Abstract
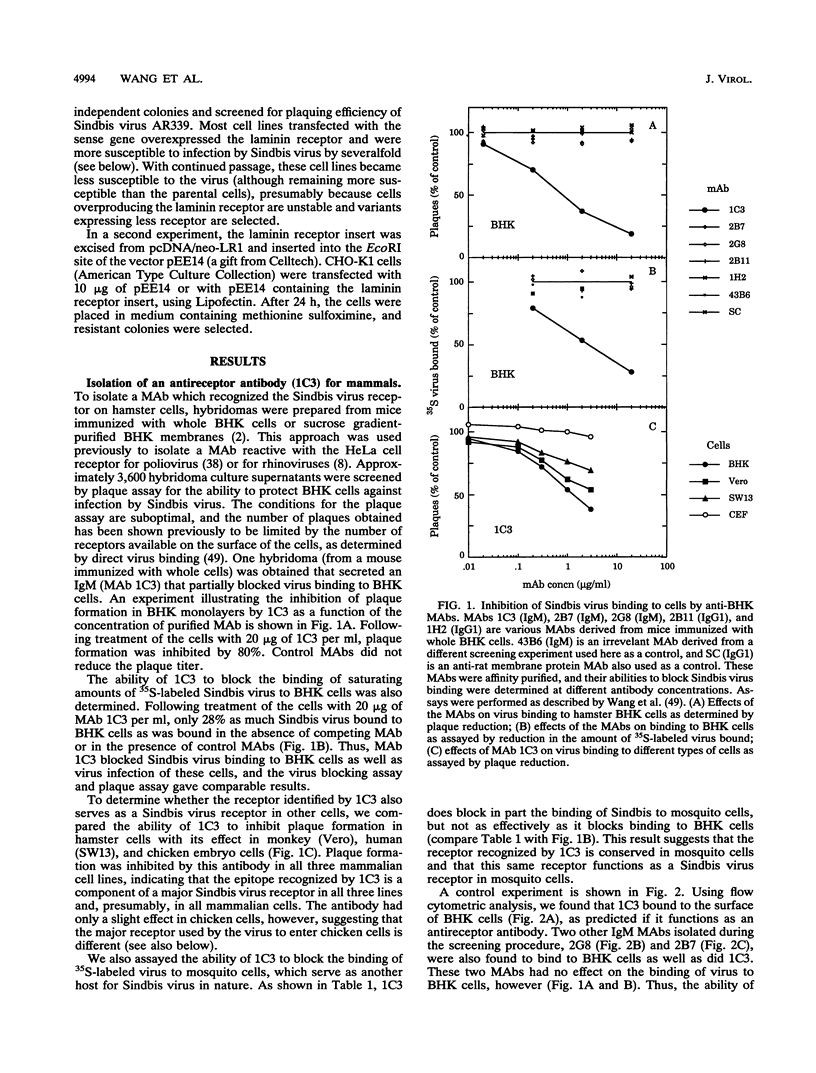
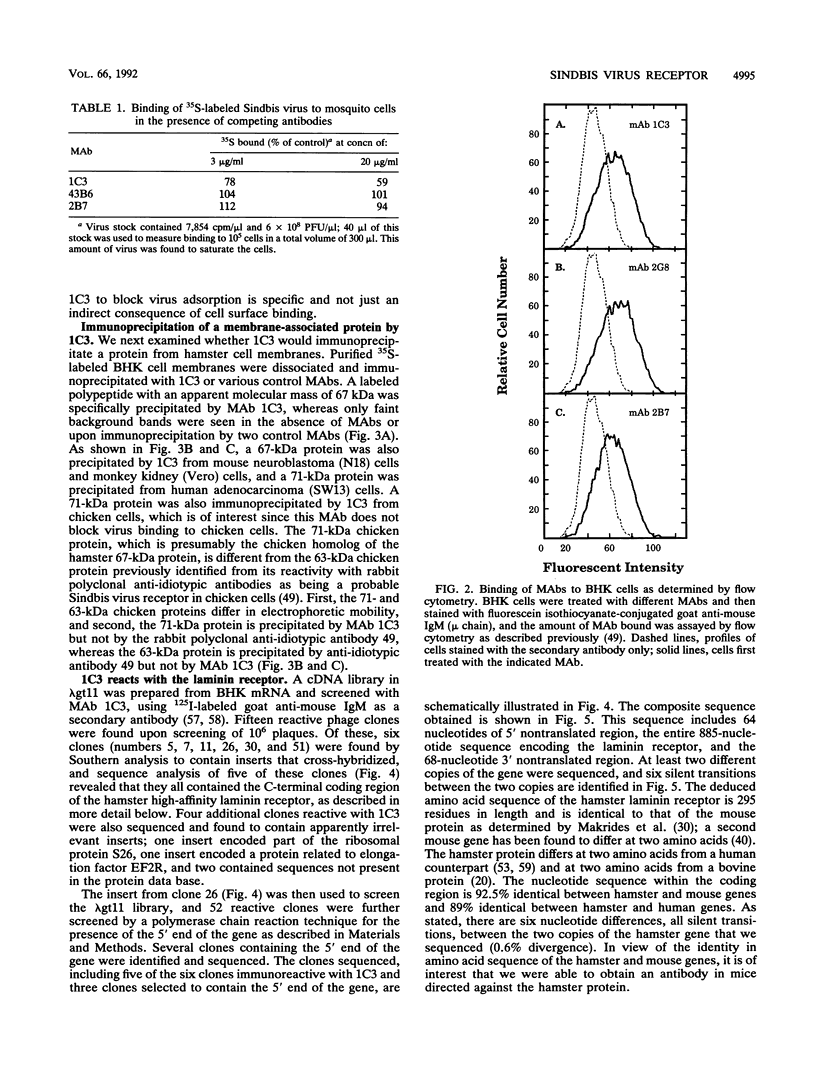
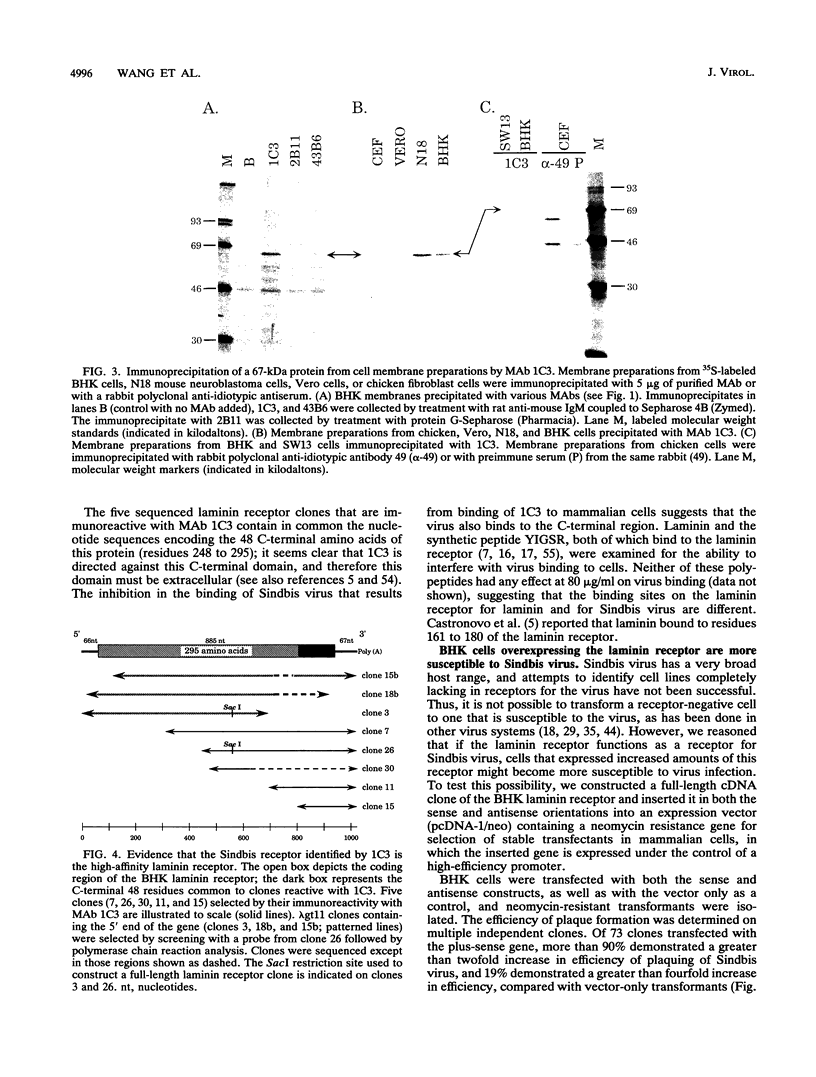
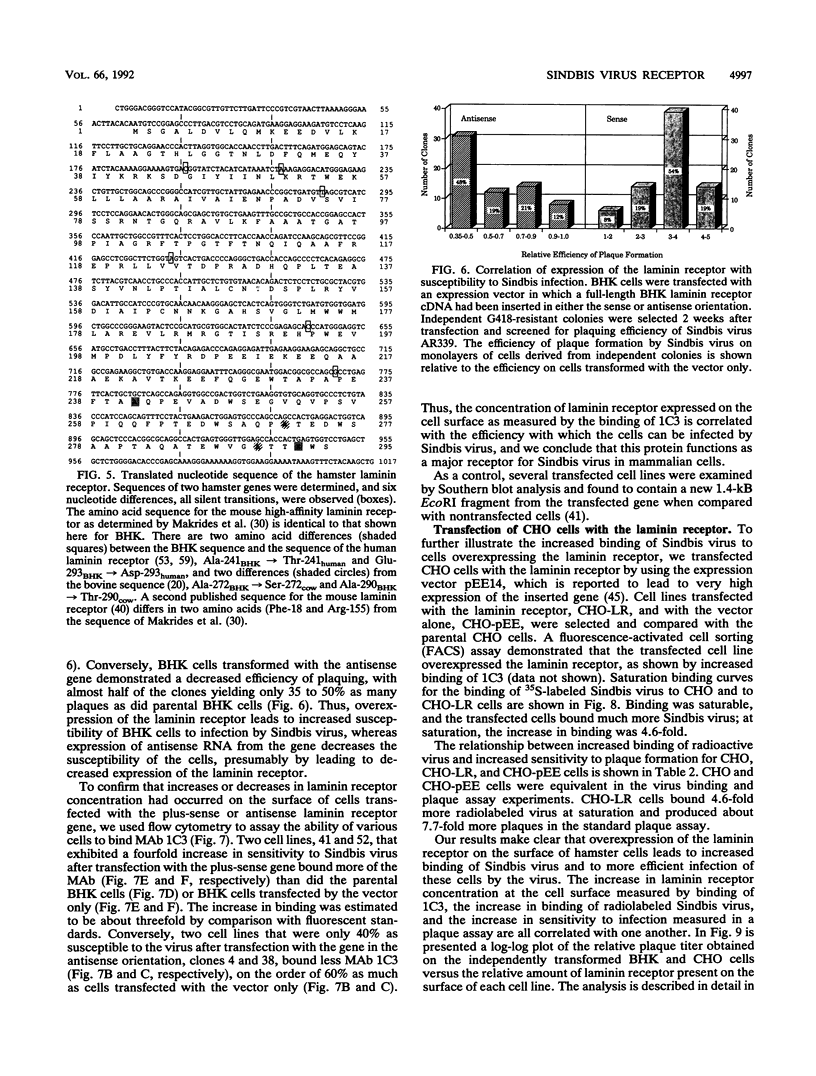
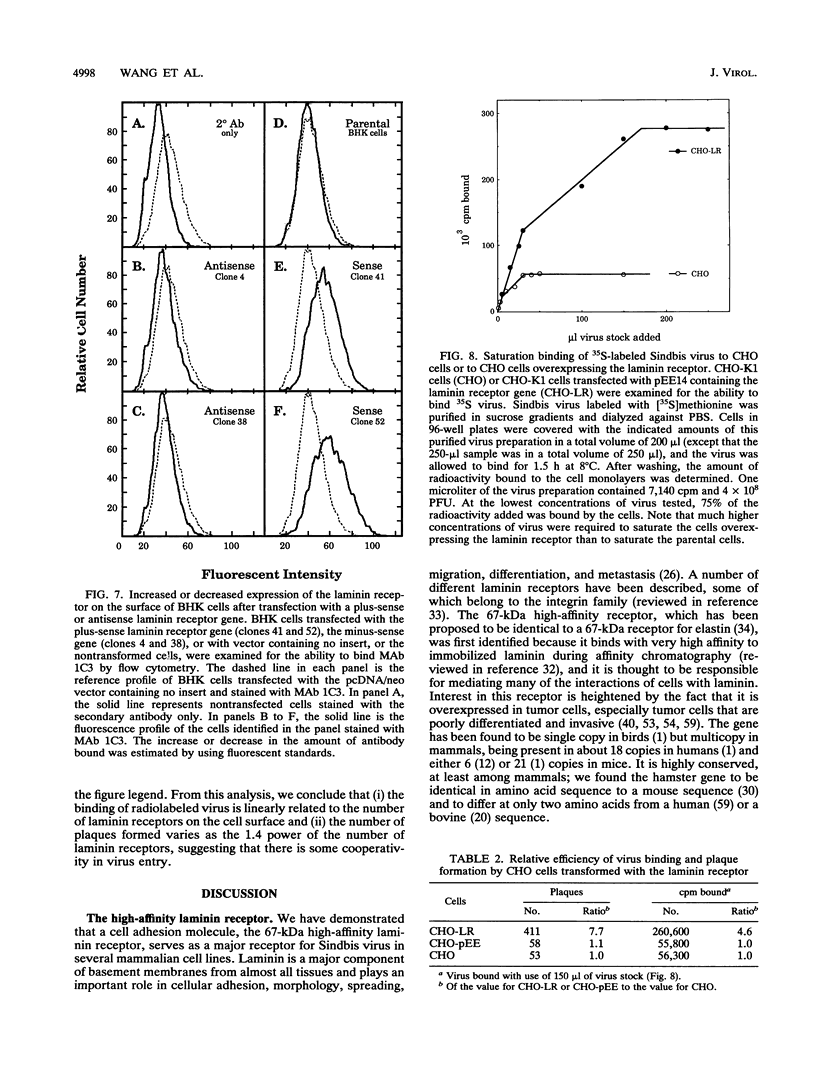
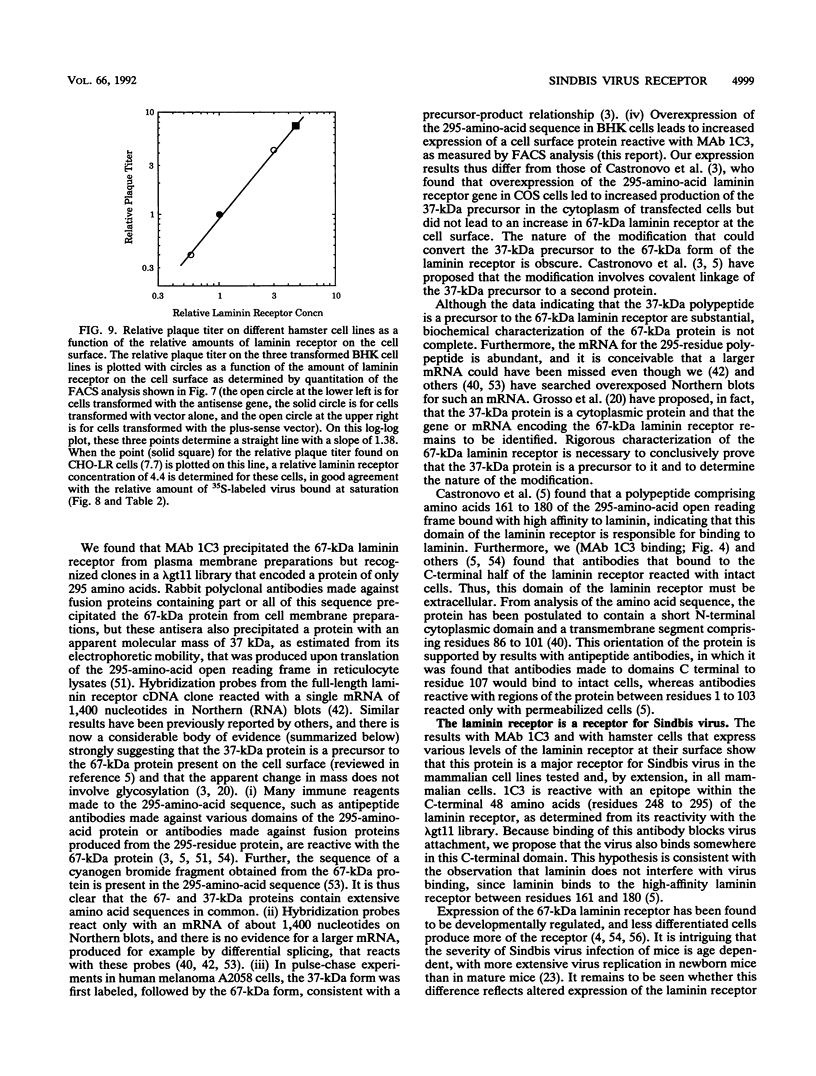
Sindbis virus is an alphavirus with a very wide host range, being able to infect many birds and mammals as well as mosquitoes. We have isolated a monoclonal antibody that largely blocks virus binding to mammalian cells. This antibody was found to be directed against the C-terminal domain of the high-affinity laminin receptor, a 67-kDa protein present on the cell surface that binds with high affinity to basement membrane laminin and that is known to be important in development and in tumor invasion. This receptor is believed to be formed from a 295-amino-acid polypeptide that is modified in some unknown way after translation. The primary sequence of this 295-amino-acid protein is highly conserved among mammals. We found the hamster amino acid sequence to be identical to a mouse sequence and to differ at only two amino acids from a human sequence and at two amino acids from a bovine sequence. To verify the importance of the laminin receptor for infection by Sindbis virus, hamster cells were stably transfected with the gene encoding the 295-amino-acid protein under the control of a high-efficiency promoter. Such transfected hamster cells overexpressed the laminin receptor at the cell surface, bound severalfold more Sindbis virions than did the parental cells, and became infected by Sindbis virus with a higher efficiency. In contrast, cells transfected with the antisense gene expressed less laminin receptor on the surface and were less susceptible to the virus. Binding of the virus varied linearly with the amount of laminin receptor on the cell surface, whereas infectivity measured with a plaque assay varied with the 1.4 power of the receptor concentration, suggesting that interaction with more than one receptor aids virus penetration. By these criteria, the laminin receptor functions