Abstract
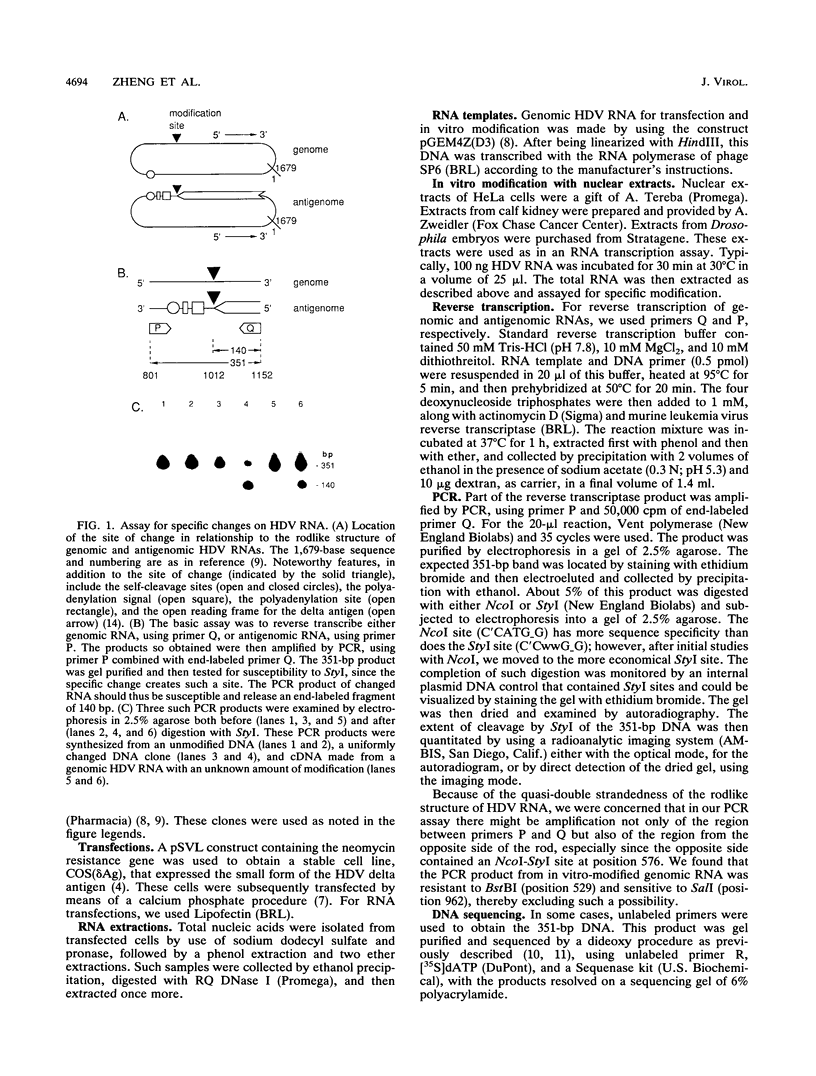
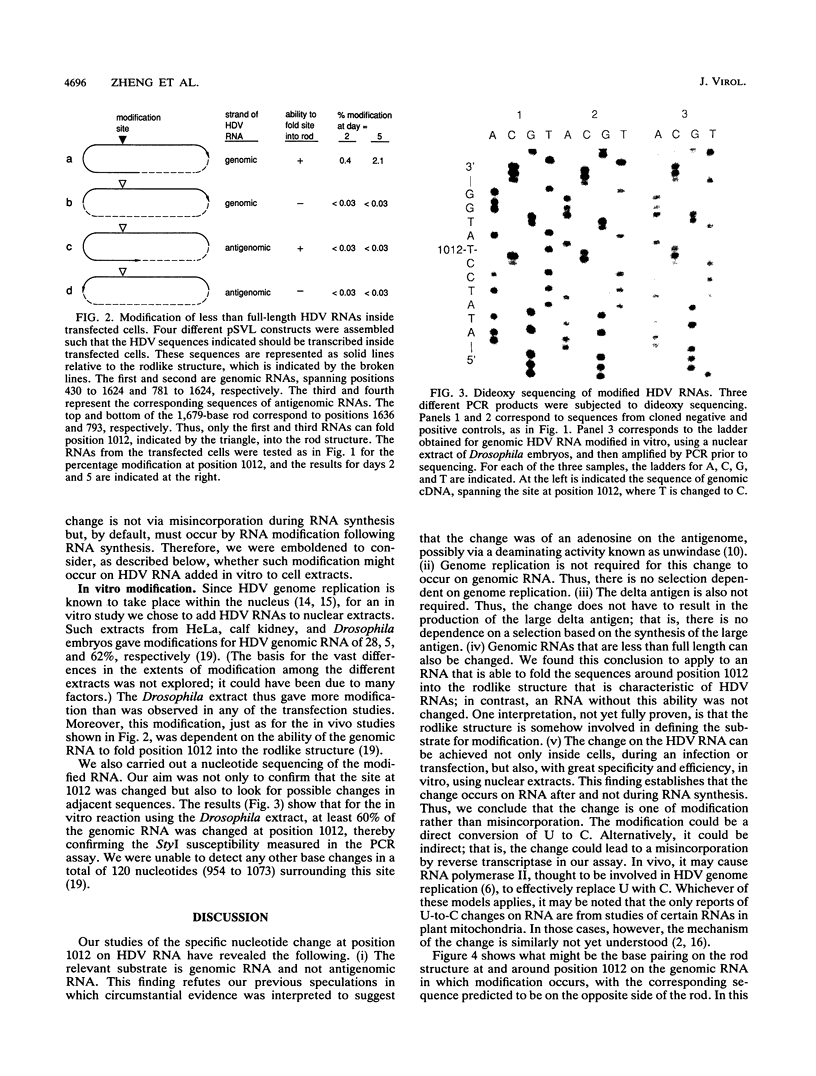
It has been shown previously that during replication of the genome of human hepatitis delta virus (HDV), a specific nucleotide change occurs to eliminate the termination codon for the small delta antigen (G. Luo, M. Chao, S.-Y. Hsieh, C. Sureau, K. Nishikura, and J. Taylor, J. Virol. 64:1021-1027, 1990). This change creates an extension in the length of the open reading frame for the delta antigen from 195 to 214 amino acids. These two proteins, the small and large delta antigens, have important and distinct roles in the life cycle of HDV. To further investigate the mechanism of this specific nucleotide alteration, we developed a sensitive assay involving the polymerase chain reaction to monitor changes on HDV RNA sequences as they occurred in transfected cells. We found that the substrate for the sequence change was the viral genomic RNA rather than the antigenomic RNA. This sequence change occurred independently of genome replication or the presence of the delta antigen. Less than full-length genomic RNA could act as a substrate, but only if it also contained a corresponding RNA sequences from the other side of the rodlike structure, which is characteristic of HDV. We were also able to reproduce the HDV base change in vitro, by addition of purified viral RNA to nuclear extracts of cells from a variety of species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergmann K. F., Gerin J. L. Antigens of hepatitis delta virus in the liver and serum of humans and animals. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):702–706. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R. RNA editing: in Chloroplast and brain. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):4–5. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. L., Chen P. J., Tu S. J., Wang C. J., Chen D. S. The large form of hepatitis delta antigen is crucial for assembly of hepatitis delta virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8490–8494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M., Hsieh S. Y., Taylor J. Role of two forms of hepatitis delta virus antigen: evidence for a mechanism of self-limiting genome replication. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5066–5069. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5066-5069.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. S., Taylor J. M., White J. M. In vitro-synthesized hepatitis delta virus RNA initiates genome replication in cultured cells. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3104–3107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3104-3107.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowans E. J., Macnaughton T. B., Jilbert A. R., Burrell C. J. Cell culture model systems to study HDV expression, replication and pathogenesis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;364:299–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. Y., Chao M., Taylor J. Initiation of replication of the human hepatitis delta virus genome from cloned DNA: role of delta antigen. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1945–1950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1945-1950.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. Y., Goldberg J., Coates L., Mason W., Gerin J., Taylor J. Molecular cloning of hepatitis delta virus RNA from an infected woodchuck liver: sequence, structure, and applications. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1855–1861. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1855-1861.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo G. X., Chao M., Hsieh S. Y., Sureau C., Nishikura K., Taylor J. A specific base transition occurs on replicating hepatitis delta virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1021–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1021-1027.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu W. S., Bayer M., Taylor J. Assembly of hepatitis delta virus particles. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2310–2315. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2310-2315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Taylor J., Chao M., Eichberg J. W., Lanford R. E. Cloned hepatitis delta virus cDNA is infectious in the chimpanzee. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4292–4297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4292-4297.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M. Human hepatitis delta virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;168:141–166. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76015-0_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J., Mason W., Summers J., Goldberg J., Aldrich C., Coates L., Gerin J., Gowans E. Replication of human hepatitis delta virus in primary cultures of woodchuck hepatocytes. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2891–2895. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2891-2895.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walbot V. RNA editing fixes problems in plant mitochondrial transcripts. Trends Genet. 1991 Feb;7(2):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90225-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. S., Choo Q. L., Weiner A. J., Ou J. H., Najarian R. C., Thayer R. M., Mullenbach G. T., Denniston K. J., Gerin J. L., Houghton M. Structure, sequence and expression of the hepatitis delta (delta) viral genome. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):508–514. doi: 10.1038/323508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. J., Choo Q. L., Wang K. S., Govindarajan S., Redeker A. G., Gerin J. L., Houghton M. A single antigenomic open reading frame of the hepatitis delta virus encodes the epitope(s) of both hepatitis delta antigen polypeptides p24 delta and p27 delta. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):594–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.594-599.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]