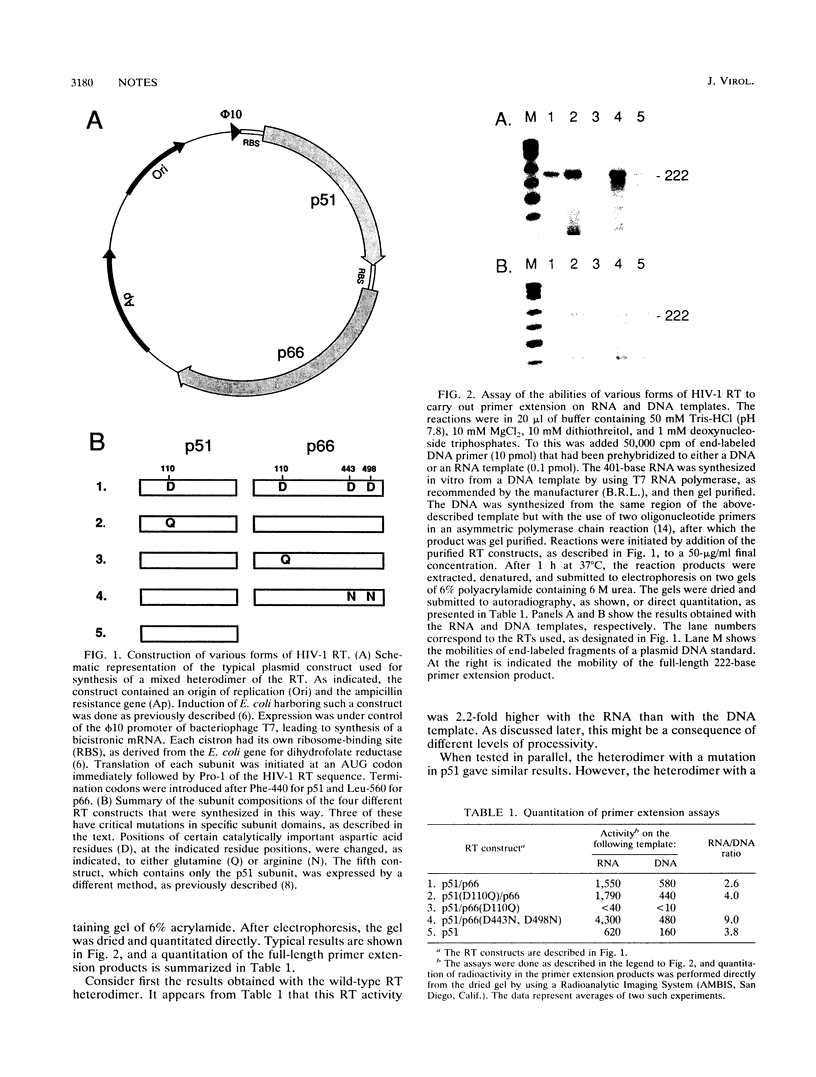
From an in vitro analysis of the DNA-synthesizing abilities of certain specifically mutated forms of the heterodimeric reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, we can conclude that in a heterodimer, the functionality of p66 is necessary while the functionality of the p51 subunit is not needed. Conversely, p51 is not able to catalyze DNA synthesis when associated with p66, and yet when the p66 protein is absent, p51 can function. These conclusions applied to DNA synthesis on heteropolymeric RNA and DNA templates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng N., Painter G. R., Furman P. A. Crosslinking of substrates occurs exclusively to the p66 subunit of heterodimeric HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):785–789. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91486-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. F., 2nd, Hostomska Z., Hostomsky Z., Jordan S. R., Matthews D. A. Crystal structure of the ribonuclease H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):88–95. doi: 10.1126/science.1707186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P. Retroviral reverse transcriptase: synthesis, structure, and function. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(8):817–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostomska Z., Matthews D. A., Davies J. F., 2nd, Nodes B. R., Hostomsky Z. Proteolytic release and crystallization of the RNase H domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14697–14702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostomsky Z., Appelt K., Ogden R. C. High-level expression of self-processed HIV-1 protease in Escherichia coli using a synthetic gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 30;161(3):1056–1063. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91350-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostomsky Z., Hostomska Z., Hudson G. O., Moomaw E. W., Nodes B. R. Reconstitution in vitro of RNase H activity by using purified N-terminal and C-terminal domains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1148–1152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. C., Court D. L., Zweig M., Levin J. G. Murine leukemia virus pol gene products: analysis with antisera generated against reverse transcriptase and endonuclease fusion proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):267–274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.267-274.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., McCoy J. M., Seehra J. S., Richardson C. C. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 reverse transcriptase. Template binding, processivity, strand displacement synthesis, and template switching. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4669–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L., Darby G. Site-specific mutagenesis of AIDS virus reverse transcriptase. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):716–717. doi: 10.1038/327716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grice S. F., Naas T., Wohlgensinger B., Schatz O. Subunit-selective mutagenesis indicates minimal polymerase activity in heterodimer-associated p51 HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3905–3911. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04960.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoote M. M., Coligan J. E., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Martin M. A., Venkatesan S. Structural characterization of reverse transcriptase and endonuclease polypeptides of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):771–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.771-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi V., Usdin M. T., Harington A., Dudding L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis of the conserved Asp-443 and Asp-498 carboxy-terminal residues of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5359–5363. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Restle T., Weiss S., Gautel M., Sczakiel G., Goody R. S. Co-expression of the subunits of the heterodimer of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):13975–13978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restle T., Müller B., Goody R. S. Dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. A target for chemotherapeutic intervention. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):8986–8988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Warren T. C., Adams J., Proudfoot J., Skiles J., Raghavan P., Perry C., Potocki I., Farina P. R., Grob P. M. A novel dipyridodiazepinone inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase acts through a nonsubstrate binding site. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2022–2026. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Marzo Veronese F., Copeland T. D., DeVico A. L., Rahman R., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of highly immunogenic p66/p51 as the reverse transcriptase of HTLV-III/LAV. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1289–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.2418504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]