Abstract
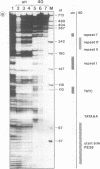
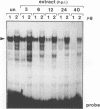
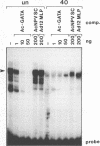
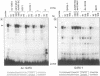
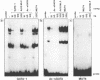
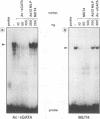
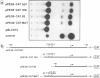
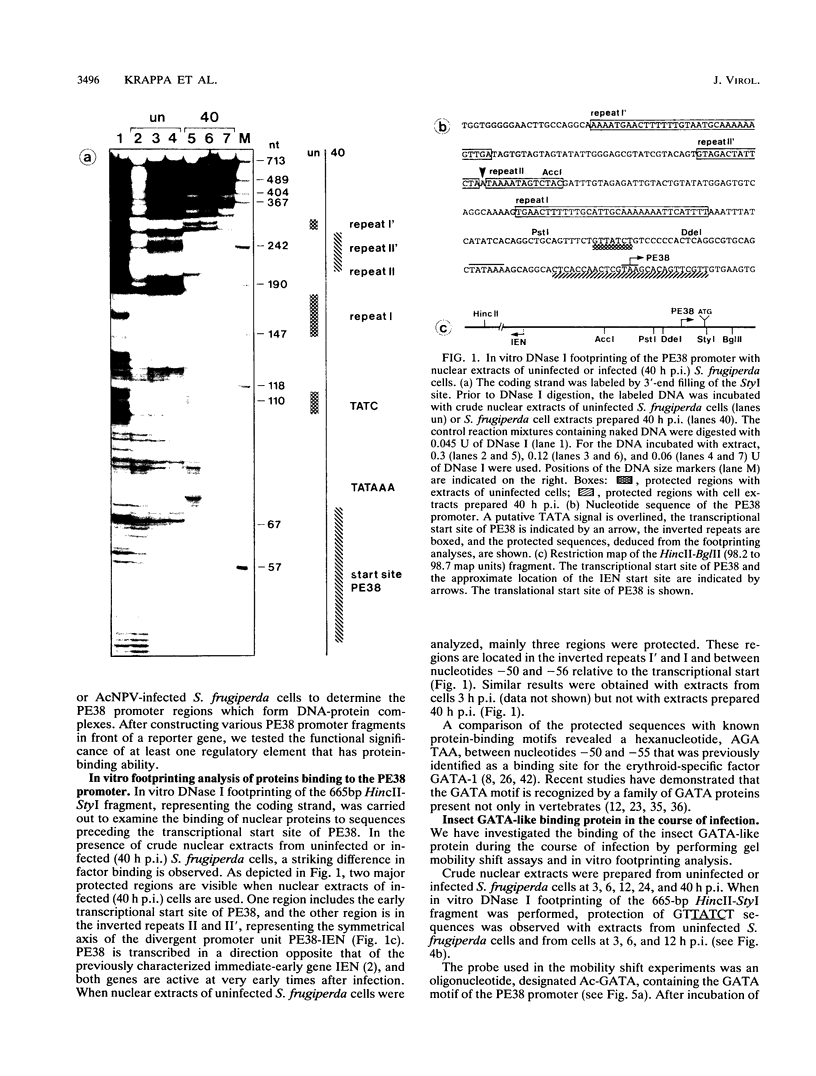
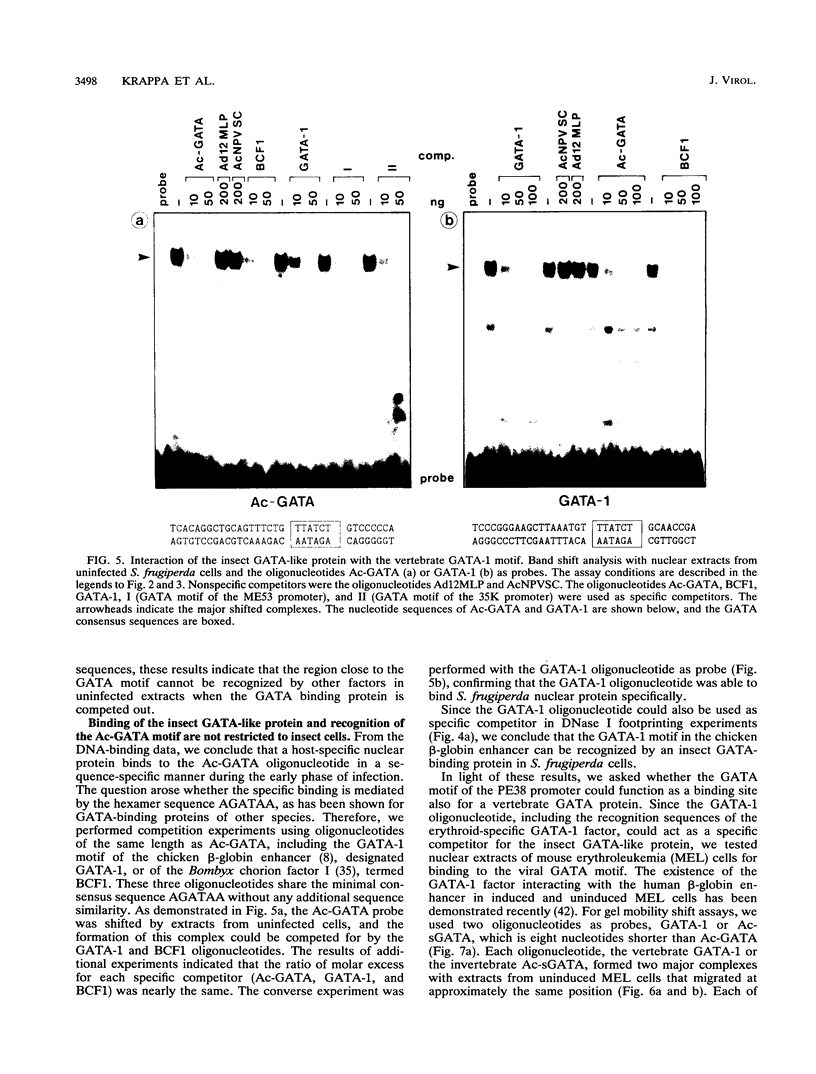
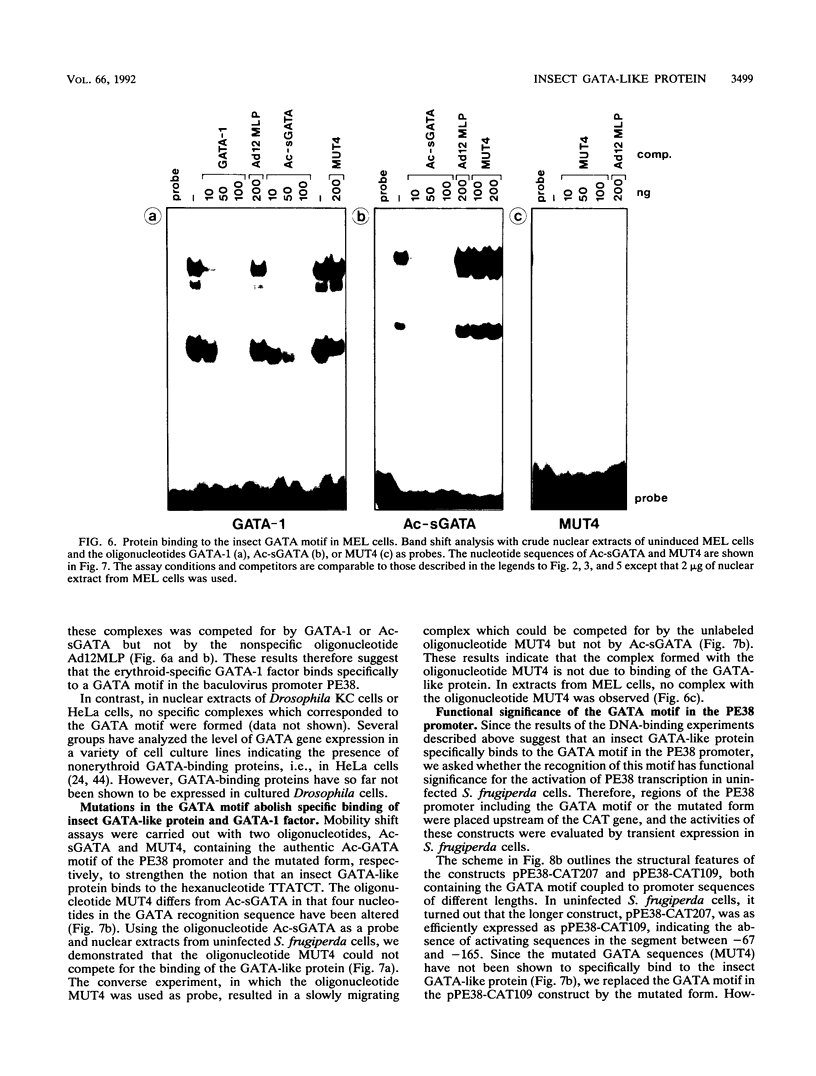
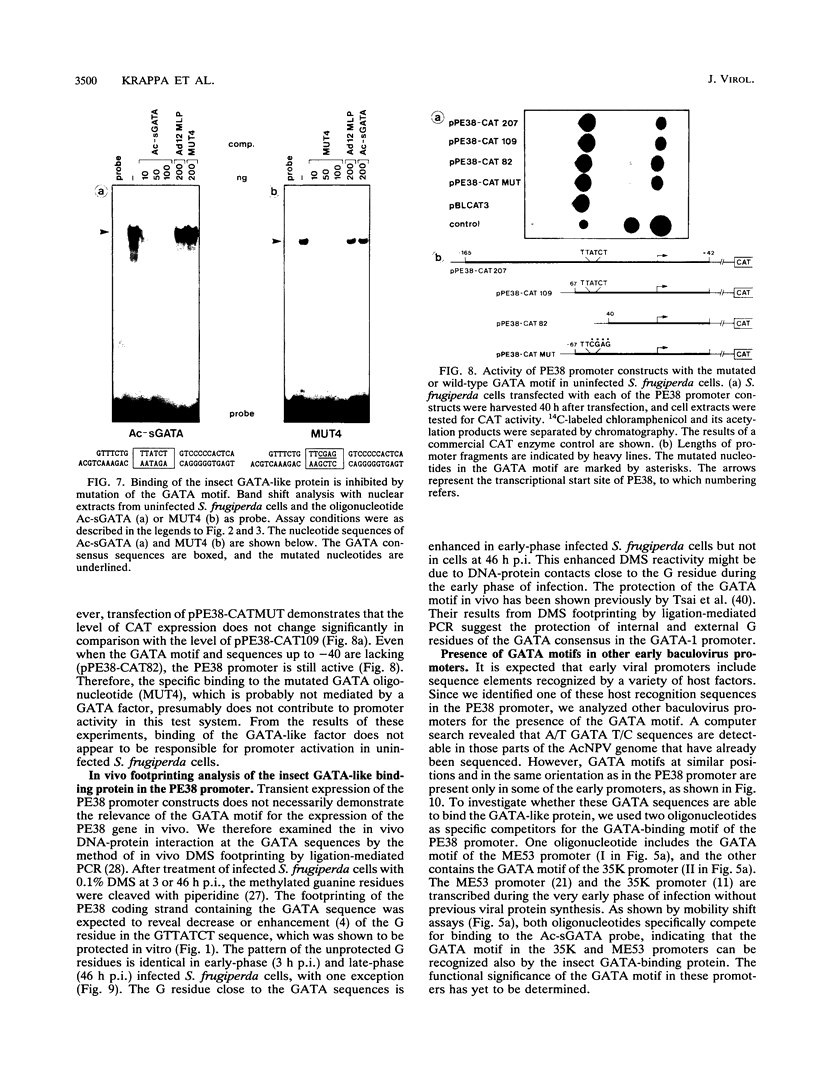
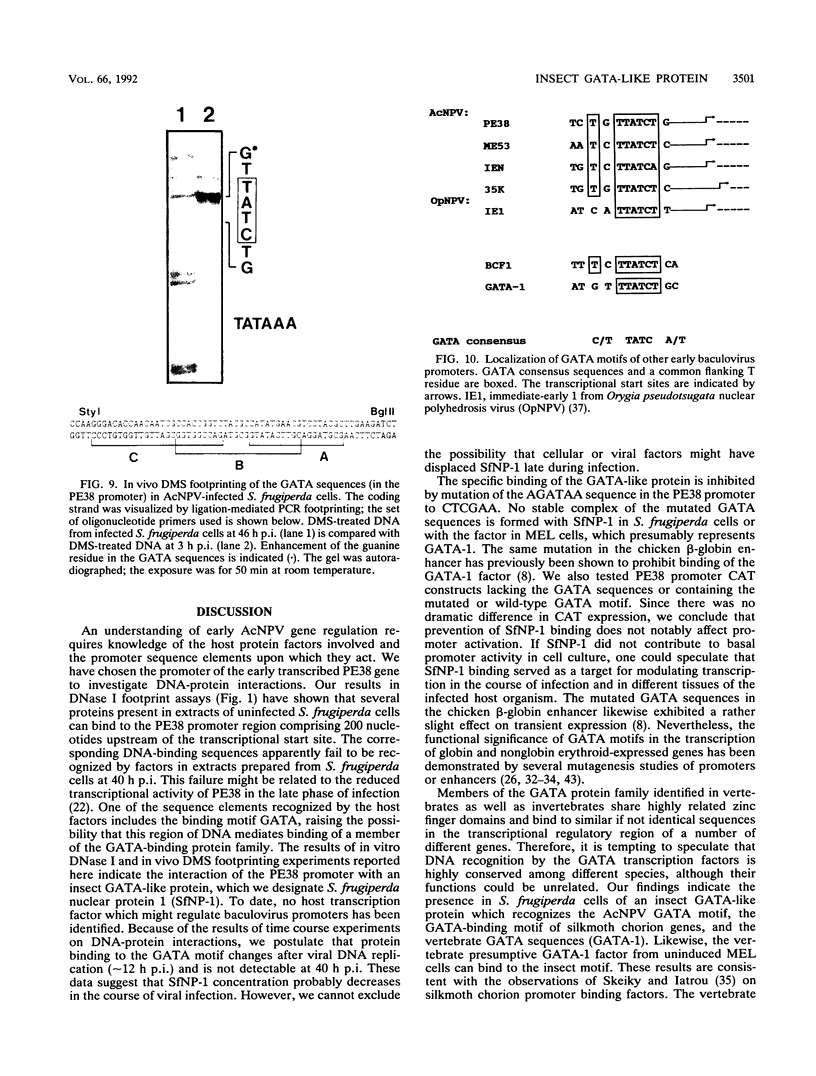
Regulatory elements interacting with DNA-binding proteins have been investigated in the promoter sequence of the early PE38 gene in the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcNPV). A GATA motif located 50 nucleotides upstream of the PE38 transcriptional start site is recognized differentially in the course of infection. As demonstrated by footprint and gel mobility shift assays, the GATA sequences TTATCT are protected by nuclear extracts from uninfected Spodoptera frugiperda cells and from S. frugiperda cells early postinfection (p.i.) but not by S. frugiperda cell extracts isolated 40 h p.i. We have compared the binding capacity of the insect GATA-like protein with that of the vertebrate GATA-1 factor identified as erythroid-specific factor. Our results indicate that a factor present in mouse erythroleukemia cells, presumably GATA-1, can bind to the insect GATA motif and vice versa. Evidence from transient expression studies suggests that the mutated GATA sequences do not influence PE38 promoter activity in cell culture.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Baculovirus diversity and molecular biology. Annu Rev Entomol. 1990;35:127–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. D., Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of an AcNPV immediately early gene which augments expression of the IE-1 trans-activated 39K gene. