Abstract
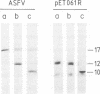
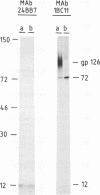
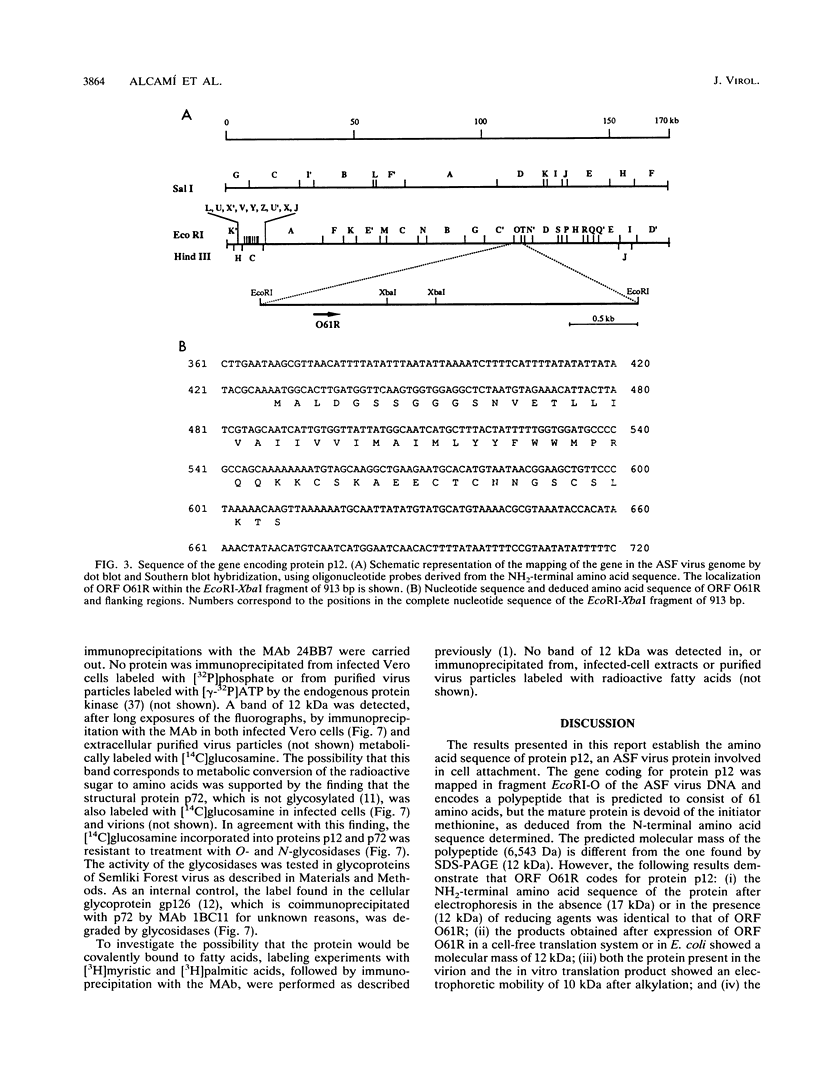
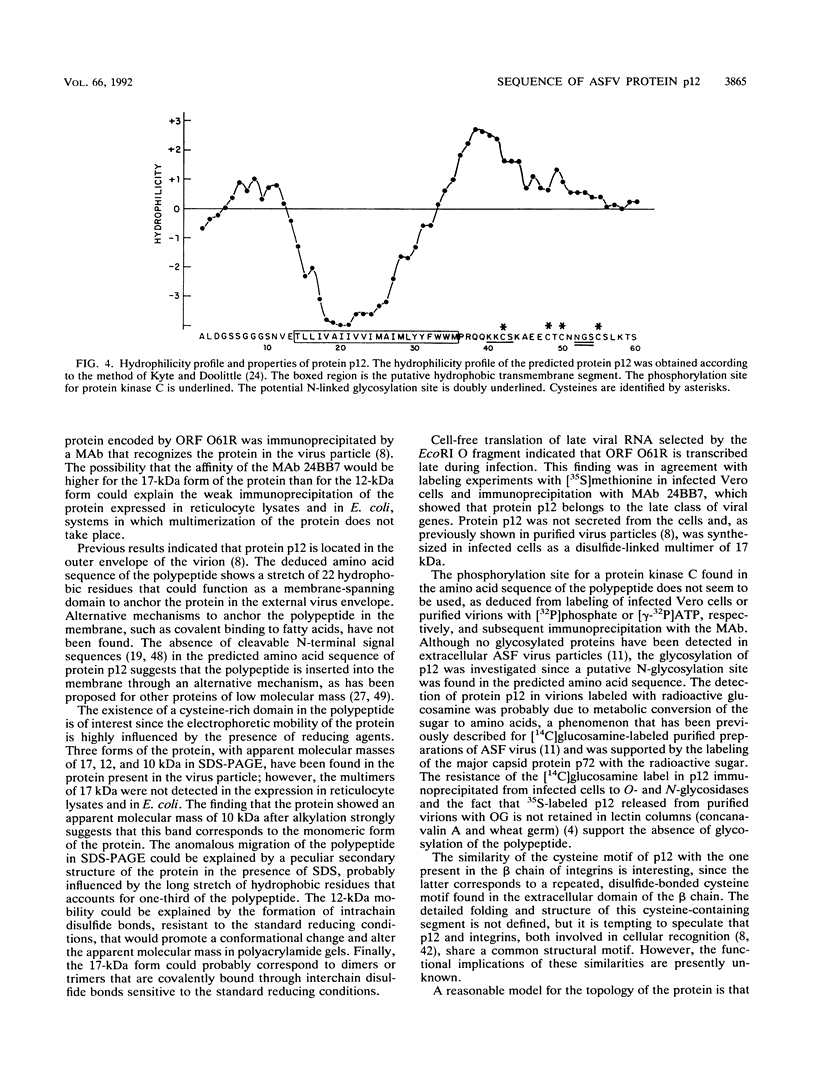
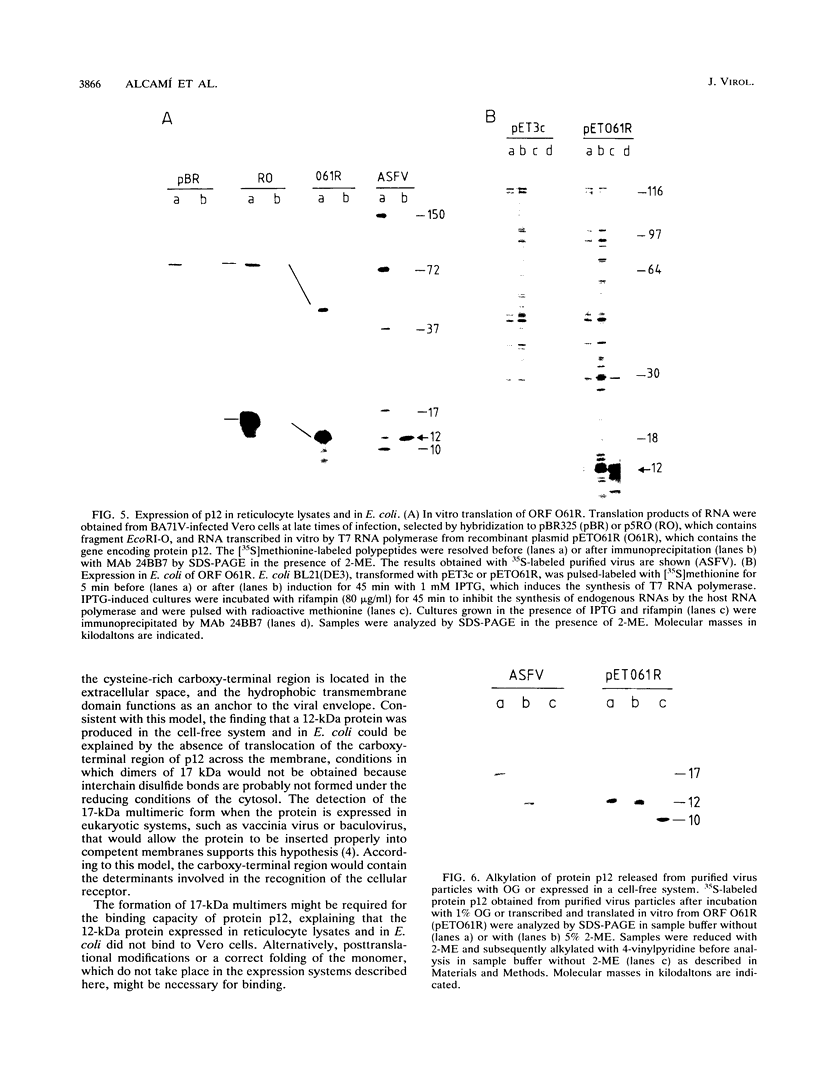
The gene encoding the African swine fever virus protein p12, which is involved in virus attachment to the host cell, has been mapped and sequenced in the genome of the Vero-adapted virus strain BA71V. The determination of the N-terminal amino acid sequence and the hybridization of oligonucleotide probes derived from this sequence to cloned restriction fragments allowed the mapping of the gene in fragment EcoRI-O, located in the central region of the viral genome. The DNA sequence of an EcoRI-XbaI fragment showed an open reading frame which is predicted to encode a polypeptide of 61 amino acids. The expression of this open reading frame in rabbit reticulocyte lysates and in Escherichia coli gave rise to a 12-kDa polypeptide that was immunoprecipitated with a monoclonal antibody specific for protein p12. The hydrophilicity profile indicated the existence of a stretch of 22 hydrophobic residues in the central part that may anchor the protein in the virus envelope. Three forms of the protein with apparent molecular masses of 17, 12, and 10 kDa in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis have been observed, depending on the presence of 2-mercaptoethanol and alkylation with 4-vinylpyridine, indicating that disulfide bonds are responsible for the multimerization of the protein. This result was in agreement with the existence of a cysteine-rich domain in the C-terminal region of the predicted amino acid sequence. The protein was synthesized at late times of infection, and no posttranslational modifications such as glycosylation, phosphorylation, or fatty acid acylation were detected.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguado B., Viñuela E., Alcamí A. African swine fever virus fatty acid acylated proteins. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):942–945. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90578-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcamí A., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Interaction of African swine fever virus with macrophages. Virus Res. 1990 Oct;17(2):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90071-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcamí A., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Saturable binding sites mediate the entry of African swine fever virus into Vero cells. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angulo A., Viñuela E., Alcamí A. Comparison of the sequence of the gene encoding African swine fever virus attachment protein p12 from field virus isolates and viruses passaged in tissue culture. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3869–3872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3869-3872.