as the major receptor for Sindbis virus entry into mammalian cells. We also found that the anti-laminin receptor antibody partially blocked Sindbis virus binding to mosquito cells, suggesting that the laminin receptor is conserved in mosquitoes and functions as a Sindbis virus receptor in this host. The wide distribution of this highly conserved receptor may be in part responsible for the broad host range exhibited by the virus, which infects a wide range of mammals and birds as well as its mosquito vector and can infect many different tissues within these hosts.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bignon C., Roux-Dosseto M., Zeigler M. E., Mattei M. G., Lissitzky J. C., Wicha M. S., Martin P. M. Genomic analysis of the 67-kDa laminin receptor in normal and pathological tissues: circumstantial evidence for retroposon features. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90336-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringman T. S., Lindquist P. B., Derynck R. Different transforming growth factor-alpha species are derived from a glycosylated and palmitoylated transmembrane precursor. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castronovo V., Claysmith A. P., Barker K. T., Cioce V., Krutzsch H. C., Sobel M. E. Biosynthesis of the 67 kDa high affinity laminin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91965-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castronovo V., Sobel M. E. Laminin and fibronectin increase the steady state level of the 67 kD high affinity metastasis-associated laminin receptor mRNA in human cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1110–1117. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91144-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castronovo V., Taraboletti G., Sobel M. E. Functional domains of the 67-kDa laminin receptor precursor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20440–20446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Nurcombe V., Jeffrey P., Edgar D. Developmental loss of functional laminin receptors on retinal ganglion cells is regulated by their target tissue, the optic tectum. Development. 