Abstract
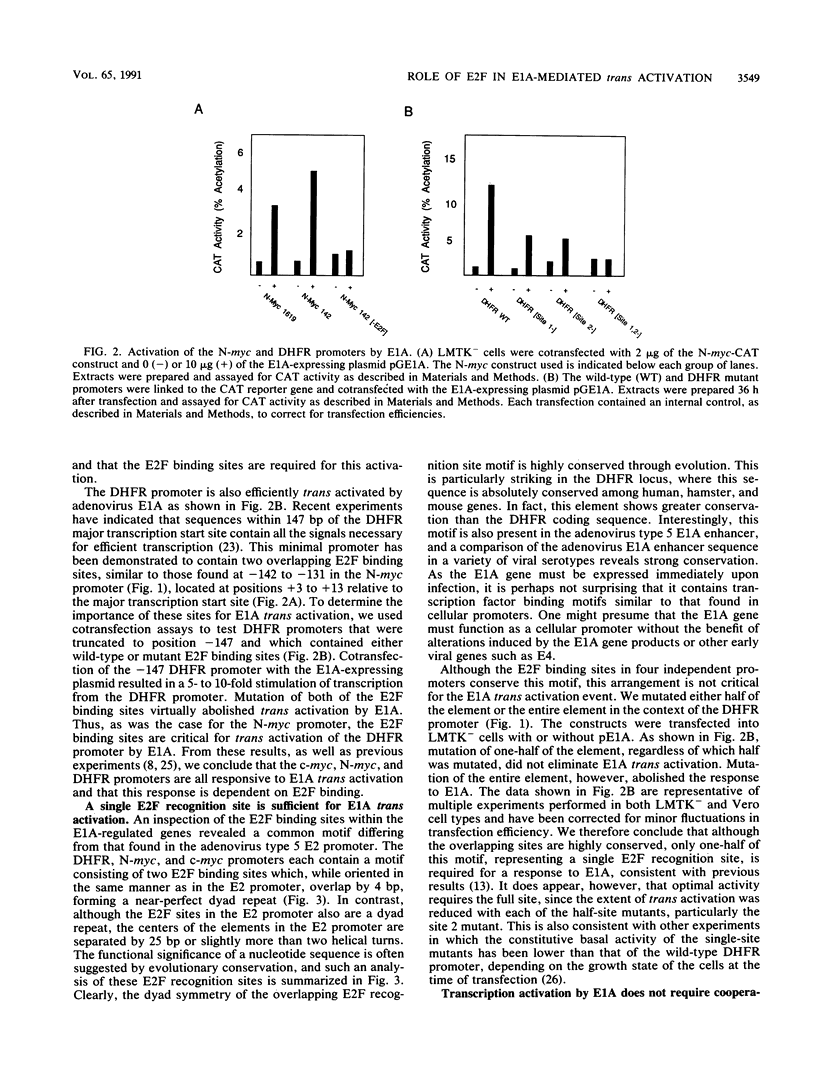
Adenovirus E1A-dependent trans activation of the adenovirus E2 gene involves the activation of the cellular transcription factor E2F. E2F binding sites have also been identified in the 5'-flanking region of a number of cellular genes, raising the possibility that such genes are targets for E1A trans activation. We now demonstrate that two genes that possess E2F recognition sites, N-myc and DHFR, are stimulated by E1A, dependent on the E2F sites. We also find that although there are multiple E2F sites in these promoters, a single intact E2F binding site is sufficient for E1A-mediated induction, although not to the full wild-type level. These results thus demonstrate that a variety of cellular genes that possess E2F binding sites are subject to E1A trans activation. Moreover, since the products of most of these genes are likely critical for cellular proliferation, there are obvious consequences of this trans activation for cellular phenotype.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Phosphorylation-dependent activation of the adenovirus-inducible E2F transcription factor in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4352–4356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Azizkhan J. C. Transcription factor E2F is required for efficient expression of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4994–5002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePinho R. A., Legouy E., Feldman L. B., Kohl N. E., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Structure and expression of the murine N-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1827–1831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Krippl B., Andrisani O., Jones N., Westphal H., Rosenberg M. E1A 13S and 12S mRNA products made in Escherichia coli both function as nucleus-localized transcription activators but do not directly bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Engel D. A., Shenk T. An adenovirus early region 4 gene product is required for induction of the infection-specific form of cellular E2F activity. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1062–1074. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Hearing P. Adenovirus early region 4 encodes two gene products with redundant effects in lytic infection. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2605–2615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2605-2615.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus 5 E2 transcription unit: an E1A-inducible promoter with an essential element that functions independently of position or orientation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):875–882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Regulation of transcription of the adenovirus EII promoter by EIa gene products: absence of sequence specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1970–1977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2180–2184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp M., Schilling R., Bernhardt G. Trans-activation of human MYC: the second promoter is target for the stimulation by adenovirus E1a proteins. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):535–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill S. D., Hemstrom C., Virtanen A., Nevins J. R. An adenovirus E4 gene product trans-activates E2 transcription and stimulates stable E2F binding through a direct association with E2F. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):2008–2012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A-dependent trans-activation of transcription. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):59–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanisms of viral-mediated trans-activation of transcription. Adv Virus Res. 1989;37:35–83. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K. Sequences involved in accurate and efficient transcription of human c-myc genes microinjected into frog oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4093–4098. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Bagchi S., Neill S. D., Nevins J. R. Activation of the E2F transcription factor in adenovirus-infected cells involves E1A-dependent stimulation of DNA-binding activity and induction of cooperative binding mediated by an E4 gene product. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2702–2710. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2702-2710.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel R., Kovesdi I., Nevins J. R. Activation of a preexisting cellular factor as a basis for adenovirus E1A-mediated transcription control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):387–390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Fisch T. M., Benecke B. J., Nevins J. R., Heintz N. Definition of multiple, functionally distinct TATA elements, one of which is a target in the hsp70 promoter for E1A regulation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):723–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick A. G., Blake M. C., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Functional analysis of GC element binding and transcription in the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9291–9304. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. E1a transactivation of human HSP70 gene promoter substitution mutants is independent of the composition of upstream and TATA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):176–183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalmeier K., Synovzik H., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L., Lipp M. Nuclear factor E2F mediates basic transcription and trans-activation by E1a of the human MYC promoter. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):527–536. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., McClanahan T. K., Morimoto R. I. E1a transactivation of the human HSP70 promoter is mediated through the basal transcriptional complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2574–2587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Rosser D. S., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. A TATA box implicated in E1A transcriptional activation of a simple adenovirus 2 promoter. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):512–515. doi: 10.1038/326512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder S. S., Berget S. M. Posttranscriptional control of DHFR gene expression during adenovirus 2 infection. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.72-77.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder S. S., Robberson B. L., Leys E. J., Hook A. G., Al-Ubaidi M., Yeung C. Y., Kellems R. E., Berget S. M. Control of cellular gene expression during adenovirus infection: induction and shut-off of dihydrofolate reductase gene expression by adenovirus type 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):819–828. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]