Abstract
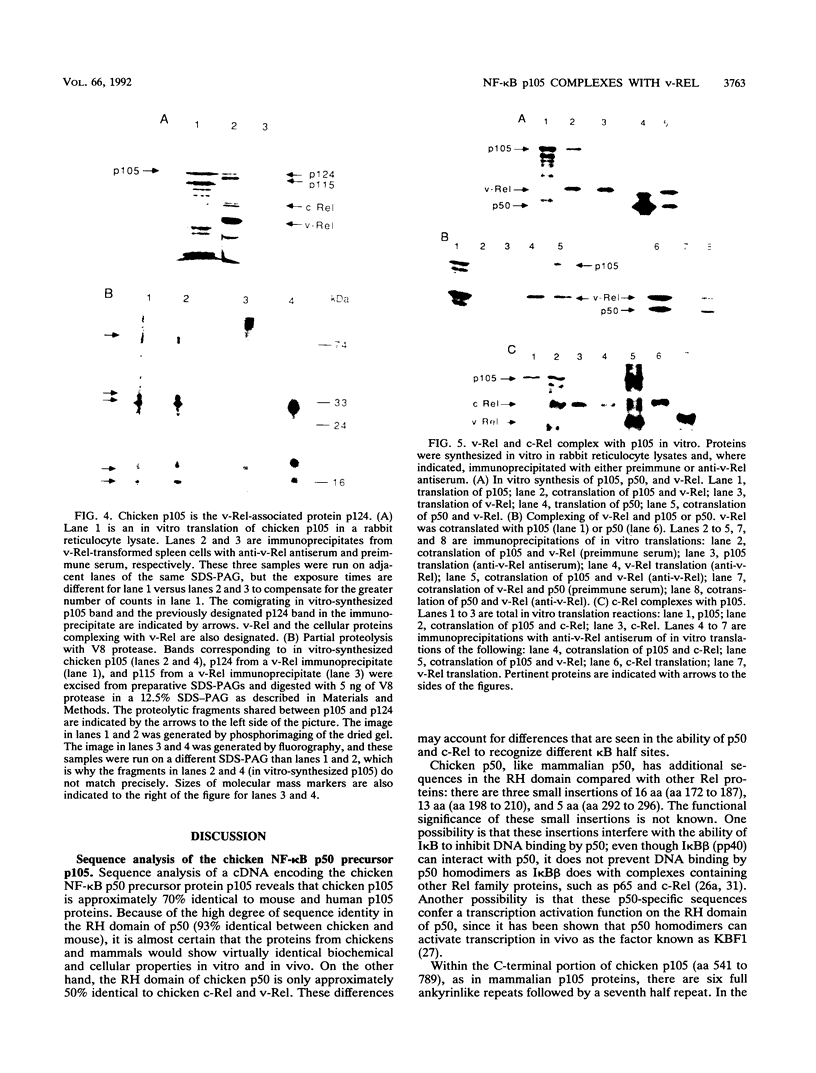
Active NF-kappa B-like transcription complexes are multimers consisting of one or two members of a family of proteins related to the c-Rel proto-oncoprotein. We have isolated a chicken cDNA encoding p105, the precursor protein for the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B. Sequence analysis shows that chicken p105 is approximately 70% identical to the mouse and human p105 proteins, containing the Rel homology domain in its N-terminal 370 amino acids and several ankyrinlike repeats in the C-terminal portion of the protein. The Rel homology domain is particularly highly conserved between chicken and mammalian p50, and an in vitro-synthesized, truncated chicken p105 protein, containing sequences that correspond to the predicted p50 protein, bound to a consensus kappa B site in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. In v-Rel-transformed chicken spleen cells, v-Rel is found in high-molecular-weight complexes which include cellular proteins of approximately 124 kDa (p124) and 115 kDa (p115). Here we report that in vitro-produced p105 comigrates with p124 from v-Rel-transformed spleen cells and that p105 and p124 appear to be identical by partial proteolytic mapping with V8 protease. Furthermore, both p105 and p50 can complex directly with v-Rel and chicken c-Rel in vitro. However, in vitro association with p105 by v-Rel does not necessarily correlate with transformation, since one nontransforming v-Rel mutant can associate with p105 in vitro.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1689–1698. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, LeClair K. P., Singh H., Sharp P. A. A large protein containing zinc finger domains binds to related sequence elements in the enhancers of the class I major histocompatibility complex and kappa immunoglobulin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1406–1414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Cytoplasmic retention, DNA binding and processing of the NF-kappa B p50 precursor are controlled by a small region in its C-terminus. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4159–4167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04994.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Villalobos J., Burd P. R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Cloning of a mitogen-inducible gene encoding a kappa B DNA-binding protein with homology to the rel oncogene and to cell-cycle motifs. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):76–80. doi: 10.1038/348076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Morley K. L., Hoekstra M. F., Hunter T., Verma I. M. The mouse c-rel protein has an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal transcriptional transactivation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5473–5485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco A. J., Gilmore T. D. Repression of the chicken c-rel promoter by vRel in chicken embryo fibroblasts is not mediated through a consensus NF-kappa B binding site. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2203–2210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco A. J., Simmons D. L., Gilmore T. D. Cloning and expression of a chicken c-rel cDNA: unlike p59v-rel, p68c-rel is a cytoplasmic protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N., Bargmann W., Bose H. R., Jr Identification of protein complexes containing the c-rel proto-oncogene product in avian hematopoietic cells. Oncogene. 1990 Aug;5(8):1109–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Bargmann W., Lim M. Y., Bose H., Jr Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus-transformed lymphoid cells contain multiple pp59v-rel complexes. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.584-591.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Ghosh S., Simmons D. L., Tempst P., Liou H. C., Baltimore D., Bose H. R., Jr Rel-associated pp40: an inhibitor of the rel family of transcription factors. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1268–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.1891714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. A DNA-binding protein containing two widely separated zinc finger motifs that recognize the same DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–42. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. Generation of p50 subunit of NF-kappa B by processing of p105 through an ATP-dependent pathway. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):395–398. doi: 10.1038/354395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. Malignant transformation by mutant Rel proteins. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):318–322. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90421-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. NF-kappa B, KBF1, dorsal, and related matters. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):841–843. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90257-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. Different localization of the product of the v-rel oncogene in chicken fibroblasts and spleen cells correlates with transformation by REV-T. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):791–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90845-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. v-rel oncoproteins in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm transform chicken spleen cells. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):703–714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.703-714.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Temin H. M. Transactivation of gene expression by nuclear and cytoplasmic rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4323–4336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Beg A. A., Tompkins S. M., Morris J. S., Yurochko A. D., Sampson-Johannes A., Mondal K., Ralph P., Baldwin A. S., Jr Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Kakizuka A., Verma I. M. I kappa B gamma, a 70 kd protein identical to the C-terminal half of p110 NF-kappa B: a new member of the I kappa B family. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1109–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90082-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Bengal E., Hunter T., Verma I. M. c-rel activates but v-rel suppresses transcription from kappa B sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Kimura A., Kieran M., Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. A common positive trans-acting factor binds to enhancer sequences in the promoters of mouse H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabrun N., Hodgson J. W., Doemer M., Mak G., Franza B. R., Jr, Enrietto P. J. Interaction of the v-rel protein with an NF-kappa B DNA binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1783–1787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamens J., Richardson P., Mosialos G., Brent R., Gilmore T. Oncogenic transformation by vrel requires an amino-terminal activation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2840–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Inoue J., Davis N., Link E., Baeuerle P. A., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. The rel-associated pp40 protein prevents DNA binding of Rel and NF-kappa B: relationship with I kappa B beta and regulation by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1464–1476. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochel T., Mushinski J. F., Rice N. R. The v-rel and c-rel proteins exist in high molecular weight complexes in avian and murine cells. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):615–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim M. Y., Davis N., Zhang J. Y., Bose H. R., Jr The v-rel oncogene product is complexed with cellular proteins including its proto-oncogene product and heat shock protein 70. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90195-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logeat F., Israël N., Ten R., Blank V., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Inhibition of transcription factors belonging to the rel/NF-kappa B family by a transdominant negative mutant. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1827–1832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauxion F., Sen R. Alteration of a single nucleotide allows efficient binding of H2TF1/KBF1 to the immunoglobulin kappa enhancer B motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3548–3552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R., Hatada E. N., Hohmann H. P., Haiker M., Bartsch C., Röthlisberger U., Lahm H. W., Schlaeger E. J., van Loon A. P., Scheidereit C. Cloning of the DNA-binding subunit of human nuclear factor kappa B: the level of its mRNA is strongly regulated by phorbol ester or tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):966–970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Kabrun N., Mudri S., Hayman M. J., Enrietto P. J. Viral rel and cellular rel associate with cellular proteins in transformed and normal cells. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):677–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Hamer P., Capobianco A. J., Laursen R. A., Gilmore T. D. A protein kinase-A recognition sequence is structurally linked to transformation by p59v-rel and cytoplasmic retention of p68c-rel. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5867–5877. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Copeland T. D., Simek S., Oroszlan S., Gilden R. V. Detection and characterization of the protein encoded by the v-rel oncogene. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. M., Gilmore T. D. vRel is an inactive member of the Rel family of transcriptional activating proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3122–3130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3122-3130.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivière Y., Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Processing of the precursor of NF-kappa B by the HIV-1 protease during acute infection. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):625–626. doi: 10.1038/350625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Habener J. F. Angiotensinogen gene-inducible enhancer-binding protein 1, a member of a new family of large nuclear proteins that recognize nuclear factor kappa B-binding sites through a zinc finger motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2887–2895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bull P., Takamiya M., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Dobrzanski P., Bravo R. RelB, a new Rel family transcription activator that can interact with p50-NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):674–684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R. M., Perkins N. D., Duckett C. S., Andrews P. C., Nabel G. J. Cloning of an NF-kappa B subunit which stimulates HIV transcription in synergy with p65. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):733–736. doi: 10.1038/352733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Baeuerle P. A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3805–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Henkel T., Baeuerle P. A. Proteins controlling the nuclear uptake of NF-kappa B, Rel and dorsal. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;1(5):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90118-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S. L., Stephens R. M., Rice N. R. Localization of the v-rel protein in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T-transformed lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):120–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.120-126.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S., Rice N. R. Detection and characterization of the protein encoded by the chicken c-rel protooncogene. Oncogene Res. 1988;2(2):103–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1817–1825. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]