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):444–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstens E. B., Tjia S. T., Doerfler W. Infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus I. Synthesis of intracellular proteins after virus infection. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):386–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson J. A., Friesen P. D. Identification of upstream promoter elements mediating early transcription from the 35,000-molecular-weight protein gene of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4006–4016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4006-4016.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. Expression of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome in insect cells: homologous viral and heterologous vertebrate genes--the baculovirus vector system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;131:51–68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71589-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. The erythroid-specific transcription factor Eryf1: a new finger protein. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Divergent transcription of early 35- and 94-kilodalton protein genes encoded by the HindIII K genome fragment of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2264–2272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2264-2272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. The regulation of baculovirus gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;131:31–49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71589-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Marzluf G. A. nit-2, the major nitrogen regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa, encodes a protein with a putative zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1056–1065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. Transformation of rat cells by DNA of human adenovirus 5. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):536–539. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of a trans-activating gene required for expression of a baculovirus delayed-early gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.563-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt Y., Alexander W. S., Barri G., Klinken S. P., Adams J. M. Novel zinc finger gene implicated as myc collaborator by retrovirally accelerated lymphomagenesis in E mu-myc transgenic mice. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90383-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., Tjian R. Temporal pattern of alcohol dehydrogenase gene transcription reproduced by Drosophila stage-specific embryonic extracts. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):410–415. doi: 10.1038/331410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoopes R. R., Jr, Rohrmann G. F. In vitro transcription of baculovirus immediate early genes: accurate mRNA initiation by nuclear extracts from both insect and human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4513–4517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krappa R., Knebel-Mörsdorf D. Identification of the very early transcribed baculovirus gene PE-38. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):805–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.805-812.