Abstract
UL9, the origin-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), has been overexpressed in an insect cell overexpression system and purified to homogeneity. In this report, we confirm and extend recent findings on the physical properties, enzymatic activities, and binding properties of UL9. We demonstrate that UL9 exists primarily as a homodimer in solution and that these dimers associate to form a complex nucleoprotein structure when bound to the HSV origin of replication. We also show that UL9 is an ATP-dependent helicase, capable of unwinding partially duplex DNA in a sequence-independent manner. Although the helicase activity of UL9 is demonstrable on short duplex substrates in the absence of single-stranded DNA-binding proteins, the HSV single-stranded DNA-binding protein ICP8 (but not heterologous binding proteins) stimulates UL9 to unwind long DNA sequences of over 500 bases. We were not able to demonstrate unwinding of fully duplex DNA sequences containing the HSV origin of replication. However, in experiments designed to detect origin-dependent unwinding, we did find that UL9 wraps supercoiled DNA independent of sequence or ATP hydrolysis.
Full text
PDF


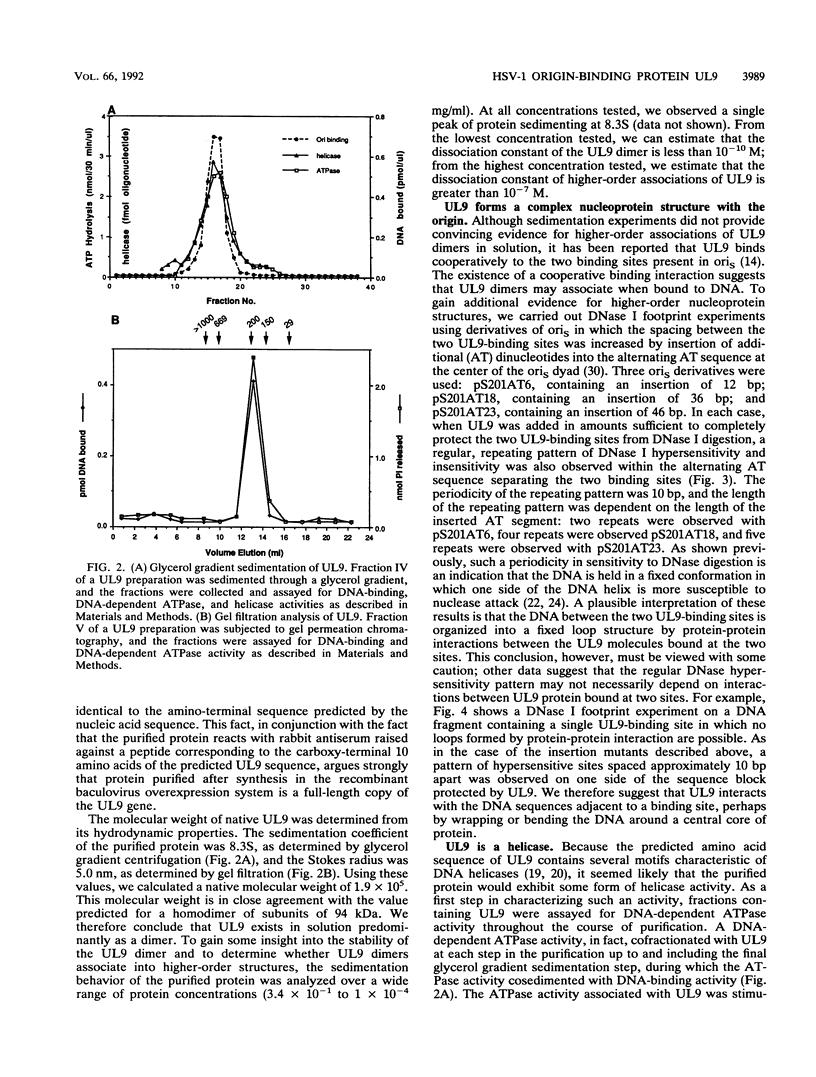





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K. MOLECULAR EXCLUSION AND RESTRICTED DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN MOLECULAR-SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:723–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackers G. K., Shea M. A., Smith F. R. Free energy coupling within macromolecules. The chemical work of ligand binding at the individual sites in co-operative systems. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):223–242. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y., Dym H., Sarov I. Herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1968 Oct;36(2):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Crumpacker C. S., Schaffer P. A., Wilkie N. M. Physical and genetic analysis of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Aschman D. P., Gelep P. T., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Schaffer P. A. Fine mapping and molecular cloning of mutations in the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):236–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.236-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus-1 helicase-primase. Physical and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4484–4488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Tsurumi T., Zhu L. A., Weller S. K., Olivo P. D., Challberg M. D., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase: a complex of three herpes-encoded gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2186–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowski C. E., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-specific binding protein: oriS-binding properties and effects of cellular proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3140–3150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3140-3150.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Deb S. P. A 269-amino-acid segment with a pseudo-leucine zipper and a helix-turn-helix motif codes for the sequence-specific DNA-binding domain of herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2829–2838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2829-2838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreiseikelmann B., Velleman M., Schuster H. The c1 repressor of bacteriophage P1. Isolation and characterization of the repressor protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1391–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Gustafsson C. M., Hammarsten O. The origin binding protein of herpes simplex virus 1 binds cooperatively to the viral origin of replication oris. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17167–17173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Lehman I. R. Interaction of origin binding protein with an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo M. L., Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S., Parris D. S. The essential 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus stimulates the virus-encoded DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5023–5029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5023-5029.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo M. L., Jackwood D. H., Murphy M., Marsden H. S., Parris D. S. Purification of the herpes simplex virus type 1 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein: properties of the protein and evidence of its association with the virus-encoded DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2874–2883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2874-2883.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. A conserved NTP-motif in putative helicases. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–22. doi: 10.1038/333022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4713–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb J., Marcy A. I., Coen D. M., Challberg M. D. The herpes simplex virus type 1 UL42 gene product: a subunit of DNA polymerase that functions to increase processivity. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5976–5987. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5976-5987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Hochschild A., Ptashne M. DNA loops induced by cooperative binding of lambda repressor. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):750–752. doi: 10.1038/322750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez T. R., Dutch R. E., Lehman I. R., Gustafsson C., Elias P. Mutations in a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin that inhibit interaction with origin-binding protein also inhibit DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1649–1652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1649-1652.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Schwedes J. F., Tegtmeyer P. Herpes simplex virus origin-binding protein (UL9) loops and distorts the viral replication origin. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3284–3292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3284-3292.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Characterization of major recognition sequences for a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4096–4103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4096-4103.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Galloway D. A. Sequence and structural requirements of a herpes simplex viral DNA replication origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4018–4027. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. W., Deb S. P., Klauer J. S., Deb S. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 OriS sequence: mapping of functional domains. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4359–4369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4359-4369.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W. Escherichia coli helicase II (urvD gene product) translocates unidirectionally in a 3' to 5' direction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10169–10175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products required for DNA replication: identification and overexpression. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):196–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.196-204.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris D. S., Cross A., Haarr L., Orr A., Frame M. C., Murphy M., McGeoch D. J., Marsden H. S. Identification of the gene encoding the 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):818–825. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.818-825.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Littler E., Purifoy D. J. Nonstructural proteins of herpes simplex virus. II. Major virus-specific DNa-binding protein. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):894–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.894-902.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Lewis R. B., Powell K. L. Identification of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):621–623. doi: 10.1038/269621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin S. D., Hanlon B. Nucleoprotein complex formed between herpes simplex virus UL9 protein and the origin of DNA replication: inter- and intramolecular interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10946–10950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Golder M., Moss B. Characterization of vaccinia virus DNA topoisomerase I expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16401–16407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velleman M., Dreiseikelmann B., Schuster H. Multiple repressor binding sites in the genome of bacteriophage P1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5570–5574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Calder J. M., Stow N. D. Binding of the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 gene product to an origin of viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1409–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Stow N. D. Two binding sites for the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 protein are required for efficient activity of the oriS replication origin. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1379–1385. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Lee K. J., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the gene for the major herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):354–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.354-366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]