Abstract
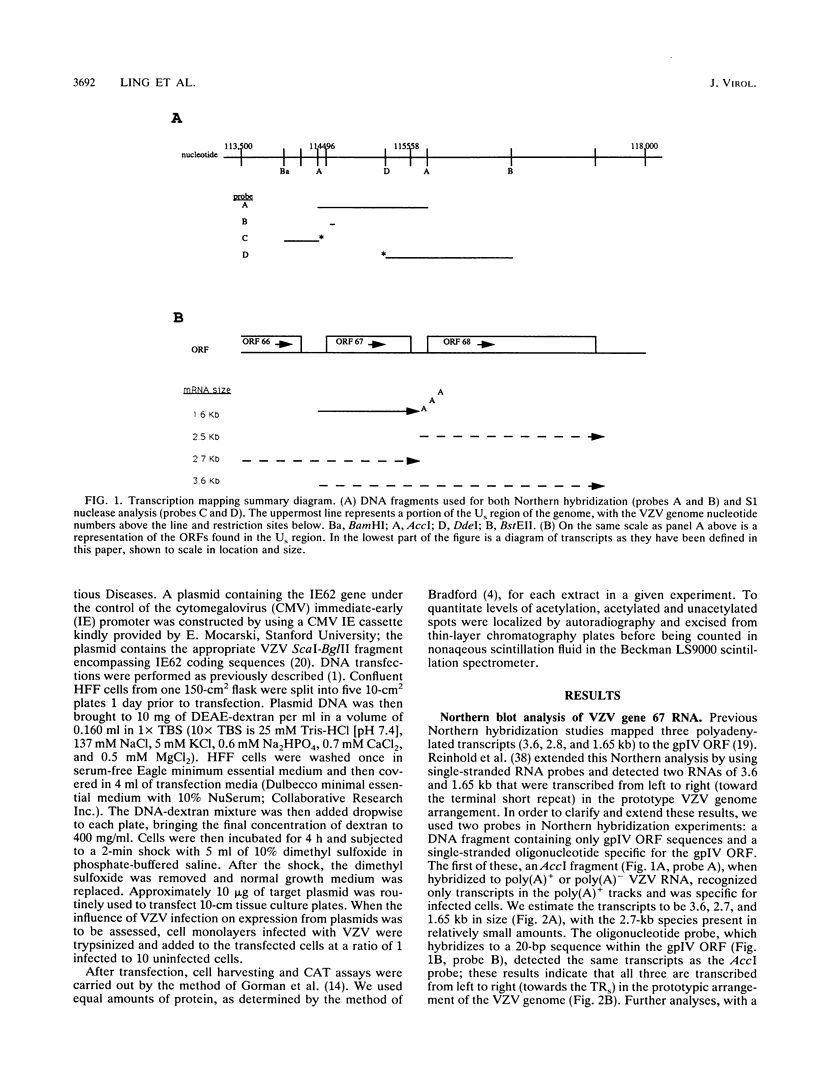
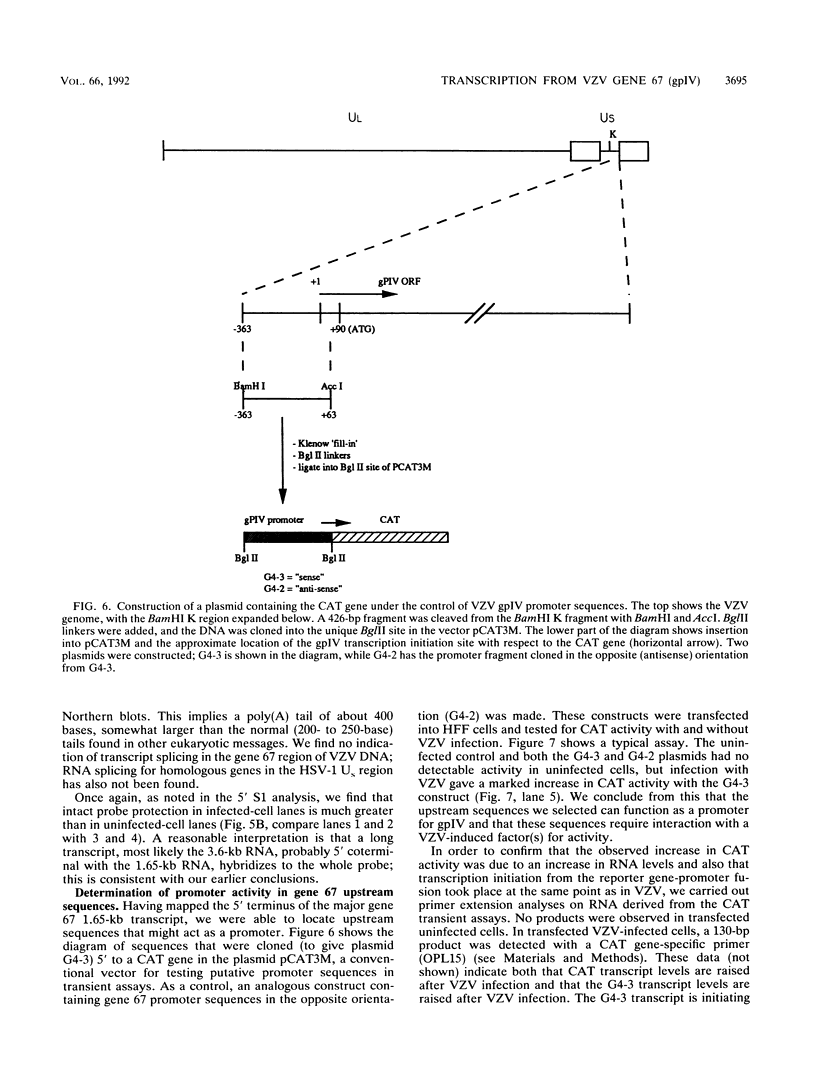
Three transcripts map to the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) open reading frame (ORF) 67, which encodes glycoprotein IV (gpIV). All of these transcripts are polyadenylated and are transcribed from left to right towards the genomic terminal short repeats. Previous Northern (RNA) blot analyses suggested that the most abundant of these transcripts (1.65 kb) might code for gpIV. We performed S1 nuclease protection and primer extension assays and determined that the 5' terminus of the 1.65-kb transcript maps 91 bp upstream from the gpIV initiation codon. An AT-rich region (ATAAA), -28 bp from the cap site, is a potential TATA box, and at -71 bp there is a consensus CCAAT box motif. The 3' end of the 1.65-kb transcript is 20 bp downstream of two overlapping polyadenylation signals, AATAAA and ATTAAA, and just downstream of the 3' terminus is a GU-rich sequence. These results are reminiscent of data from our analysis of the VZV gpV gene, confirming that VZV appears able to use unusual TATA box motifs. Many canonical TATA sequences are present upstream from these VZV transcriptional start sites but, apparently, are not used. We tested sequences upstream from the gpIV cap site for promoter activity in transient expression experiments by cloning a DNA fragment (+63 to -343 bp) into pCAT3M, which contains a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene. This clone showed little constitutive promoter activity but was activated more than 200-fold by infection with VZV and 5-fold with herpes simplex virus. The two known VZV transactivating genes (those for ORF 4 and ORF 62) were tested for their abilities to activate expression from the gpIV promoter by using their cognate promoters. The ORF 4 gene was minimally active, whereas the ORF 62 gene gave twofold induction; both genes, acting together, gave fivefold induction. However, replacement of the IE62 promoter with the immediate-early cytomegalovirus promoter in the ORF 62 construct gave over 40-fold induction of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity under the gpIV promoter in the same assay.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabirac G. F., Mahalingam R., Wellish M., Gilden D. H. Trans-activation of viral tk promoters by proteins encoded by varicella zoster virus open reading frames 61 and 62. Virus Res. 1990 Jan;15(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Edson C. M., Ellis R. W., Forghani B., Gilden D., Grose C., Keller P. M., Vafai A., Wroblewska Z., Yamanishi K. New common nomenclature for glycoprotein genes of varicella-zoster virus and their glycosylated products. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1195–1197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1195-1197.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Waters D. J., Edson C. M. Identification of the products of a varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein gene. J Gen Virol. 1985 Oct;66(Pt 10):2237–2242. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-10-2237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. The products of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) immediate early genes 1, 2 and 3 can activate HSV-1 gene expression in trans. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2507–2513. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Mapping of two varicella-zoster virus-encoded genes that activate the expression of viral early and late genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):700–709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Ostrove J. M. Differential regulation by varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and herpes simplex virus type-1 trans-activating genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):710–714. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Cech T. R. Secondary structure of the circular form of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: a technique for RNA structure analysis using chemical probes and reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Frame M. C., Ligas M. W., Cross A. M., Stow N. D. Herpes simplex virus immunoglobulin G Fc receptor activity depends on a complex of two viral glycoproteins, gE and gI. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1347–1354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1347-1354.