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., Sastre I., Viñuela E. African swine fever virus attachment protein. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2283–2289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2283-2289.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., del Val M., Santarén J. F., Viñuela E. Purification and properties of African swine fever virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.337-344.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer C. J. Studies to determine neutralizing antibody in sera from animals recovered from African swine fever and laboratory animals inoculated with African virus with adjuvants. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(2):164–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01241270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Mechanisms of neutralization of animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jun;65(Pt 6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-6-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Barreno B., Sanz A., Nogal M. L., Viñuela E., Enjuanes L. Monoclonal antibodies of African swine fever virus: antigenic differences among field virus isolates and viruses passaged in cell culture. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.385-392.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Kondor-Koch C., Riedel H. Structure and assembly of alphaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:1–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierasch L. M. Signal sequences. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):923–930. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., O'Connor K., Lee A., Roberts T. M., Springer T. A. Cloning of the beta subunit of the leukocyte adhesion proteins: homology to an extracellular matrix receptor defines a novel supergene family. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Katan M. Viral aspects of protein phosphorylation. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1441–1464. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Beckwith J. Cotranslational and posttranslational protein translocation in prokaryotic systems. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:315–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley V., Almendral J. M., Carbonero P., Beloso A., Viñuela E., Talavera A. Molecular cloning of African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín C., Simón-Mateo C., Martínez L., Viñuela E. Gly-Gly-X, a novel consensus sequence for the proteolytic processing of viral and cellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9107–9110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín C., Simón C., Méndez E., Viñuela E. Mapping and sequence of the gene encoding protein p37, a major structural protein of African swine fever virus. Virus Genes. 