1989 Oct;107(2):381–387. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.2.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Callahan P. L., Long W. J. Isolation of a monoclonal antibody that blocks attachment of the major group of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.7-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. One-step growth curve of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus on chicken embryo cells grown in vitro and analysis of virus yields from single cells. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):183–199. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández M. T., Castronovo V., Rao C. N., Sobel M. E. The high affinity murine laminin receptor is a member of a multicopy gene family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):84–90. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingeroth J. D., Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R., Barel M., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Klein G. gp140, the C3d receptor of human B lymphocytes, is also the Epstein-Barr virus receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1490–1493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by interactions with a complementary T=3 capsid. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlsen K. R., Dillner L., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. The human laminin receptor is a member of the integrin family of cell adhesion receptors. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1228–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.2970671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Ogle R. C., Robey F. A., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Yamada Y., Kleinman H. K. A pentapeptide from the laminin B1 chain mediates cell adhesion and binds the 67,000 laminin receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6896–6900. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosso L. E., Park P. W., Mecham R. P. Characterization of a putative clone for the 67-kilodalton elastin/laminin receptor suggests that it encodes a cytoplasmic protein rather than a cell surface receptor. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3346–3350. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. R., Strauss J. H. Processing the nonstructural polyproteins of Sindbis virus: study of the kinetics in vivo by using monospecific antibodies. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):998–1007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.998-1007.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., McFarland H. F., Levy S. E. Age-dependent resistance to viral encephalitis: studies of infections due to Sindbis virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):257–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Rao C. N., Wewer U. M. Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1037–1057. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig S., Jackson A. C., Hahn C. S., Griffin D. E., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Molecular basis of Sindbis virus neurovirulence in mice. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2329–2336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2329-2336.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassen J. A., Terhorst C. Identification of a cell-surface protein involved in the binding site of Sindbis virus on human lymphoblastic cell lines using a heterobifunctional cross-linker. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):153–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makrides S., Chitpatima S. T., Bandyopadhyay R., Brawerman G. Nucleotide sequence for a major messenger RNA for a 40 kilodalton polypeptide that is under translational control in mouse tumor cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2349–2349. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Adsorptive endocytosis of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Timpl R. Laminin and other basement membrane components. