Abstract
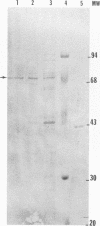
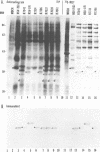
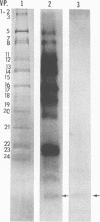
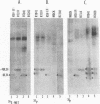
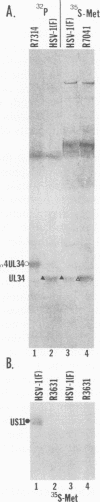
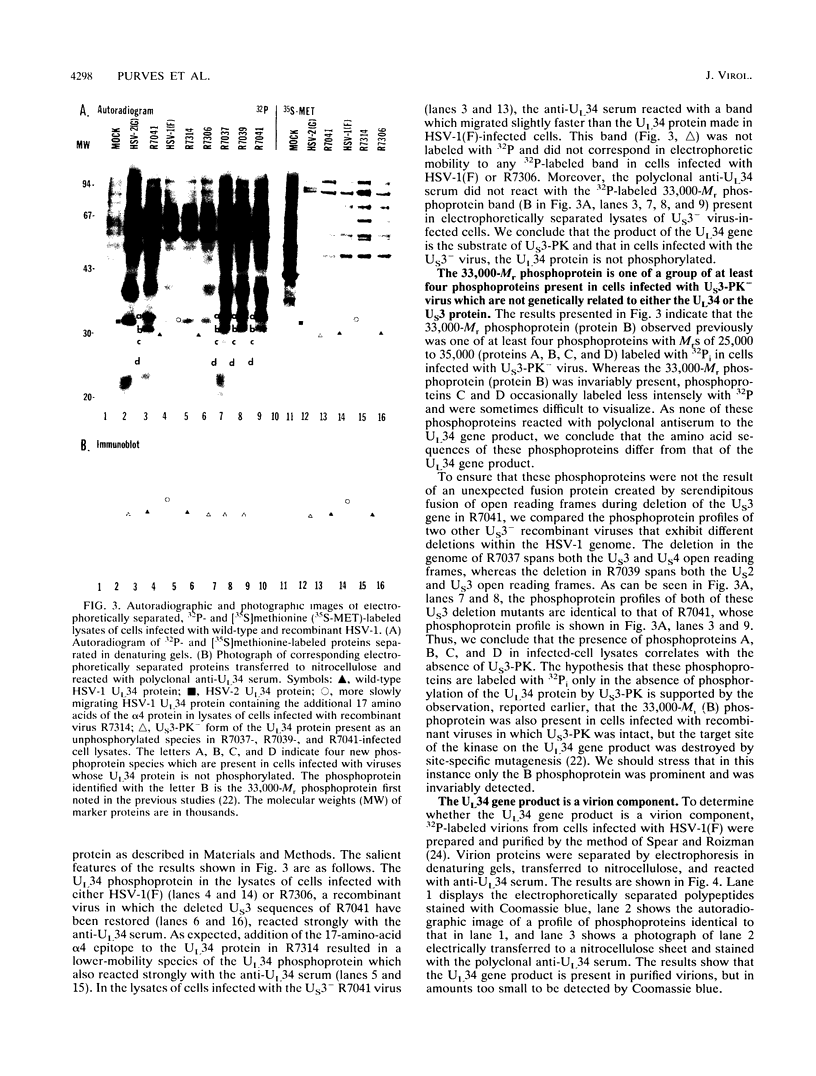
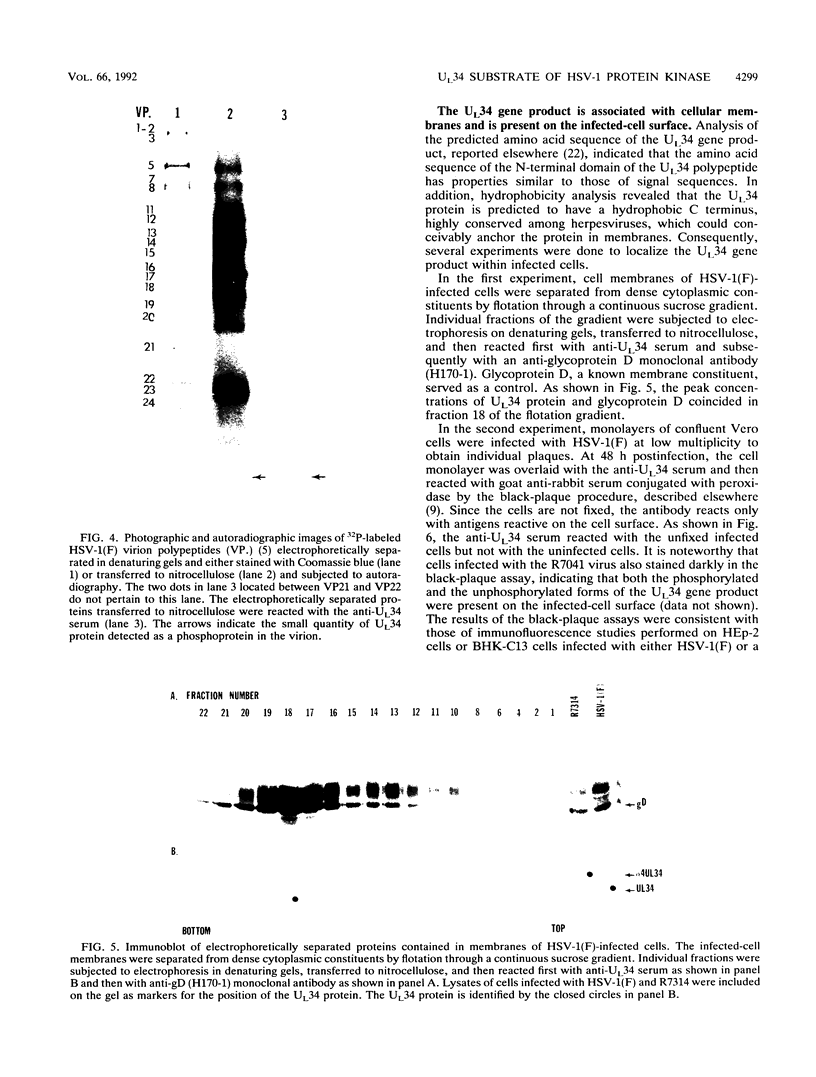
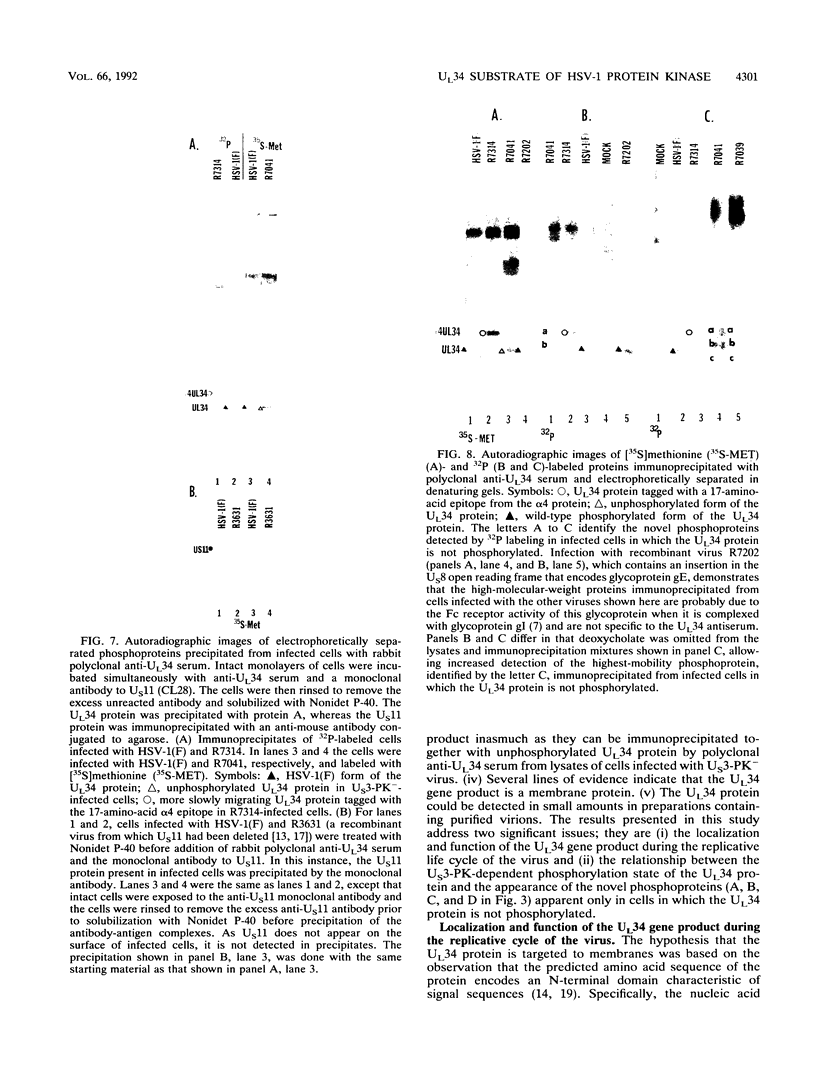
Previous studies (F. C. Purves, D. Spector, and B. Roizman, J. Virol. 65:5757-5764, 1991) have shown that the protein kinase encoded by the U(S)3 gene mediates posttranslational modification of a viral phosphoprotein with an apparent M(r) of 30,000 encoded by the UL34 gene. Here we report the following. (i) UL34 protein is not phosphorylated in cells infected with recombinant viruses deleted in the U(S)3 gene. (ii) Several new phosphoproteins (apparent M(r)s, 25,000 to 35,000) are present in cells infected with recombinant viruses deleted in the U(S)3 gene or with viruses carrying a mutation in the UL34 gene that precluded phosphorylation of the UL34 gene product by the U(S)3 protein kinase, but not in cells infected under conditions which permit phosphorylation of the UL34 protein. These proteins are genetically unrelated to the product of the UL34 gene. (iii) Polyclonal rabbit anti-UL34 protein serum precipitated not only the UL34 protein but also the other (25,000- to 35,000-M(r)) phosphoproteins from lysates of cells infected with U(S)3- virus. (iv) The UL34 gene product is a membrane protein inasmuch as the polyclonal anti-UL34 serum reacted with surfaces of intact, unfixed, infected cells and the antigen-antibody complex formed in this reaction contained the UL34 protein. (v) Small amounts of the UL34 protein were present in virions of infected cells. We conclude that the UL34 gene product is a membrane protein exclusively phosphorylated by the U(S)3 protein kinase which can either directly or indirectly form complexes with several other phosphoproteins. Experiments done thus far suggest that these phosphoproteins are present only under conditions in which the UL34 protein is not phosphorylated.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Purves F. C., McGeoch D. J., Marsden H. S., Leader D. P. Identification of the herpes simplex virus protein kinase as the product of viral gene US3. J Gen Virol. 