Abstract
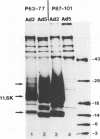
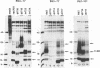
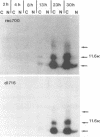
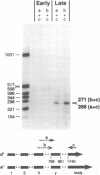
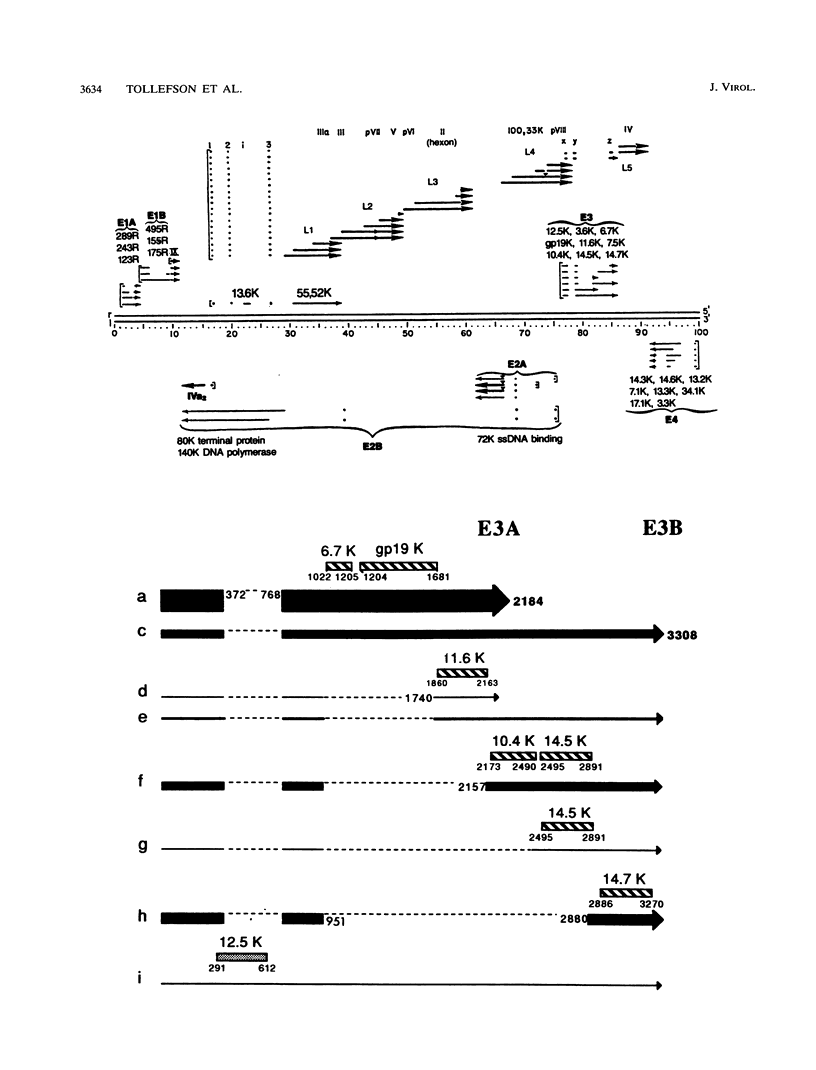
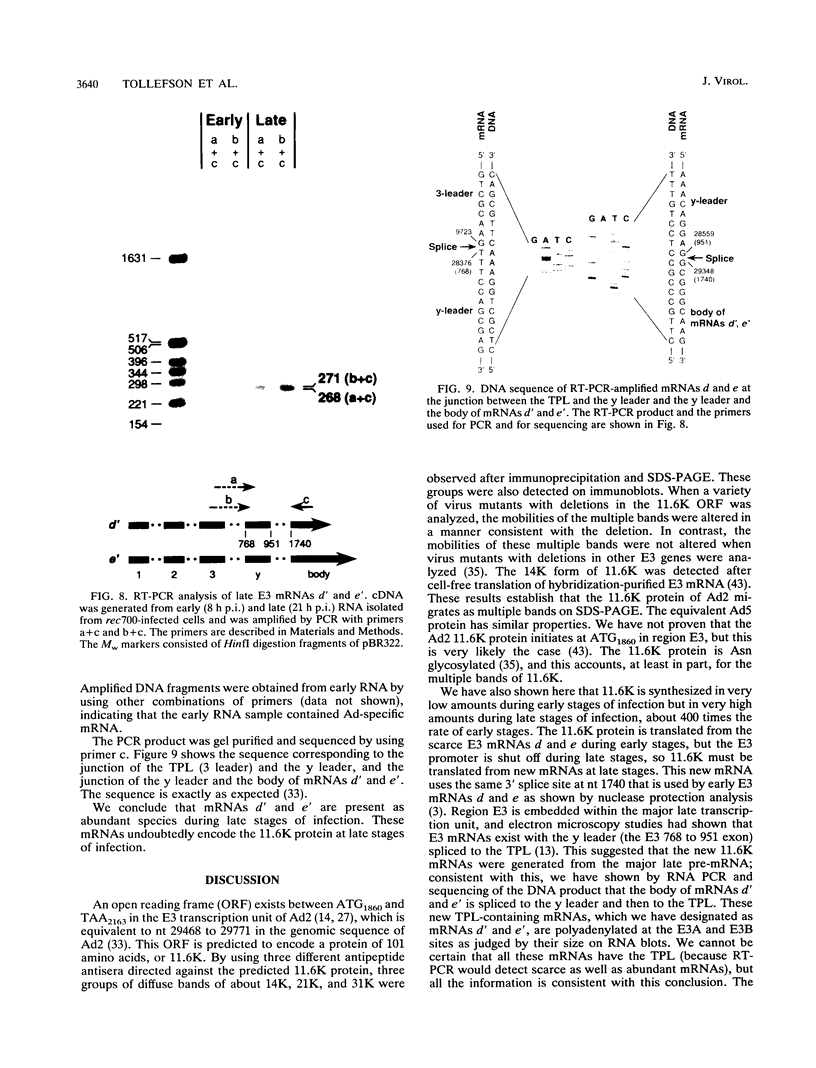
We have reported that an 11,600-MW (11.6K) protein is coded by region E3 of adenovirus. We have now prepared two new antipeptide antisera that have allowed us to characterize this protein further. The 11.6K protein migrates as multiple diffuse bands having apparent Mws of about 14,000, 21,000, and 31,000 on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Immunoblotting as well as virus mutants with deletions in the 11.6K gene were used to show that the various gel bands represent forms of 11.6K. The 11.6K protein was synthesized in very low amounts during early stages of infection, from the scarce E3 mRNAs d and e which initiate from the E3 promoter. However, 11.6K was synthesized very abundantly at late stages of infection, approximately 400 times the rate at early stages, from new mRNAs termed d' and e'. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and RNA blot experiments indicated that mRNAs d' and e' had the same body (the coding portion) and the same middle exon (the y leader) as early E3 mRNAs d and e, but mRNAs d' and e' were spliced at their 5' termini to the major late tripartite leader which is found in all mRNAs in the major late transcription unit. mRNAs d' and e' and the 11.6K protein were the only E3 mRNAs and protein that were scarce early and were greatly amplified at late stages of infection. This suggests that specific cis- or trans-acting sequences may function to enhance the splicing of mRNAs d' and e' at late stages of infection and perhaps to suppress the splicing of mRNAs d and e at early stages of infection. We propose that the 11.6K gene be considered not only a member of region E3 but also a member of the major late transcription unit.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Persson H. Controls of RNA splicing and termination in the major late adenovirus transcription unit. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):420–426. doi: 10.1038/292420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat B. M., Brady H. A., Pursley M. H., Wold W. S. Deletion mutants that alter differential RNA processing in the E3 complex transcription unit of adenovirus. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):543–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat B. M., Brady H. A., Wold W. S. Virus deletion mutants that affect a 3' splice site in the E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2405–2413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat B. M., Wold W. S. A small deletion distant from a splice or polyadenylation site dramatically alters pre-mRNA processing in region E3 of adenovirus. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3938–3945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3938-3945.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat B. M., Wold W. S. Genetic analysis of mRNA synthesis in adenovirus region E3 at different stages of productive infection by RNA-processing mutants. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):54–63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.54-63.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binger M. H., Flint S. J. Accumulation of early and intermediate mRNA species during subgroup C adenovirus productive infections. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):387–403. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady H. A., Wold W. S. Competition between splicing and polyadenylation reactions determines which adenovirus region E3 mRNAs are synthesized. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3291–3297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady H. A., Wold W. S. Identification of a novel sequence that governs both polyadenylation and alternative splicing in region E3 of adenovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9397–9416. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R. The spliced structures of adenovirus 2 fiber message and the other late mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Lewis J. B., Broker T. R. RNA transcription and splicing at early and intermediate times after adenovirus-2 infection. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):401–414. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Roberts J. M., Lewis J. B., Broker T. R. A map of cytoplasmic RNA transcripts from lytic adenovirus type 2, determined by electron microscopy of RNA:DNA hybrids. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):819–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Bhat B., Wold W. S. Mapping the 5' ends, 3' ends, and splice sites of mRNAs from the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):44–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90444-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Wold W. S. DNA sequence of the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):28–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delsert C., Morin N., Klessig D. F. cis-acting elements and a trans-acting factor affecting alternative splicing of adenovirus L1 transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4364–4371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Bhat B. M., Pursley M. H., Cladaras C., Wold W. S. Novel deletion mutants that enhance a distant upstream 5' splice in the E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5771–5788. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint J., Shenk T. Adenovirus E1A protein paradigm viral transactivator. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:141–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J. Regulation of adenovirus mRNA formation. Adv Virus Res. 1986;31:169–228. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. W., Baker C. C., Moore M. A., Ziff E. B. Poly(A) sites of adenovirus serotype 2 transcription units. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):207–233. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Sciaky D., Gelinas R. E., Bing-Dong J., Yen C. E., Kelly M. M., Bullock P. A., Parsons B. L., O'Neill K. E., Roberts R. J. Nucleotide sequences from the adenovirus-2 genome. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13475–13491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Wold W. S. Human adenoviruses: growth, purification, and transfection assay. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:425–435. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Shanmugam G., Wold W. S., Green M. Detection of adenovirus type 2-induced early polypeptides using cycloheximide pretreatment to enhance viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):232–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.232-242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. T., Schneider R. J. Adenovirus inhibition of cellular protein synthesis involves inactivation of cap-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90161-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Westphal H. The structure of adenovirus 2 early nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):23–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Shenk T. Adenovirus tripartite leader sequence enhances translation of mRNAs late after infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3655–3659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Ginsberg H. S., Blanchard J. M., Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Regulation of the primary expression of the early adenovirus transcription units. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):727–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.727-733.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T., Flint J. Transcriptional and transforming activities of the adenovirus E1A proteins. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:47–85. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60995-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Ziff E. B. HeLa cell beta-tubulin gene transcription is stimulated by adenovirus 5 in parallel with viral early genes by an E1a-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2792–2801. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefson A. E., Wold W. S. Identification and gene mapping of a 14,700-molecular-weight protein encoded by region E3 of group C adenoviruses. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):33–39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.33-39.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén M., Svensson C., Josephson S., Aleström P., Chattapadhyaya J. B., Pettersson U., Philipson L. Leader arrangement in the adenovirus fiber mRNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):249–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson-Rawls J., Saha S. K., Krajcsi P., Tollefson A. E., Gooding L. R., Wold W. S. A 6700 MW membrane protein is encoded by region E3 of adenovirus type 2. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):204–212. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Cladaras C., Magie S. C., Yacoub N. Mapping a new gene that encodes an 11,600-molecular-weight protein in the E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):307–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.307-313.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Deutscher S. L., Takemori N., Bhat B. M., Magie S. C. Evidence that AGUAUAUGA and CCAAGAUGA initiate translation in the same mRNA region E3 of adenovirus. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):168–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90412-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Green M., Brackmann K. H., Cartas M. A., Devine C. Genome expression and mRNA maturation at late stages of productive adenovirus type 2 infection. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):465–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.465-477.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain S., Sambrook J., Roberts R. J., Keller W., Fried M., Dunn A. R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the leader segments in a cloned copy of adenovirus 2 fiber mRNA. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):851–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]