Abstract
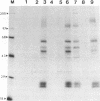
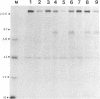
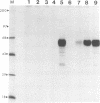
Glycoproteins gp50, gII, and gIII of pseudorabies virus (PRV) were expressed either individually or in combination by vaccinia virus recombinants. In vitro analysis by immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence demonstrated the expression of a gII protein of approximately 120 kDa that was proteolytically processed to the gIIb (67- to 74-kDa) and gIIc (58-kDa) mature protein species similar to those observed in PRV-infected cells. Additionally, the proper expression of the 90-kDa gIII and 50-kDa gp50 was observed. All three of these PRV-derived glycoproteins were detectable on the surface of vaccinia virus-PRV recombinant-infected cells. In vivo, mice were protected against a virulent PRV challenge after immunization with the PRV glycoprotein-expressing vaccinia virus recombinants. The coexpression of gII and gIII by a single vaccinia virus recombinant resulted in a significantly reduced vaccination dose required to protect mice against PRV challenge. Inoculation of piglets with the various vaccinia virus-PRV glycoprotein recombinants also resulted in protection against virulent PRV challenge as measured by weight gain. The simultaneous expression of gII and gp50 in swine resulted in a significantly enhanced level of protection as evaluated by weight evolution following challenge with live PRV.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., DeMarchi J. M., Lomniczi B., Kaplan A. S. Role of glycoproteins of pseudorabies virus in eliciting neutralizing antibodies. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., DeMarchi J., Pendrys J., Veach R. A., Kaplan A. S. Proteins specified by the short unique region of the genome of pseudorabies virus play a role in the release of virions from certain cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):191–196. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.191-196.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Synthesis of proteins in cells infected with herpesvirus. V. Viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1970 Jun;41(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Rixon F. J., Blankenship M. L. Analysis of the structure of the genome of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90484-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. Two spontaneously transformed cell lines derived from the same hamster embryo culture. Int J Cancer. 1967 Mar 15;2(2):143–152. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eloit M., Fargeaud D., L'Haridon R., Toma B. Identification of the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gp50 as a major target of neutralizing antibodies. Arch Virol. 1988;99(1-2):45–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01311022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs W., Rziha H. J., Lukàcs N., Braunschweiger I., Visser N., Lütticken D., Schreurs C. S., Thiel H. J., Mettenleiter T. C. Pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gI: in vitro and in vivo analysis of immunorelevant epitopes. J Gen Virol. 1990 May;71(Pt 5):1141–1151. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-5-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Santos R. E., Spear P. G. Neutralizing antibodies specific for glycoprotein H of herpes simplex virus permit viral attachment to cells but prevent penetration. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3435–3443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3435-3443.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel S. J., Johnson G. P., Perkus M. E., Davis S. W., Winslow J. P., Paoletti E. The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):247-66, 517-63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gompels U. A., Minson A. C. Antigenic properties and cellular localization of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein H synthesized in a mammalian cell expression system. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4744–4755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4744-4755.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo P. X., Goebel S., Davis S., Perkus M. E., Languet B., Desmettre P., Allen G., Paoletti E. Expression in recombinant vaccinia virus of the equine herpesvirus 1 gene encoding glycoprotein gp13 and protection of immunized animals. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4189–4198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4189-4198.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo P. X., Goebel S., Perkus M. E., Taylor J., Norton E., Allen G., Languet B., Desmettre P., Paoletti E. Coexpression by vaccinia virus recombinants of equine herpesvirus 1 glycoproteins gp13 and gp14 results in potentiated immunity. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2399–2406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2399-2406.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad R. S., Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Depletion of glycoprotein gp85 from virosomes made with Epstein-Barr virus proteins abolishes their ability to fuse with virus receptor-bearing cells. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):4998–5005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.4998-5005.