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:57–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Hinek A., Griffin G. L., Senior R. M., Liotta L. A. The elastin receptor shows structural and functional similarities to the 67-kDa tumor cell laminin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16652–16657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P. Laminin receptors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:71–91. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Johnson B., Lionetti K. A., Nobis P., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Transformation of a human poliovirus receptor gene into mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobis P., Zibirre R., Meyer G., Kühne J., Warnecke G., Koch G. Production of a monoclonal antibody against an epitope on HeLa cells that is the functional poliovirus binding site. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2563–2569. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. N., Castronovo V., Schmitt M. C., Wewer U. M., Claysmith A. P., Liotta L. A., Sobel M. E. Evidence for a precursor of the high-affinity metastasis-associated murine laminin receptor. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7476–7486. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Tignor G. H. Host cell receptors for two strains of Sindbis virus. Arch Virol. 1980;66(1):11–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01315041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Cockett M. I. The construction of a highly efficient and versatile set of mammalian expression vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):7110–7110. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.7110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. C., Griffin D. E. Mechanism of altered Sindbis virus neurovirulence associated with a single-amino-acid change in the E2 Glycoprotein. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1551–1557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1551-1557.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubol S., Griffin D. E. Identification of a putative alphavirus receptor on mouse neural cells. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6913–6921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6913-6921.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. S., Schmaljohn A. L., Kuhn R. J., Strauss J. H. Antiidiotypic antibodies as probes for the Sindbis virus receptor. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):694–702. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90903-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Liotta L. A., Jaye M., Ricca G. A., Drohan W. N., Claysmith A. P., Rao C. N., Wirth P., Coligan J. E., Albrechtsen R. Altered levels of laminin receptor mRNA in various human carcinoma cells that have different abilities to bind laminin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7137–7141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Taraboletti G., Sobel M. E., Albrechtsen R., Liotta L. A. Role of laminin receptor in tumor cell migration. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5691–5698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yannariello-Brown J., Wewer U., Liotta L., Madri J. A. Distribution of a 69-kD laminin-binding protein in aortic and microvascular endothelial cells: modulation during cell attachment, spreading, and migration. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1773–1786. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yenofsky R., Cereghini S., Krowczynska A., Brawerman G. Regulation of mRNA utilization in mouse erythroleukemia cells induced to differentiate by exposure to dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1197–1203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yow H. K., Wong J. M., Chen H. S., Lee C. G., Davis S., Steele G. D., Jr, Chen L. B. Increased mRNA expression of a laminin-binding protein in human colon carcinoma: complete sequence of a full-length cDNA encoding the protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