1987 Oct;68(Pt 10):2699–2704. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-10-2699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. VI. Viral proteins in the plasma membrane. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):431–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.431-439.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubenthal-Voss J., Houghten R. A., Pereira L., Roizman B. Mapping of functional and antigenic domains of the alpha 4 protein of herpes simplex virus 1. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):454–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.454-462.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Frame M. C., Ligas M. W., Cross A. M., Stow N. D. Herpes simplex virus immunoglobulin G Fc receptor activity depends on a complex of two viral glycoproteins, gE and gI. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1347–1354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1347-1354.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberger T., Shenk T. A protein kinase is present in a complex with adenovirus E1A proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11143–11147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousoulas K. G., Pellett P. E., Pereira L., Roizman B. Mutations affecting conformation or sequence of neutralizing epitopes identified by reactivity of viable plaques segregate from syn and ts domains of HSV-1(F) gB gene. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):379–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Deana A. D., Marchiori F., Purves F. C., Pinna L. A. Further definition of the substrate specificity of the alpha-herpesvirus protein kinase and comparison with protein kinases A and C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 19;1091(3):426–431. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90210-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Clustering of genes dispensable for growth in culture in the S component of the HSV-1 genome. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.3033823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Ackermann M., Roizman B. Construction and properties of a viable herpes simplex virus 1 recombinant lacking coding sequences of the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):807–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.807-812.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Davison A. J. Alphaherpesviruses possess a gene homologous to the protein kinase gene family of eukaryotes and retroviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1765–1777. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meignier B., Longnecker R., Mavromara-Nazos P., Sears A. E., Roizman B. Virulence of and establishment of latency by genetically engineered deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus 1. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90417-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., Kousoulas K. G., Pereira L., Roizman B. Anatomy of the herpes simplex virus 1 strain F glycoprotein B gene: primary sequence and predicted protein structure of the wild type and of monoclonal antibody-resistant mutants. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.243-253.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Deana A. D., Marchiori F., Leader D. P., Pinna L. A. The substrate specificity of the protein kinase induced in cells infected with herpesviruses: studies with synthetic substrates [corrected] indicate structural requirements distinct from other protein kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 28;889(2):208–215. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Longnecker R. M., Leader D. P., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 protein kinase is encoded by open reading frame US3 which is not essential for virus growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2896–2901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2896-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Spector D., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 protein kinase encoded by the US3 gene mediates posttranslational modification of the phosphoprotein encoded by the UL34 gene. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5757–5764. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5757-5764.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]