Abstract
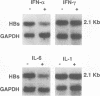
It is well known that several inflammatory cytokines can modulate hepatocellular gene expression in a complex physiological process known as the hepatic acute-phase response. Since hepatitis B virus (HBV) characteristically induces a vigorous lymphomononuclear inflammatory response in the liver during acute and chronic hepatitis, it is possible that hepatocellular HBV gene expression may also be modulated by one or more of the cytokines produced by these cells. Using bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) as a surrogate inducer of inflammatory cytokines in vivo, we have tested this hypothesis in a transgenic mouse model system. In experiments with two independent transgenic mouse lineages that express the HBV envelope region under the control of either HBV or cellular promoters, we observed a 50 to 80% reduction in the hepatic steady-state content of a 2.1-kb HBV mRNA following administration of a single intraperitoneal dose of LPS. The regulatory influence of several inflammatory cytokines known to be induced by LPS was also examined in this system. The negative regulatory effect of LPS was consistently reproduced by the administration of a single nontoxic dose of tumor necrosis factor alpha, and it was occasionally observed following the administration of high doses of alpha interferon and interleukin-6, while no effect was detectable in response to high-dose interleukin-1 alpha or to gamma interferon. These observations suggest that tumor necrosis factor alpha and perhaps other cytokines may activate a heretofore unsuspected intracellular pathway that negatively regulates HBV gene expression. The intracellular mechanism(s) responsible for this effect and its pathophysiologic relevance remain to be elucidated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham L. J., Bradshaw A. D., Fletcher R. G., Fey G. H. Interleukin 6 is a negative regulator of the acute phase alpha 1-inhibitor III gene. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Jun;7(3):261–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andus T., Bauer J., Gerok W. Effects of cytokines on the liver. Hepatology. 1991 Feb;13(2):364–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andus T., Geiger T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Action of recombinant human interleukin 6, interleukin 1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha on the mRNA induction of acute-phase proteins. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):739–746. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter H., Skuntz S., Noteborn M., Chang S., Meier E. Transgenic mice with intracellular immunity to influenza virus. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90239-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H. Hepatic acute phase reaction in vivo and in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;25(2):115–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02626167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunda M. J., Rosenbaum D. Modulation of murine natural killer cell activity in vitro and in vivo by recombinant human interferons. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):597–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Pourcel C., Louise A., Fritsch A., Tiollais P. Cloning in Escherichia coli and physical structure of hepatitis B virion DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2222–2226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Filippi P., McLachlan A., Milich D. R., Riggs M., Lee S., Palmiter R. D., Pinkert C. A., Brinster R. L. Expression of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide inhibits hepatitis B surface antigen secretion in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):880–887. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.880-887.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Pinkert C. A., Milich D. R., Filippi P., McLachlan A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A transgenic mouse model of the chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier state. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1157–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.3865369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels H. M., Meager A., Eddleston A. L., Alexander G. J., Williams R. Spontaneous production of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta during interferon-alpha treatment of chronic HBV infection. Lancet. 1990 Apr 14;335(8694):875–877. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90475-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLoia J. A., Burk R. D., Gearhart J. D. Developmental regulation of hepatitis B surface antigen expression in two lines of hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4069–4073. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4069-4073.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De S. K., McMaster M. T., Andrews G. K. Endotoxin induction of murine metallothionein gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15267–15274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker K. Biologically active products of stimulated liver macrophages (Kupffer cells). Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):245–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikstein R., Faktor O., Shaul Y. Hierarchic and cooperative binding of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP at the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4427–4430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farza H., Salmon A. M., Hadchouel M., Moreau J. L., Babinet C., Tiollais P., Pourcel C. Hepatitis B surface antigen gene expression is regulated by sex steroids and glucocorticoids in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1187–1191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Soued M., Serio M. K., Moser A. H., Dinarello C. A., Grunfeld C. Multiple cytokines stimulate hepatic lipid synthesis in vivo. Endocrinology. 1989 Jul;125(1):267–274. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-1-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glibetic M. D., Baumann H. Influence of chronic inflammation on the level of mRNA for acute-phase reactants in the mouse liver. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1616–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Koike K. Interferon inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in a stable expression system of transfected viral DNA. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2936–2940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2936-2940.