Abstract
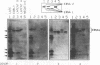
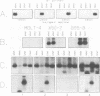
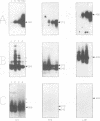
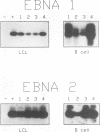
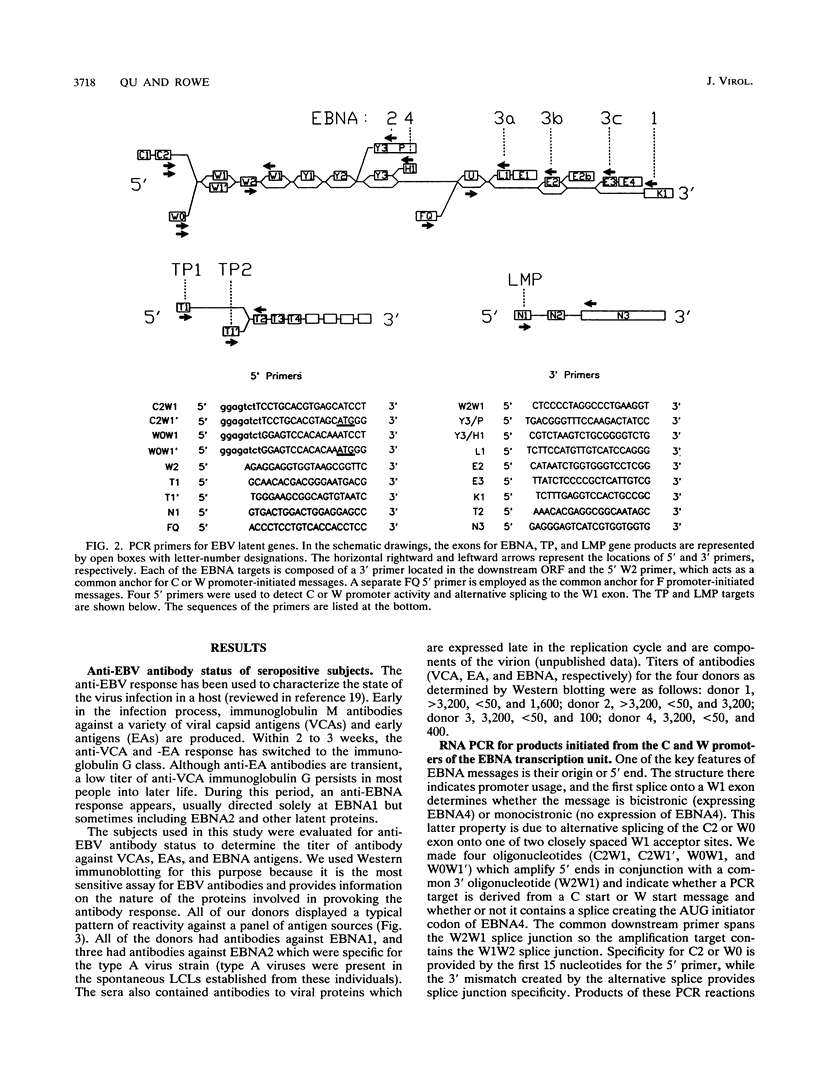
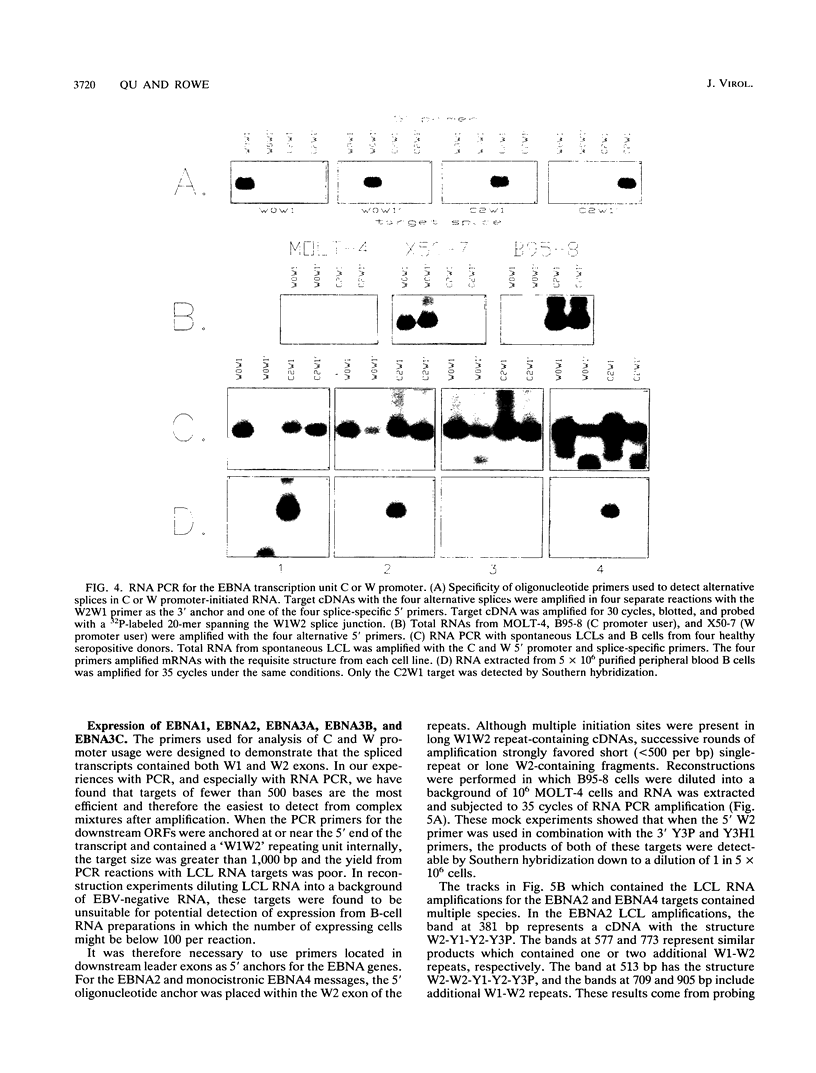
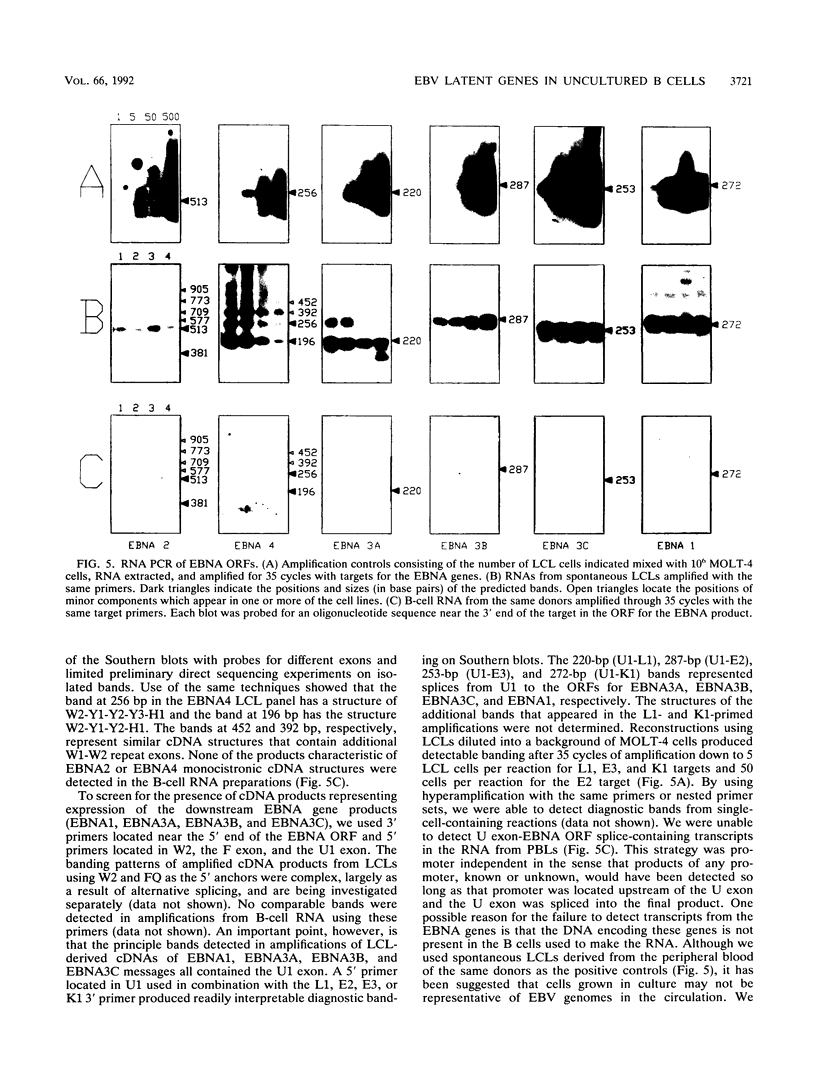
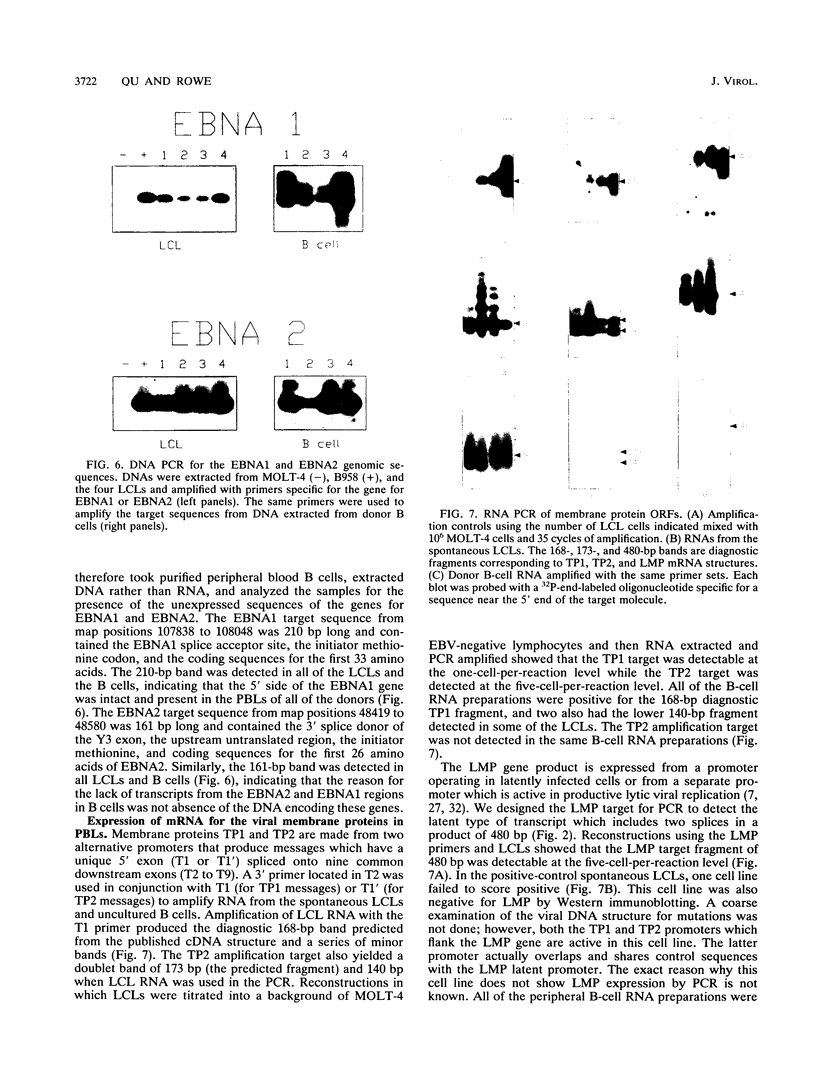
In this study of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latency, the polymerase chain reaction was used in modified form for amplification and detection of viral mRNA sequences in peripheral blood lymphocytes from healthy seropositive adults. Six known promoters for latent gene expression and eight known gene products were identified in in vitro-immortalized lymphocytes and in the cell lines established spontaneously from seropositive adults. We examined whether mRNA expression in uncultured B cells from four seropositive adults was the same as that which occurred in spontaneously established EBV-positive B-cell lines from the same individuals. A minimum of 17 polymerase chain reaction targets was required to circumscribe the known latent mRNA structures. Expression of the C promoter for the EBNA genes was detected in B-cell RNA from three of the four subjects. Transcripts initiated from the alternative W promoter for EBNA expression were not detected. The spliced transcripts detected in the B cells contained only the C2-to-W1 alternative splice, which was nonproductive for EBNA4 gene expression. None of the other EBNA open reading frames were detected spliced onto the 3' ends of the C promoter-initiated RNAs. Spliced RNA from the TP gene was detected in all four subjects. Expression of the TP gene was restricted to TP1 promoter-initiated RNAs, as no TP2 promoter-initiated transcripts were detected. Expression of RNA from the LMP gene was not detected. The F promoter which is active in the restricted expression latency that occurs in Burkitt's lymphoma cells was not detected being expressed in peripheral blood B cells. This pattern of latent gene expression is unique to uncultured B cells, indicating that there are profound differences between viral latent states in vitro and in situ and suggesting a central role for the TP gene in the latency of EBV.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfieri C., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90893-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allday M. J., Crawford D. H., Griffin B. E. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1755–1764. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Brison O., Perricaudet M. An Epstein-Barr virus transcription unit is at least 84 kilobases long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2611–2620. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Chambraud B., Farrell P., Perricaudet M. Spliced RNA from the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus: presence of an open reading frame for a repetitive polypeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1913–1917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernberg I., Falk K., Minarovits J., Busson P., Tursz T., Masucci M. G., Klein G. The role of methylation in the phenotype-dependent modulation of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2 and latent membrane protein genes in cells latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):2989–3002. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-2989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Fu H. L., Ernberg I., Finke J., Rowe M., Klein G., Falk K., Nilsson E., Yadav M., Busson P. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1988 Sep 15;42(3):329–338. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P., Monroe J. H. Studies on leukocytes growing in continuous culture derived from normal human donors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Apr;40(4):855–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Oosterveer M. A., Zwaan F. E., Lepoutre J., Klein G., Ernberg I. Eradication of Epstein-Barr virus by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: implications for sites of viral latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8693–8696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Murray R. J., Edwards C. F., Rickinson A. B. Downregulation of cell adhesion molecules LFA-3 and ICAM-1 in Epstein-Barr virus-positive Burkitt's lymphoma underlies tumor cell escape from virus-specific T cell surveillance. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1811–1824. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L. Efficiency of transformation of lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):152–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Viral latency and transformation: the strategy of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin N., Aman P., Masucci M. G., Klein E., Klein G., Oberg B., Strander H., Henle W., Henle G. Characterization of EBV-carrying B-cell populations in healthy seropositive individuals with regard to density, release of transforming virus and spontaneous outgrowth. Int J Cancer. 1987 Apr 15;39(4):472–476. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Druker B., Roberts T. M., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus protein associated with cell growth transformation interacts with a tyrosine kinase. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3681–3692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3681-3692.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci M. G., Torsteindottir S., Colombani J., Brautbar C., Klein E., Klein G. Down-regulation of class I HLA antigens and of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein in Burkitt lymphoma lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4567–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Bishop C. J., Burrows S. R., Ryan J. M. T lymphocytes in infectious mononucleosis. I. T cell death in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Apr;60(1):61–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Rickinson A. B., Pope J. H. Long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr virus in man. I. Complete regression of virus-induced transformation in cultures of seropositive donor leukocytes. Int J Cancer. 1978 Dec;22(6):662–668. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers R. P., Woisetschlaeger M., Speck S. H. Alternative splicing dictates translational start in Epstein-Barr virus transcripts. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2273–2277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Hall L., Joab I., Laux G. Identification of the Epstein-Barr virus terminal protein gene products in latently infected lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2866–2875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2866-2875.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Rowe M., Evan G. I., Wallace L. E., Farrell P. J., Rickinson A. B. Restricted expression of EBV latent genes and T-lymphocyte-detected membrane antigen in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Kieff E. Transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus genome during latency in growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1667–1674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1667-1674.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer B. C., Woisetschlaeger M., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Exclusive expression of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 in Burkitt lymphoma arises from a third promoter, distinct from the promoters used in latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6550–6554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Nedrud J. G., Raab-Traub N., Hanes R. A., Pagano J. S. Epstein-Barr virus replication in oropharyngeal epithelial cells. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 10;310(19):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405103101905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Griffin B. E. Differential expression of Epstein Barr viral transcripts for two proteins (TP1 and LMP) in lymphocyte and epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2435–2440. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Pfitzner A., Strominger J. L. An Epstein-Barr virus transcript from a latently infected, growth-transformed B-cell line encodes a highly repetitive polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9298–9302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torsteinsdottir S., Brautbar C., Klein G., Klein E., Masucci M. G. Differential expression of HLA antigens on human B-cell lines of normal and malignant origin: a consequence of immune surveillance or a phenotypic vestige of the progenitor cells? Int J Cancer. 1988 Jun 15;41(6):913–919. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Petti L., Braun D., Seung S., Kieff E. A bicistronic Epstein-Barr virus mRNA encodes two nuclear proteins in latently infected, growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):945–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.945-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Jin X. W., Yandava C. N., Furmanski L. A., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Role for the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 in viral promoter switching during initial stages of infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3942–3946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Mutually exclusive use of viral promoters in Epstein-Barr virus latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6498–6502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Yandava C. N., Furmanski L. A., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Promoter switching in Epstein-Barr virus during the initial stages of infection of B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Q. Y., Czarnecka H., Rickinson A. B. Spontaneous outgrowth of Epstein-Barr virus-positive B-cell lines from circulating human B cells of different buoyant densities. Int J Cancer. 1991 May 10;48(2):253–257. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Q. Y., Ogan P., Rowe M., Wood M., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells persist in the circulation of acyclovir-treated virus carriers. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jan 15;43(1):67–71. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA VII: size and direction of transcription of virus-specified cytoplasmic RNAs in a transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]