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Kitamura K., Hayakawa Y., Takahashi M., Kojima A., Sato S., Yamanishi K. Transcription mapping of glycoprotein I (gpI) and gpIV of varicella-zoster virus and immunological analysis of the gpI produced in cells infected with the recombinant vaccinia virus. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(4):299–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb01979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinchington P. R., Hougland J. K., Arvin A. M., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The varicella-zoster virus immediate-early protein IE62 is a major component of virus particles. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.359-366.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinchington P. R., Ling P., Pensiero M., Moss B., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The glycoprotein products of varicella-zoster virus gene 14 and their defective accumulation in a vaccine strain (Oka). J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4540–4548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4540-4548.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinchington P. R., Remenick J., Ostrove J. M., Straus S. E., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. Putative glycoprotein gene of varicella-zoster virus with variable copy numbers of a 42-base-pair repeat sequence has homology to herpes simplex virus glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):660–668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.660-668.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P., Kinchington P. R., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. A detailed analysis of transcripts mapping to varicella zoster virus gene 14 (glycoprotein V). Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):625–635. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90432-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin V., Sandor M., Grose C. Cell surface expression of the varicella-zoster virus glycoproteins and Fc receptor. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90402-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Chatterjee S., Whitley R. J., Roizman B. Identification of a herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein gene within a gene cluster dispensable for growth in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4303–4307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. M., McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 deletion mutants exhibit altered patterns of transcription and are DNA deficient. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.18-27.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Brauer D. H. Complete DNA sequence of the short repeat region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1727–1745. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee T. A., Disney G. H., Everett R. D., Preston C. M. Control of expression of the varicella-zoster virus major immediate early gene. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):897–906. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold W. C., Straus S. E., Ostrove J. M. Directionality and further mapping of varicella zoster virus transcripts. Virus Res. 1988 Feb;9(2-3):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Knipe D. M. Gene-specific transactivation by herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3814–3823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3814-3823.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Schaffer P. A. Deletion mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 exhibit impaired growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.829-839.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekulovich R. E., Leary K., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 can act as a trans-repressor or a trans-activator in combination with ICP4 and ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4510-4522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Stow E. C. Isolation and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a deletion within the gene encoding the immediate early polypeptide Vmw110. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2571–2585. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