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Boczko E. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. The mouse albumin enhancer contains a negative regulatory element that interacts with a novel DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3896–3905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Le Bail O., Hatat D., Piette J., Kieran M., Logeat F., Wallach D., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. TNF stimulates expression of mouse MHC class I genes by inducing an NF kappa B-like enhancer binding activity which displaces constitutive factors. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3793–3800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Boumpas D., Mann D., Yoakum G. H. Direct modulation of HBV surface antigen in a human, HBsAg-producing hepatocellular carcinoma cell line by alpha, beta, or gamma interferons. J Med Virol. 1990 Aug;31(4):272–276. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890310406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitman D. C., Ribeiro R. C., Mackow E. R., Baxter J. D., West B. L. Identification of a tumor necrosis factor-responsive element in the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9343–9346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell C. A., Stearman R. S., Morrow J. F. Transcriptional regulation of serum amyloid A gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8453–8461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukaida N., Mahe Y., Matsushima K. Cooperative interaction of nuclear factor-kappa B- and cis-regulatory enhancer binding protein-like factor binding elements in activating the interleukin-8 gene by pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21128–21133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulé J. J., McIntosh J. K., Jablons D. M., Rosenberg S. A. Antitumor activity of recombinant interleukin 6 in mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):629–636. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neta R., Oppenheim J. J., Douches S. D. Interdependence of the radioprotective effects of human recombinant interleukin 1 alpha, tumor necrosis factor alpha, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and murine recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):108–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape M. E., Kim K. H. Transcriptional regulation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene expression by tumor necrosis factor in 30A-5 preadipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):974–982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D. Q., Shih C. H. Transcriptional activation and repression by cellular DNA-binding protein C/EBP. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1517–1522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1517-1522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Dinarello C. A., Punsal P. I., Colten H. R. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor regulates hepatic acute-phase gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Shafritz D. A., Hoofnagle J. H. Relation of the hepatitis B virus carrier state to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):764–772. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers T. J., Wiltrout T. A., McCormick K., Husted C., Wiltrout R. H. Antitumor effects of alpha-interferon and gamma-interferon on a murine renal cancer (Renca) in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17):5414–5420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Davison B. L., Stuart G. W., Wilkie T. M., Norstedt G., Palmiter R. D. Regulation, linkage, and sequence of mouse metallothionein I and II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1221–1230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Lau J. Y., Daniels H. M., Webster J., Eddleston A. L., Alexander G. J., Williams R. Tumour necrosis factor to treat chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 1990 Aug 4;336(8710):321–322. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91866-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Vogel S. N., Douches S., Neta R. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin is a less potent inducer of serum amyloid A synthesis than interleukin 1. Lymphokine Res. 1987 Spring;6(2):93–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoskiewicz M. J., Colvin R. B., Schneeberger E. E., Russell P. S. Widespread and selective induction of major histocompatibility complex-determined antigens in vivo by gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1645–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solis-Herruzo J. A., Brenner D. A., Chojkier M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits collagen gene transcription and collagen synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5841–5845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge J. E., Bowersox O., Tribble H., Lee S. H., Shepard H. M., Liggitt D. Toxicity of tumor necrosis factor is synergistic with gamma-interferon and can be reduced with cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Am J Pathol. 1987 Sep;128(3):410–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiegs G., Wendel A. Leukotriene-mediated liver injury. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 1;37(13):2569–2573. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90248-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti S. V., Kwak E. L., Miller S. C., Miller L. L., Ringold G. M., Myambo K. B., Young A. P., Torti F. M. The molecular cloning and characterization of murine ferritin heavy chain, a tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12638–12644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Teicher L., Laub O., Itin A., Dagan D., Bloom B. R., Shafritz D. A. Alpha interferon suppresses hepatitis B virus enhancer activity and reduces viral gene transcription. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1821–1824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1821-1824.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. S., Rosenberg S. A. Modulation of murine tumor major histocompatibility antigens by cytokines in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 15;48(20):5818–5824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wispé J. R., Clark J. C., Warner B. B., Fajardo D., Hull W. E., Holtzman R. B., Whitsett J. A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits expression of pulmonary surfactant protein. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1954–1960. doi: 10.1172/JCI114929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]