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias G., Molitor T., Reed D., L'Italien J. Antibodies to Aujeszky's disease virus in pigs immunized with purified virus glycoproteins. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Jul;24(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90045-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii H., Kobayashi Y., Kuroki M., Kodama Y. Protection of mice from lethal infection with Aujeszky's disease virus by immunization with purified gVI. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1411–1414. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. M., Davison A. J., Lowe R. S., Riemen M. W., Ellis R. W. Identification and sequence of the gene encoding gpIII, a major glycoprotein of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):526–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90295-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensinger M., Eskew M. L., Scheuchenzuber W., Zarkower A. Porcine effector mechanisms: antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of pseudorabies-infected target cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Mar;14(3):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(87)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killington R. A., Yeo J., Honess R., Watson D. H., Duncan B. E., Halliburton I. W., Mumford J. Comparative analyses of the proteins and antigens of five herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Nov;37(2):297–310. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-2-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klupp B. G., Mettenleiter T. C. Sequence and expression of the glycoprotein gH gene of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):732–741. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90614-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost T. A., Jones E. V., Smith K. M., Reed A. P., Brown A. L., Miller T. J. Biological evaluation of glycoproteins mapping to two distinct mRNAs within the BamHI fragment 7 of pseudorabies virus: expression of the coding regions by vaccinia virus. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukàcs N., Thiel H. J., Mettenleiter T. C., Rziha H. J. Demonstration of three major species of pseudorabies virus glycoproteins and identification of a disulfide-linked glycoprotein complex. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):166–173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.166-173.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Post L. E. Evaluation of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gp50 as a vaccine for Aujeszky's disease in mice and swine: expression by vaccinia virus and Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3977–3982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3977-3982.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Wardley R. C., Thomsen D. R., Post L. E. A vaccine strain of pseudorabies virus with deletions in the thymidine kinase and glycoprotein X genes. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Nov;48(11):1577–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchioli C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Timmins J. G., Post L. E., Young B. R., Povendo D. A. Protection of mice and swine from pseudorabies virus-induced mortality by administration of pseudorabies virus-specific mouse monoclonal antibodies. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jun;49(6):860–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Wardley R. C. Natural cytotoxicity detected in swine using Aujeszky's disease virus infected targets. Res Vet Sci. 1984 Sep;37(2):211–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C. Glycoprotein gIII deletion mutants of pseudorabies virus are impaired in virus entry. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):623–625. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90635-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lukacs N., Rziha H. J. Mapping of the structural gene of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein A and identification of two non-glycosylated precursor polypeptides. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.52-57.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lukàcs N., Rziha H. J. Pseudorabies virus avirulent strains fail to express a major glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):307–311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.307-311.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lukàcs N., Thiel H. J., Schreurs C., Rziha H. J. Location of the structural gene of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein complex gII. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Zsak L., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Kern H., Ben-Porat T. Interaction of glycoprotein gIII with a cellular heparinlike substance mediates adsorption of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.278-286.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N., Hutt-Fletcher L. M. A monoclonal antibody to glycoprotein gp85 inhibits fusion but not attachment of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2366–2372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2366-2372.