1988 Jun;1(3):291–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00572708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMQUIST W. A., HAY D. Hemadsorption and cytopathic effect produced by African Swine Fever virus in swine bone marrow and buffy coat cultures. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Jan;21:104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURER F. D., GRIESEMER R. A. The pathology of African swine fever; a comparison with hog cholera. Am J Vet Res. 1958 Jul;19(72):517–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G. The canyon hypothesis. Hiding the host cell receptor attachment site on a viral surface from immune surveillance. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14587–14590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M. L., Rey-Campos J., Almendral J. M., Talavera A., Viñuela E. Transcription and translation maps of African swine fever virus. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):228–240. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M. L., Salas J., Viñuela E. Phosphorylation of African swine fever virus proteins in vitro and in vivo. Biochimie. 1988 May;70(5):627–635. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz A., García-Barreno B., Nogal M. L., Viñuela E., Enjuanes L. Monoclonal antibodies specific for African swine fever virus proteins. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):199–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.199-206.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Hamer D. H. Cloning and sequence analysis of two monkey metallothionein cDNAs. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarés E., Martínez J., Martín E., Escribano J. M. Proteins specified by African Swine Fever virus. IV. Glycoproteins and phosphoproteins. Arch Virol. 1983;77(2-4):167–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01309265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Kumar S., Takio K., Ericsson L. H., Wade R. D., Ashida K., Walsh K. A., Chopek M. W., Sadler J. E., Fujikawa K. Amino acid sequence of human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3171–3184. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Val M., Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E. Glycosylated components of African swine fever virus particles. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90369-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Val M., Viñuela E. Glycosylated components induced in African swine fever (ASF) virus-infected Vero cells. Virus Res. 1987 Jun;7(4):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Transcending the impenetrable: how proteins come to terms with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):307–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]