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudla B., Caddick M. X., Langdon T., Martinez-Rossi N. M., Bennett C. F., Sibley S., Davies R. W., Arst H. N., Jr The regulatory gene areA mediating nitrogen metabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mutations affecting specificity of gene activation alter a loop residue of a putative zinc finger. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1355–1364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. E., Temizer D. H., Clifford J. A., Quertermous T. Cloning of the GATA-binding protein that regulates endothelin-1 gene expression in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16188–16192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H. Increased gamma-globin expression in a nondeletion HPFH mediated by an erythroid-specific DNA-binding factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):435–438. doi: 10.1038/338435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Globin gene regulation and switching: circa 1990. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Steigerwald S. D., Mueller P. R., Wold B., Riggs A. D. Genomic sequencing and methylation analysis by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2814502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Frampton J., Wainwright H., Walker M., Macleod K., Goodwin G., Harrison P. GATAAG; a cis-control region binding an erythroid-specific nuclear factor with a role in globin and non-globin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):73–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid K., Doi T., Beeler D. L., Kuter D. J., Rosenberg R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the rat platelet factor 4 gene: interaction between an enhancer/silencer domain and the GATA site. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6116–6127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. Mutational analysis of the chicken beta-globin enhancer reveals two positive-acting domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6267–6271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeiky Y. A., Iatrou K. Synergistic interactions of silkmoth chorion promoter-binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1954–1964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann D. A., Stewart S. Identification and characterization of the IE-1 gene of Orgyia pseudotsugata multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):492–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90063-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjia S. T., Carstens E. B., Doerfler W. Infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus II. The viral DNA and the kinetics of its replication. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):399–409. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Strauss E., Orkin S. H. Functional analysis and in vivo footprinting implicate the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 as a positive regulator of its own promoter. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):919–931. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene 3' enhancer contains multiple binding sites for an erythroid-specific protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1089–1100. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P., Lamb P., Squire L., Proudfoot N. A factor binding GATAAG confers tissue specificity on the promoter of the human zeta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1339–1350. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Dorfman D. M., Orkin S. H. A nonerythroid GATA-binding protein is required for function of the human preproendothelin-1 promoter in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]