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggeridge M. I., Wilcox W. C., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. Identification of a site on herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D that is essential for infectivity. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3617–3626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3617-3626.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicali D., Grzelecki A., Huang C. Vaccinia virus vectors utilizing the beta-galactosidase assay for rapid selection of recombinant viruses and measurement of gene expression. Gene. 1986;47(2-3):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensaert M. B., De Smet K., De Waele K. Extent and duration of virulent virus excretion upon challenge of pigs vaccinated with different glycoprotein-deleted Aujeszky's disease vaccines. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Apr;22(2-3):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90098-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkus M. E., Limbach K., Paoletti E. Cloning and expression of foreign genes in vaccinia virus, using a host range selection system. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3829–3836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3829-3836.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkus M. E., Piccini A., Lipinskas B. R., Paoletti E. Recombinant vaccinia virus: immunization against multiple pathogens. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):981–984. doi: 10.1126/science.2992092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Meyer A. L., Post L. E. Reduced yield of infectious pseudorabies virus and herpes simplex virus from cell lines producing viral glycoprotein gp50. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2196–2199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2196-2199.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Armentrout M. A., Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Post L. E. DNA sequence of the gene for pseudorabies virus gp50, a glycoprotein without N-linked glycosylation. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):216–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.216-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Post L. E. Use of lambda gt11 to isolate genes for two pseudorabies virus glycoproteins with homology to herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):185–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.185-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccini A., Perkus M. E., Paoletti E. Vaccinia virus as an expression vector. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:545–563. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup D. J., Ink B. S., Hu W., Ray C. A., Joklik W. K. Hemorrhage in lesions caused by cowpox virus is induced by a viral protein that is related to plasma protein inhibitors of serine proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7698–7702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. J., Timmins J. G., Long G. W., Post L. E. Mapping and sequence of the gene for the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein which accumulates in the medium of infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):21–29. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.21-29.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Dorney D. J., Wathen M. W., Whealy M. E., Gold C., Watson R. J., Holland L. E., Weed S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. The pseudorabies virus gII gene is closely related to the gB glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2691–2701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2691-2701.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Watson R. J., Whealy M. E., Hays W. W., Enquist L. W. Characterization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene with homology to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):339–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.339-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Weis J. H., Enquist L. W., Watson R. J. Construction of E. coli expression plasmid libraries: localization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(5):485–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Watson R. J., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus gene encoding glycoprotein gIII is not essential for growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):635–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.635-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Kaplan A. S. Electron microscopic studies of the DNA of defective and standard pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Kidd S., Kelley M. R. An improved filamentous helper phage for generating single-stranded plasmid DNA. Gene. 1986;45(3):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawitzky D., Hampl H., Habermehl K. O. Comparison of heparin-sensitive attachment of pseudorabies virus (PRV) and herpes simplex virus type 1 and identification of heparin-binding PRV glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1990 May;71(Pt 5):1221–1225. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-5-1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
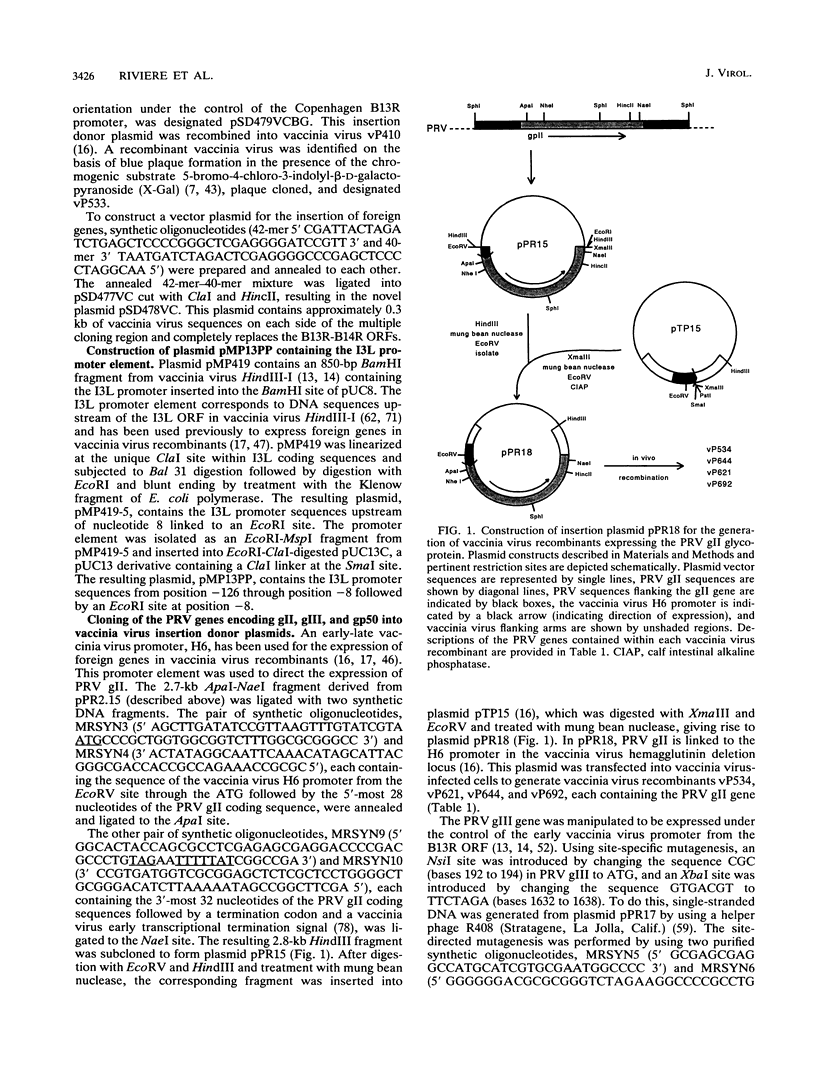
- Schmitt J. F., Stunnenberg H. G. Sequence and transcriptional analysis of the vaccinia virus HindIII I fragment. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1889–1897. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1889-1897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreurs C., Mettenleiter T. C., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Glycoprotein gIII of pseudorabies virus is multifunctional. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2251–2257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2251-2257.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellmann C., Vannier P., Chappuis G., Brun A., Dauvergne M., Fargeaud D., Bugand M., Colson X. The potency testing of pseudorabies vaccines in pigs. A proposal for a quantitative criterion and a minimum requirement. J Biol Stand. 1989 Jan;17(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(89)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevely W. S. Inverted repetition in the chromosome of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):232–234. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.232-234.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Post L. E. Replication and virulence of pseudorabies virus mutants lacking glycoprotein gX. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):229–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.229-232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd D., McFerran J. B. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Aujeszky's disease (pseudorabies) virus DNA: comparison of Northern Ireland isolates and isolates from other countries. Arch Virol. 1985;86(3-4):167–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01309822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier P., Cariolet R. Vaccination of pigs against Aujeszky's disease by the intradermal route using live attenuated and inactivated virus vaccines. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Jan;26(1-2):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90038-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. C., Stunnenberg H. G. Derepression of a novel class of vaccinia virus genes upon DNA replication. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3487–3492. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen L. M., Platt K. B., Wathen M. W., Van Deusen R. A., Whetstone C. A., Pirtle E. C. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against pseudorabies virus. Virus Res. 1985 Dec;4(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Wathen L. M. Characterization and mapping of a nonessential pseudorabies virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):173–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.173-178.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Wathen L. M. Isolation, characterization, and physical mapping of a pseudorabies virus mutant containing antigenically altered gp50. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):57–62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.57-62.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Replacement of the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII gene with its postulated homolog, the glycoprotein gC gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4055–4059. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4055-4059.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. The export pathway of the pseudorabies virus gB homolog gII involves oligomer formation in the endoplasmic reticulum and protease processing in the Golgi apparatus. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1946–1955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1946-1955.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen L., Moss B. Oligonucleotide sequence signaling transcriptional termination of vaccinia virus early genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6417–6421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsak L., Mettenleiter T. C., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Release of pseudorabies virus from infected cells is controlled by several viral functions and is modulated by cellular components. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5475–5477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5475-5477.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann F. A., Zsak L., Mettenleiter T. C., Ben-Porat T. Pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII is a major target antigen for murine and swine virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):802–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.802-812.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann F., Zsak L., Reilly L., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Early interactions of pseudorabies virus with host cells: functions of glycoprotein gIII. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3323–3329. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3323-3329.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Awar F. Y., Hahn E. C. Swine antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against pseudorabies virus-infected cells. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Mar;48(3):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]